BE3002 Transport Phenomena in Biosystem Module 2_Segment 1
Summary
TLDRThis segment on fluid kinematics, presented by Yusuf from the Institute of Technology Bandung, explores the fundamentals of fluid motion. It covers the concepts of reference frames, focusing on Eulerian and Lagrangian descriptions, and the importance of control volumes in analyzing mass, momentum, and energy flow. The script introduces key terms like velocity fields, flow rates, and acceleration, and explains their calculation through various equations. Visualization techniques such as streamlines and pathlines are discussed for better understanding of fluid flow behavior. The segment provides a comprehensive foundation for further studying fluid dynamics and momentum conservation.
Takeaways
- 😀 Fluid kinematics refers to the study of fluid motion in both time and space, where motion must be specified relative to a frame of reference.
- 😀 A fixed reference frame is commonly used in fluid mechanics, but sometimes, using a moving reference frame simplifies problem-solving.
- 😀 The Eulerian description focuses on observing fluid motion from a fixed reference frame, while the Lagrangian description follows individual fluid particles.
- 😀 Control volumes are regions of space used to analyze the flow of mass, momentum, and energy, and can either be fixed in size or move with velocity.
- 😀 The specification of control volumes is arbitrary, and their size can change with time to facilitate problem-solving.
- 😀 The Lagrangian approach is helpful in tracking the motion of proteins and cells within a fluid, while the Eulerian approach is often used for control volumes.
- 😀 The velocity field defines the motion of fluid, and understanding it allows for the calculation of forces and stresses on the fluid elements.
- 😀 Fluid velocity is a vector quantity that changes both in magnitude and direction over time and space, and it is essential for analyzing fluid flow.
- 😀 The acceleration of a fluid element consists of two components: local acceleration (due to time changes) and convective acceleration (due to spatial changes in velocity).
- 😀 Streamlines represent the trajectories of fluid particles, and in steady flow, these lines are tangent to the velocity vector, indicating no normal flow across them.
Q & A
What is the focus of this module in fluid kinematics?
-This module focuses on fluid kinematics, including conservation relations, fluid aesthetics, constitutive relations, laminar and turbulent flow, and the application of momentum balances.
What is the difference between Eulerian and Lagrangian descriptions in fluid mechanics?
-The Eulerian description observes fluid motion from a fixed reference frame, while the Lagrangian description follows the movement of individual fluid particles and tracks their variations along the trajectory.
What is a control volume in fluid mechanics?
-A control volume is a region of space used to analyze the flow of mass, momentum, and energy. It can be either fixed in size and position or move with some arbitrary velocity.
How does the Lagrangian approach apply in biosystems?
-The Lagrangian approach is useful in tracking the motion of proteins and cells within a fluid, allowing for detailed analysis of their movement and behavior.
What is the significance of the control volume's surface normal vector?
-The surface normal vector is crucial in calculating velocities and stresses, as it helps in defining the direction and magnitude of fluid flow across the control volume's surface.
What does the term 'velocity field' refer to in fluid kinematics?
-A velocity field refers to the distribution of fluid velocity at different points in space and time. Knowing this field allows for the calculation of forces and stresses acting on the fluid.
What is the formula for the mass flow rate in a fluid system?
-The mass flow rate is calculated as the integral of the product of local density and velocity, expressed mathematically as shown in equation 5 of the script.
What is the difference between local acceleration and convective acceleration?
-Local acceleration refers to the rate of change of velocity with time, while convective acceleration arises from changes in the velocity field with space.
How are streamlines used in fluid mechanics?
-Streamlines represent the path followed by fluid particles in steady flow. They are tangent to the velocity vector and help visualize the flow direction and behavior.
What are the different types of flow visualizations mentioned in the script?
-The script mentions pathlines, which track individual particles, and streamlines, which represent the continuous path of fluid flow. Additionally, puff lines and trick lines are used to visualize particle trajectories.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
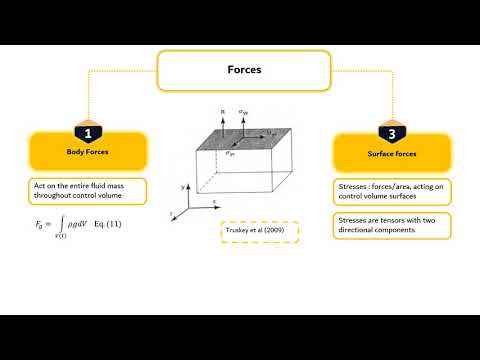
BE3002 Transport Phenomena in Biosystem Module 2_Segment 2
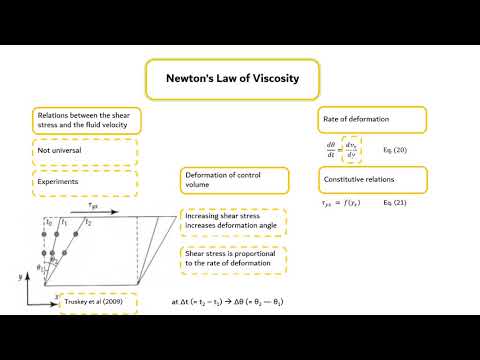
BE3002 Transport Phenomena in Biosystem Module 2_Segment 4

Fluid Mechanics | Physics

06 Analisa Secara Differensial dari Aliran Fluida Part1 MEKFLU

BE3002 Transport Phenomena in Biosystem Module 2_Segment 3

BE3002 Transport Phenomena in Biosystem_Module 3 Segment 4
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)