Honeynet and DMZ
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the presenter explains two key networking concepts: honeynets and DMZs. A honeynet is a deliberately vulnerable network designed to attract and study hackers, helping IT professionals understand attack methods and protect real systems. On the other hand, a DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) is a lightly protected network that hosts public services like web or file servers, balancing accessibility with security. The video provides an educational overview of these concepts, emphasizing their roles in cybersecurity and the trade-off between openness and protection.
Takeaways
- 😀 Honeynet is a real, intentionally vulnerable network designed to attract hackers and monitor their activities.
- 😀 Honeynets serve as a trap or bait system, allowing IT professionals to study hacker techniques and protect real company networks.
- 😀 Honeypots, the devices within a honeynet, appear legitimate but are used to deceive attackers into engaging with them.
- 😀 The main purpose of a honeynet is to understand hacker behavior, which can help improve network security practices.
- 😀 DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) is a lightly protected network zone that provides public access to services like web or file servers, while still securing sensitive data.
- 😀 The term DMZ is borrowed from the Korean War, where it referred to a buffer zone between opposing forces. In networking, it acts as a buffer zone between the Internet and the internal network.
- 😀 DMZ balances the need for public accessibility to services with the requirement for protecting a company's internal network.
- 😀 A DMZ is designed to avoid heavy traffic restrictions, ensuring that public users can access services smoothly.
- 😀 The trade-off between security and accessibility is a key factor in DMZ design, aiming to protect internal resources while offering convenient services to the public.
- 😀 The role of a DMZ is to prevent Internet users from accessing critical internal systems by placing vulnerable services in a controlled and isolated zone.
Q & A
What is a Honeynet?
-A Honeynet is a real network composed of devices and services that appear legitimate but are intentionally vulnerable. It is set up to attract hackers and monitor their activities for security purposes.
What is the primary purpose of a Honeynet?
-The main purpose of a Honeynet is to lure hackers into attacking a system so that their methods and behaviors can be studied, helping IT professionals protect real networks.
How does a Honeynet serve as an intrusion detection system?
-A Honeynet can act as a lightweight intrusion detection system by monitoring and logging the activities of attackers, providing valuable data for improving network security.
What is a Honey Pot in a Honeynet?
-A Honey Pot is a specific service or device within a Honeynet that appears legitimate but is designed to attract and trap attackers, simulating real services to deceive them.
What is a DMZ in networking?
-DMZ stands for Demilitarized Zone, a lightly protected network area that is used to host services like web servers and file servers, which are accessible by the public.
Why is a DMZ used in networking?
-A DMZ is used to provide public services to users while balancing security and accessibility. It allows external users to access services like websites without heavily compromising the security of the internal network.
What is the main difference between a Honeynet and a DMZ?
-A Honeynet is designed to attract and monitor hackers with vulnerable services, while a DMZ is a network segment that hosts publicly accessible services with some level of protection.
What are the benefits of having a DMZ in a company's network?
-A DMZ provides a way to offer convenient public services while ensuring that critical internal network resources remain protected. It also helps manage the trade-off between security and accessibility.
Why is the term 'DMZ' borrowed from the Korean War?
-The term DMZ is borrowed from the Korean War, where a demilitarized zone was created as a buffer between North and South Korea. In networking, the term represents a zone between the internal network and the internet, with limited security.
How do Honeynets help protect real networks?
-Honeynets protect real networks by diverting hackers' attention away from critical resources and providing insights into attack methods, which can be used to strengthen security on actual systems.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Basics of Networking for Beginners | Getting Started With Networking | Computer Networks|Simplilearn
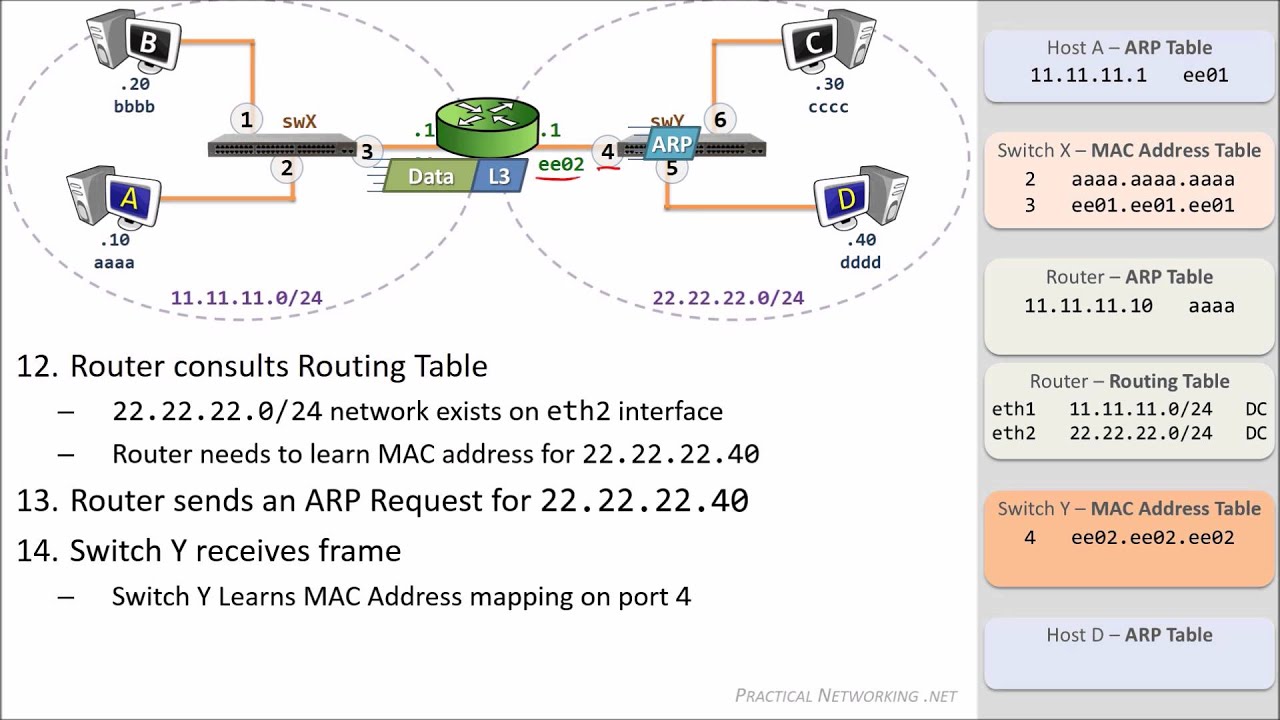
Packet Traveling - How Packets Move Through a Network

Lec-4: Physical layer in computer networks in hindi | Functions of Physical layer | OSI

Cisco Packet Tracer - Basic QoS Configuration

Day 59/100 || Create Subnets in AWS VPC Part -2 || 100 Days Cloud Challenge || AWS in English ||

Garis dan Sudut (1) | Pengenalan Garis dan Sudut | Matematika Kelas 7
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
