Teori Perkembangan Bumi
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the theories behind Earth's formation, starting with Alfred Wegener's Continental Drift Theory, which suggests that Earth's original supercontinent, Pangea, split into separate continents. It also covers the Laurasia and Gondwana Theory, which postulates that Earth was once divided into two large continents. The video continues with the Convection Theory, explaining how heat-driven currents within Earth's mantle drive plate movements. Finally, it introduces the theory of Plate Tectonics, describing how Earth's lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates that move due to convection currents in the underlying asthenosphere, leading to various geological phenomena.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Earth did not form naturally; various theories explain its development.
- 😀 Alfred Wegener proposed the Continental Drift Theory in 1912, stating that Earth initially had one supercontinent called Pangea.
- 😀 Around 225 million years ago, the supercontinent Pangea broke apart to form the continents we see today.
- 😀 Evidence for the Continental Drift Theory includes similar coastlines between South America and Africa, and between North America and Europe.
- 😀 Fossil evidence of identical plants and animals found on different continents supports the theory of continental drift.
- 😀 The Laurasia and Gondwana Theory, proposed by Eduard Douwes in 1884, suggests the Earth originally had two supercontinents: Laurasia (north) and Gondwana (south).
- 😀 Laurasia included North America, Europe, and Asia, while Gondwana consisted of South America, Africa, Australia, and Antarctica.
- 😀 The Convection Theory, proposed by Arthur Holmes, explains that heat-induced convection currents inside the Earth cause movement in the Earth's crust.
- 😀 Convection currents in the Earth's mantle create processes like volcanic activity and the formation of mid-ocean ridges, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
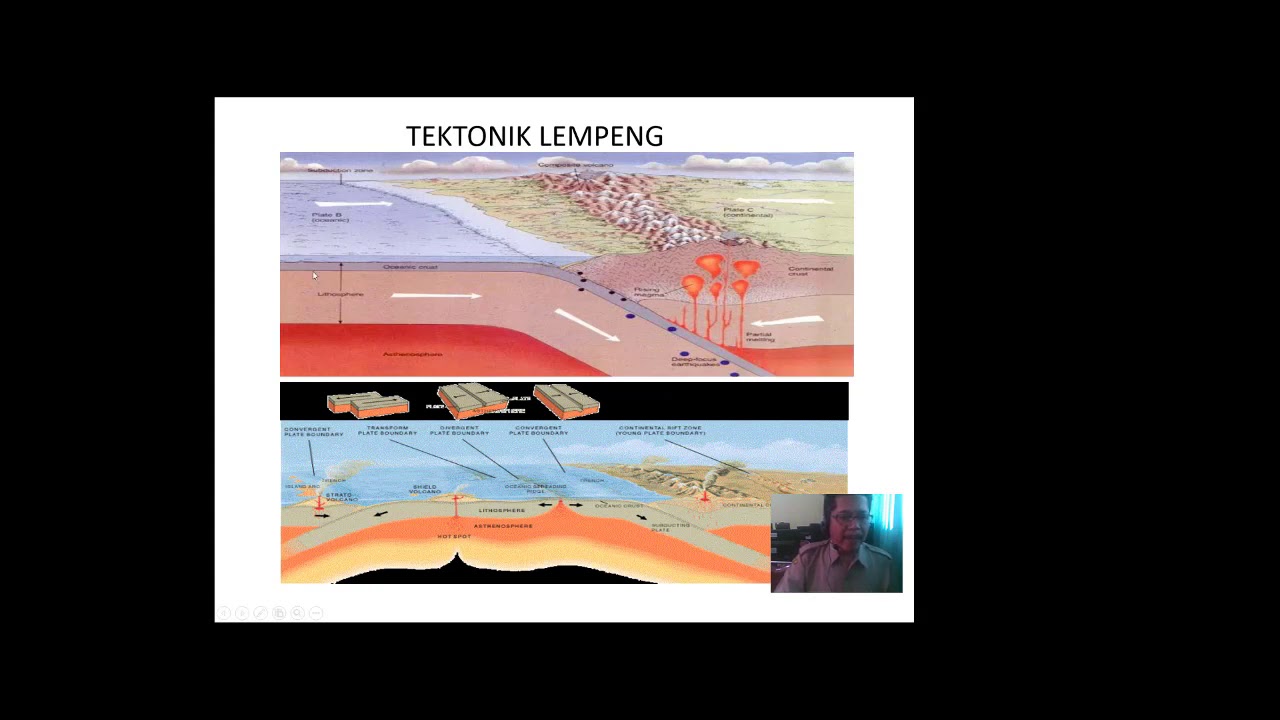
- 😀 The Plate Tectonics Theory, proposed by J. Tuzo Wilson, suggests that the Earth's lithosphere is divided into plates that float atop the asthenosphere, driven by convection currents.
- 😀 Plate movements lead to three types of interactions: convergent (plates move toward each other), divergent (plates move apart), and transform (plates slide past one another).
Q & A
What is the theory of continental drift?
-The theory of continental drift, proposed by Alfred Wegener in 1912, suggests that around 225 million years ago, Earth had a single supercontinent called Pangea, which gradually broke apart into the continents we have today.
What evidence supports the theory of continental drift?
-Evidence for the theory includes similar coastlines between South America and Africa, matching coastlines between North America and Europe, similar fossils found on different continents, and the resemblance of rock formations across continents.
What was the theory of Laurasia and Gondwana?
-The theory of Laurasia and Gondwana, proposed by Eduard Douwes in 1884, states that Earth initially consisted of two large supercontinents: Laurasia in the northern hemisphere and Gondwana in the southern hemisphere. Over time, these landmasses broke apart to form the continents as we know them today.
What are Laurasia and Gondwana, and how did they split?
-Laurasia was the northern landmass, which included North America, Asia, and Europe. Gondwana was the southern landmass, made up of South America, Africa, Australia, and Antarctica. These landmasses eventually split due to tectonic processes.
What is the convection theory, and who proposed it?
-The convection theory, proposed by Arthur Holmes and Harry Hess, suggests that Earth's mantle experiences convection currents due to temperature differences, causing the movement of tectonic plates and the formation of geological features like mountains and volcanoes.
Can you provide an example of convection in everyday life?
-An everyday example of convection is when boiling water in a pot. The hot water rises due to its lower density, while cooler water sinks, creating a circulating movement, similar to the convection currents in Earth's mantle.
What is the relationship between convection currents and tectonic plate movement?
-Convection currents in the Earth's mantle cause the movement of tectonic plates on the Earth's lithosphere. These currents push and pull the plates, leading to geological phenomena such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and the formation of mountain ranges.
What are the mid-Atlantic Ridge and Pacific-Atlantic Ridge?
-The mid-Atlantic Ridge and Pacific-Atlantic Ridge are underwater mountain ranges formed by tectonic activity and convection currents. These ridges mark divergent boundaries where new oceanic crust is created as tectonic plates move apart.
What is the theory of plate tectonics?
-The theory of plate tectonics, proposed by J. Tuzo Wilson, suggests that Earth's lithosphere is divided into several tectonic plates, which float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere beneath. The movement of these plates results in earthquakes, volcanic activity, and the creation of mountains.
What are the three types of tectonic plate movements?
-The three main types of tectonic plate movements are: convergent (plates move toward each other), divergent (plates move apart), and transform (plates slide past each other). These movements result in various geological features and activities.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
IPS KELAS 9 MATERI TEORI TERBENTUKNYA BENUA

Araling Panlipunan 8 MATATAG Q1 Week 1-2 Mga Teorya sa Pagkakabuo ng mga Kontinente with PPT and DLL

Teori pembentukan benua

Evidences Of Plate Tectonics,Continental Drift,Seafloor Spreading,Magnetic Reversal,Grade 10 Science

AWAL MULA PEMBENTUKAN BENUA DAN SAMUDRA ‼️

The continents are moving. When will they collide? - Jean-Baptiste P. Koehl
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
