The ATP CP Energy System, Explosive Power Sports, Exercise Physiology and Physical Performance
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the role of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and creatine phosphate metabolism in energy production within the human body. It highlights how ATP serves as the energy currency, powering essential physiological processes. During high-intensity exercise, ATP is rapidly regenerated through creatine phosphate metabolism, facilitated by the enzyme creatine kinase. This anaerobic process supports short-duration activities like sprinting but is limited in duration due to the finite storage of phosphocreatine in muscles. The video emphasizes the importance of these metabolic pathways for sustaining energy demands during physical exertion.
Takeaways
- ⚡ ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the energy currency of the body, essential for powering physiological processes.
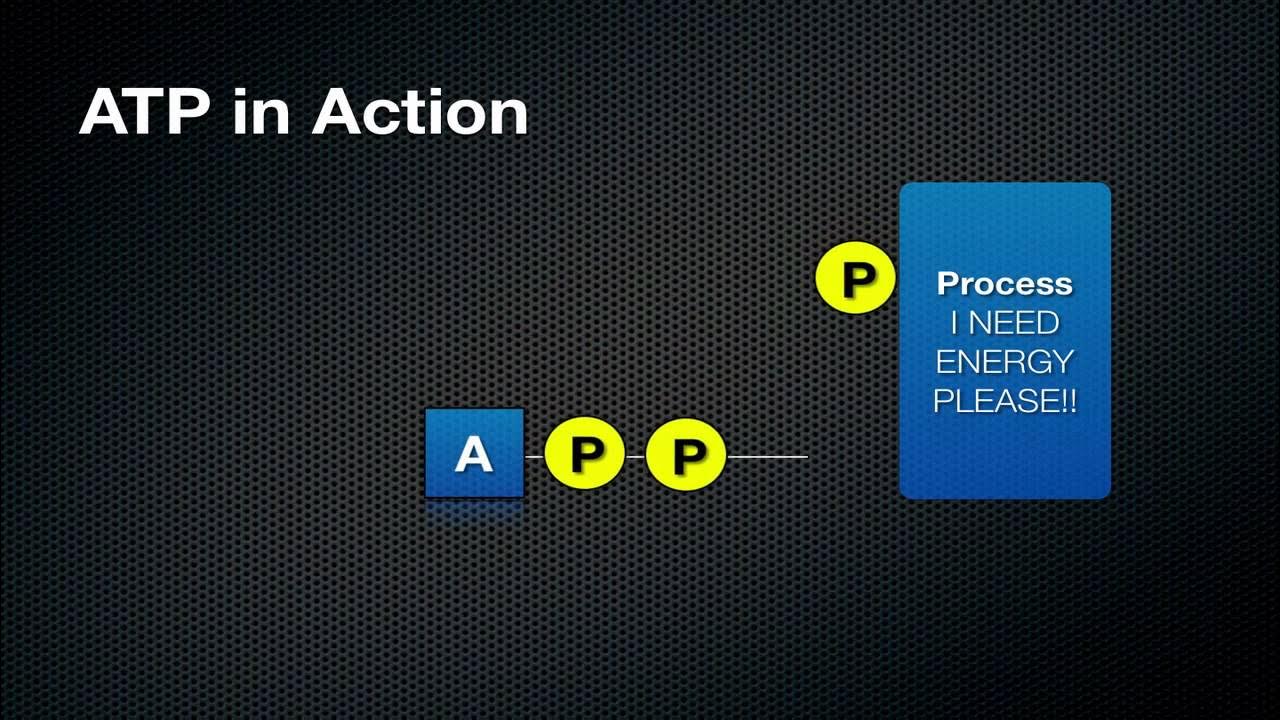
- 💧 ATP is constantly broken down into ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and phosphate, releasing free energy.
- 🔄 The energy extracted from food is used to reform ATP through metabolic processes.
- 🏋️ At rest, most ATP resynthesis occurs via cellular respiration; during exercise, the demand for ATP increases significantly.
- 🚀 The body utilizes three main metabolic pathways to regenerate ATP during high-intensity exercise: ATP-creatine phosphate metabolism, anaerobic glycolysis, and cellular respiration.
- 💪 Creatine phosphate (phosphocreatine) is a naturally occurring energy-rich molecule stored mainly in muscle tissue.
- ⏱️ ATP-creatine phosphate metabolism provides rapid ATP resynthesis but can only sustain energy for a few seconds due to limited phosphocreatine stores.
- 🏃♂️ ATP-creatine phosphate metabolism is predominant during high-intensity, short-duration exercises like sprints.
- 🔥 Anaerobic glycolysis and cellular respiration play a larger role in other types of exercise, especially at lower intensities.
- 🔔 Staying informed about ATP metabolism is crucial for understanding energy production during different physical activities.
Q & A
What is the primary energy currency in the human body?
-Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is considered the primary energy currency in the human body.
How is ATP formed from food?
-The energy contained in food is used to form ATP, but it is not transferred directly; instead, it is utilized to create ATP through metabolic processes.
What occurs during ATP hydrolysis?
-During ATP hydrolysis, ATP is broken down into adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and phosphate, releasing free energy that can be used for cellular work.
Why does the body need to constantly regenerate ATP?
-The body needs to constantly regenerate ATP because its storage is very limited, and ATP is continuously broken down to provide energy for physiological processes.
What are the three metabolic pathways used to regenerate ATP during exercise?
-The three metabolic pathways for ATP regeneration during exercise are ATP creatine phosphate metabolism, anaerobic glycolysis, and cellular respiration.
What role does creatine phosphate play in ATP resynthesis?
-Creatine phosphate, or phosphocreatine, splits into creatine and phosphate through the action of creatine kinase, releasing energy for rapid ATP resynthesis during high-intensity exercise.
What type of exercise predominantly uses ATP creatine phosphate metabolism?
-High-intensity, short-duration exercises, such as a 100-meter sprint, predominantly utilize ATP creatine phosphate metabolism for energy.
How long can the ATP creatine phosphate pathway sustain ATP resynthesis?
-The ATP creatine phosphate pathway can sustain ATP resynthesis for just a few seconds due to the limited amount of phosphocreatine stored in the body.
What is the predominant energy source at rest?
-At rest, the majority of ATP resynthesis occurs via cellular respiration.
What happens to ATP synthesis during high-intensity exercise?
-During high-intensity exercise, the energy demand by working muscles increases dramatically, and ATP creatine phosphate metabolism becomes the predominant pathway for ATP resynthesis.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

ATP: adenosín trifosfato | Energía y enzimas | Biología | Khan Academy en Español
What ATP is and How it Works - BioVid Episode 3

ATP: Adenosine triphosphate | Energy and enzymes | Biology | Khan Academy

Hydrolysis of ATP

ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate

Mecanismo de hidrólisis del ATP | Energía y enzimas | Biología | Khan Academy en Español
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
