Virtual Networks - N10-008 CompTIA Network+ : 1.2
Summary
TLDRThe video script discusses the evolution from physical to virtual servers and the impact on network management. It introduces Network Function Virtualization (NFV), which consolidates network infrastructure into the hypervisor, allowing for flexible and efficient network management through a central console. The script explains how virtual switches (vSwitches) and virtual network interface cards (vNICs) facilitate communication within the virtual environment, enabling advanced network configurations and services.
Takeaways
- 🌐 **Data Management Evolution**: The way data is managed has rapidly evolved, impacting how networks are deployed.
- 🏢 **Transition from Physical to Virtual**: Traditional server farms with individual servers are being replaced by virtual servers on a single physical device.
- 🔀 **Network Function Virtualization (NFV)**: The shift to virtual servers necessitates moving physical network infrastructure into a virtual environment managed by a hypervisor.
- 💻 **Centralized Management**: The hypervisor acts as a central management console, simplifying the management of virtual systems, networks, and resources.
- 🔌 **Virtual Switches (vSwitch)**: Physical switches are being replaced by virtual switches, which can be easily deployed and managed through the hypervisor.
- 🔄 **Automation and Orchestration**: Deployment and management of virtual switches can be automated, enhancing efficiency and reducing manual intervention.
- 📡 **vNICs for VM Communication**: Virtual Network Interface Cards (vNICs) are essential for virtual machines to communicate within the network.
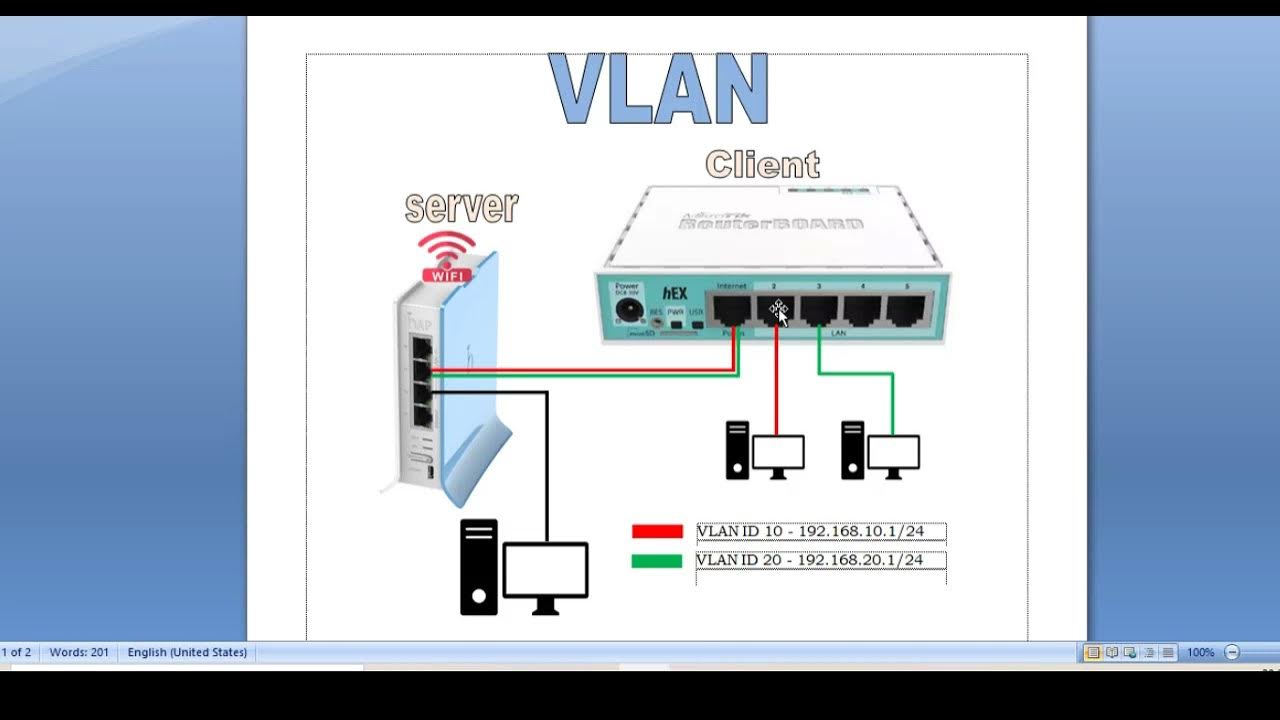
- 🛠️ **Enhanced Network Capabilities**: Virtual networks offer additional capabilities like load balancing, VLANs, and advanced monitoring not always present in physical networks.
- 🔗 **Linking Virtual to Physical**: Uplinks from virtual switches connect the virtual network to the physical world, bridging the gap between the two environments.
- 🔑 **Complex Network Configuration**: The virtual environment allows for complex and detailed network configurations tailored to specific application needs.
Q & A
What is network function virtualization (NFV)?
-Network function virtualization (NFV) is the process of moving network devices, such as switches, routers, and firewalls, into a virtualized environment within the hypervisor, replacing physical network infrastructure with virtual components.
How has virtualization changed the deployment of servers in enterprise networks?
-Virtualization has allowed enterprises to replace hundreds of physical servers with virtual servers, consolidating them into fewer physical devices. This reduces the need for physical hardware and simplifies network management.
What role does the hypervisor play in virtualization?
-The hypervisor, also known as the Virtual Machine Manager (VMM), is responsible for managing all virtual systems, including operating systems, virtual machines, and virtual network connections. It centralizes control of CPU, memory, and network access.
What are the benefits of virtualizing network components like switches and routers?
-Virtualizing network components offers the same functionality as physical devices, with additional advantages like faster deployment (through drag-and-drop interfaces), automation, and easier fault tolerance and monitoring capabilities.
How does a virtual switch (vSwitch) function in a virtual network environment?
-A virtual switch (vSwitch) replaces physical switches in a virtual network environment, connecting virtual machines and handling network traffic. It can be configured with features like link aggregation, port mirroring, and NetFlow for better traffic management.
What is a vNIC, and why is it important in virtual machines?
-A vNIC (virtual network interface card) is a virtual representation of a physical NIC, allowing virtual machines to communicate with the network. vNICs are essential for enabling network access and can be customized for load balancing, VLANs, and monitoring.
What advantages does virtualization provide for scaling and managing network infrastructure?
-Virtualization allows for easier scaling and management of network infrastructure, as new virtual devices can be deployed rapidly without needing physical installation. Additionally, features can be automated through APIs, providing flexibility and efficiency.
What is meant by the 'single pane of glass' in the context of virtualization?
-The 'single pane of glass' refers to the centralized management console of the hypervisor, where administrators can manage all virtual machines, network connections, and resources from one interface, simplifying oversight and control.
How does virtualization impact fault tolerance and monitoring in network infrastructure?
-Virtualization enhances fault tolerance and monitoring by allowing administrators to easily add monitoring services and configure virtual devices to handle failovers, making networks more resilient and easier to manage.
How does the virtual network connect to the physical network in a virtualized environment?
-The virtual network connects to the physical network through uplink interfaces, which bridge the virtual and physical worlds. These interfaces allow virtual machines to communicate with devices outside of the virtual environment.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)