THE CONDITIONALS - 0,1,2 & 3 Conditionals& QUIZ - English Grammar Lesson (+ Free PDF & Quiz)
Summary
TLDRIn this English with Lucy video, Lucy delivers an engaging lesson on the four types of conditionals: zero, first, second, and third. She explains each with examples, noting their use in expressing general truths, probable future events, hypothetical situations, and past unrealized conditions. Lucy offers a free PDF and quiz for practice, encouraging viewers to sign up for her mailing list to receive weekly lessons and engage with her on social media for further learning opportunities.
Takeaways
- 📘 The lesson covers the four conditionals in English: zero, first, second, and third conditionals.
- 📝 A free PDF and quiz are available to help practice and reinforce the lesson.
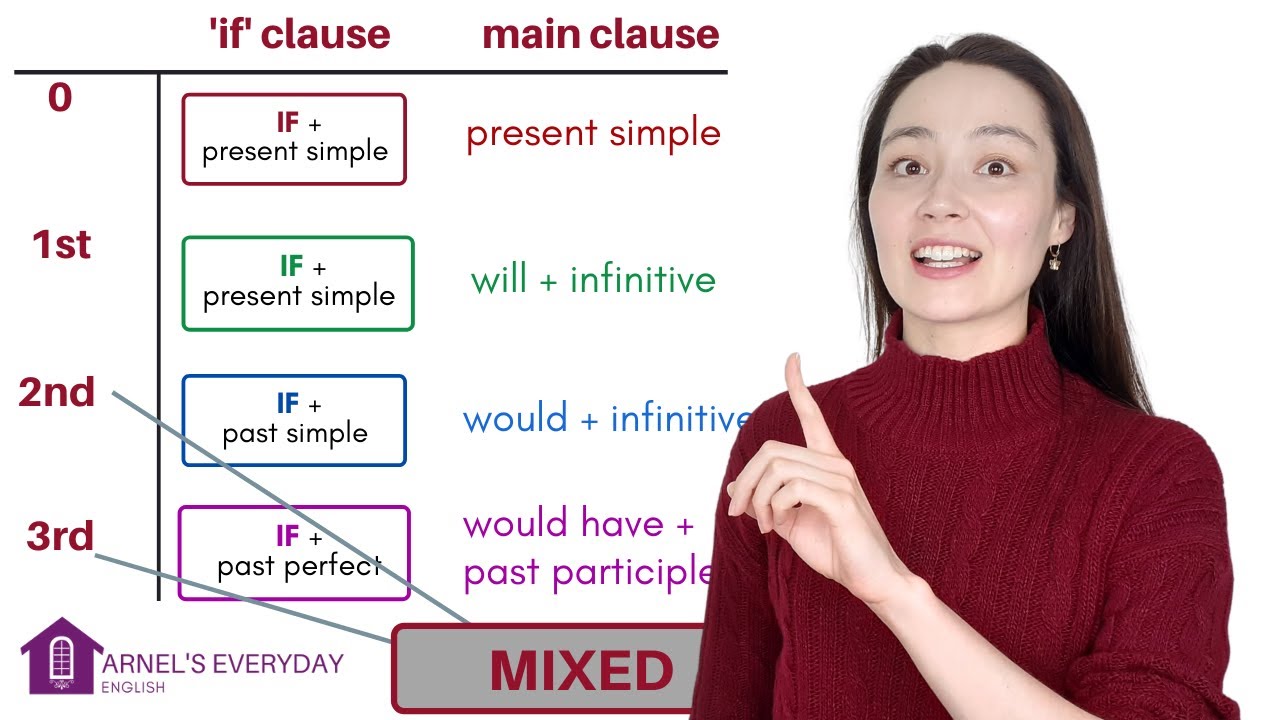
- 💡 The zero conditional discusses general truths and scientific facts, using the present simple in both clauses (e.g., 'If you heat water, it evaporates').
- 🔄 In conditional sentences, the order of clauses (if clause and main clause) can be swapped without changing the meaning.
- 🌍 The first conditional talks about real-world situations and future possibilities, using the present simple after 'if' and the future in the main clause (e.g., 'If you study hard, you will pass the exam').
- 🤔 Modals can be used in the first conditional to express recommendations or uncertainty (e.g., 'If you study hard, you might pass the exam').
- 🎲 The second conditional discusses hypothetical or unreal situations in the present or future, using the past simple after 'if' and 'would' in the main clause (e.g., 'If I won the lottery, I would buy a house').
- 🐾 The second conditional is also used for giving advice or warnings (e.g., 'If I were you, I would stop poking the cat').
- ⏳ The third conditional talks about past situations that didn’t happen, using the past perfect after 'if' and 'would have' in the main clause (e.g., 'If I had studied harder, I would have passed the exam').
- 🎓 To test understanding, a quiz on conditionals is provided in the PDF, and weekly lessons are delivered to subscribers' inboxes.
Q & A
What are the four conditionals discussed in the video?
-The four conditionals discussed are the zero conditional, the first conditional, the second conditional, and the third conditional.
What is the structure of a zero conditional sentence?
-A zero conditional sentence consists of two present simple verbs, one in the if clause and one in the main clause, both in the present tense.
Why is the zero conditional used?
-The zero conditional is used to talk about general truths and scientific facts where there is a guaranteed result.
Can the order of the if clause and the main clause be changed in a conditional sentence?
-Yes, the order of the if clause and the main clause can be changed in a conditional sentence without changing the meaning.
What is the structure of the first conditional?
-The first conditional has the present simple after 'if' and then the future in the main clause.
How is the first conditional used in real-life situations?
-The first conditional is used to talk about things that might happen in the future, expressing probable outcomes in specific situations.
What is the structure of the second conditional?
-The second conditional uses the past simple after 'if', then 'would' and the infinitive, or 'would' and the present continuous.
What kind of situations are discussed using the second conditional?
-The second conditional is used to talk about improbable future situations, dreams, fantasies, or present situations that are impossible.
What is the structure of the third conditional?
-The third conditional uses 'if' and past perfect, then 'would have' and past participle in the main clause.
How is the third conditional different from the other conditionals?
-The third conditional is used to talk about a situation in the past that did not happen and to imagine the results of this imaginary situation.
What additional resources does Lucy offer to help with learning English?
-Lucy offers a PDF with a quiz covering the lesson, a vlogging channel with subtitled daily life vlogs, and a pronunciation tool on her website.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
ALL CONDITIONALS | 0,1,2,3 and MIXED CONDITIONALS - English Grammar | if....

English Conditional Sentences (with examples!)

The 4 Conditionals (Stop Confusing Them)

CONDITIONALS | Learn all the conditionals | English grammar

APRENDA TODAS AS CONDICIONAIS EM INGLÊS | Do Zero à Fluência

CONDITIONALS in Expressing Arguments | GRADE 9 || MELC-based VIDEO LESSON | QUARTER 1| MODULE 2
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
