Mesh Analysis
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script introduces mesh analysis, a method for analyzing electrical networks to determine unknown currents. It explains the concept of a mesh as a loop without any inner loops and outlines the four steps for performing mesh analysis: identifying meshes, assigning mesh currents, developing KVL equations for each mesh, and solving these equations. The script also highlights that mesh analysis is applicable only to planar networks and emphasizes the importance of choosing the direction of mesh currents. It concludes with an example demonstrating how to apply these steps to calculate power loss in a resistor.
Takeaways
- 🔍 Mesh analysis is a method used to analyze electrical networks by determining the unknown currents flowing through various elements.
- 🎯 The primary purpose of mesh analysis is to calculate the power delivered or absorbed by different components within an electrical network.
- 🔌 A mesh is defined as a loop in a circuit that does not contain any other loops within it, and it is a fundamental concept in mesh analysis.
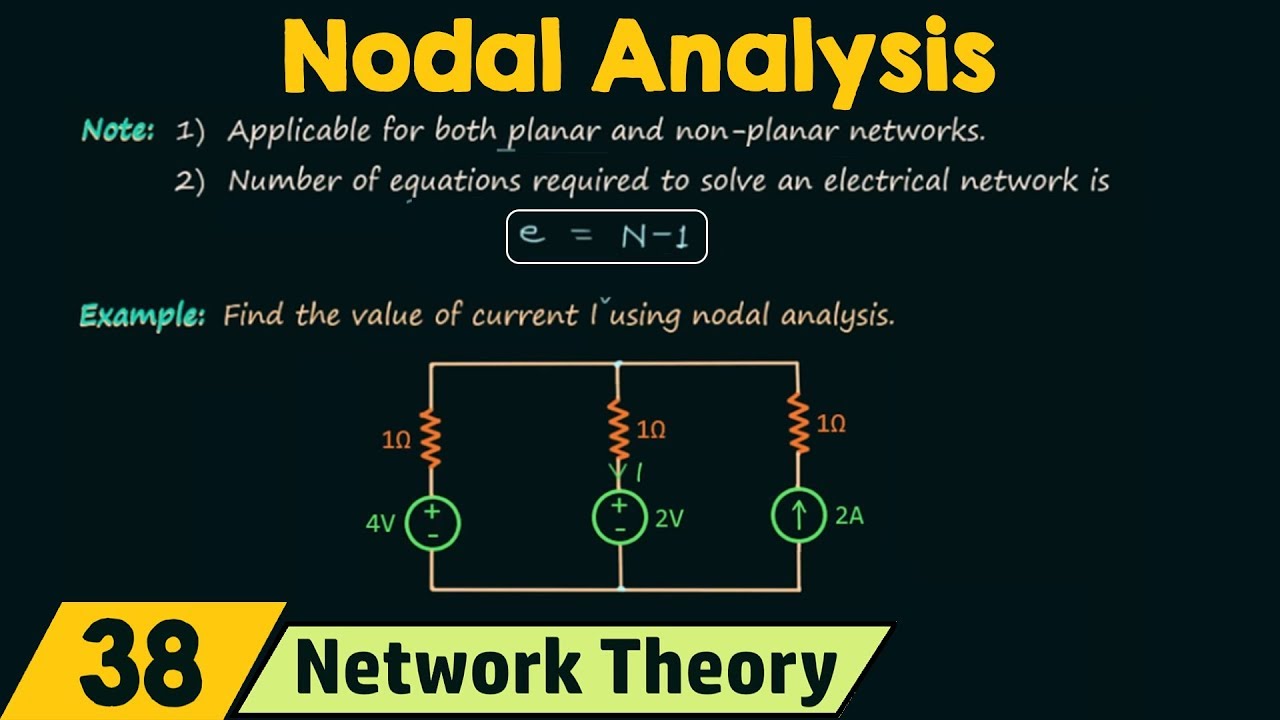
- 📚 Mesh analysis is applicable only to planar networks, where no branch crosses over another, ensuring the network can be drawn on a single plane without any intersections.
- ✏️ The process of mesh analysis involves four main steps: identifying meshes, assigning mesh currents, developing KVL equations for each mesh, and solving those equations.
- 🔄 The direction of mesh current can be chosen as clockwise or counterclockwise, but a clockwise direction is often preferred for convenience and consistency with typical current flow from sources.
- 📉 The number of equations needed for mesh analysis is equal to the number of meshes, which can be calculated using the formula: number of meshes = (number of branches - number of nodes + 1).
- 🧮 Once the mesh currents are determined, further calculations such as power loss in resistors can be performed using the values obtained from the mesh analysis.
- 📝 When developing KVL equations, the mesh current of the particular mesh being considered is given priority in the calculation of net currents through shared resistors.
- 🔑 A key takeaway is the importance of considering the mesh current as the dominant current when formulating KVL equations for a specific mesh, which affects the calculation of voltage drops across resistors.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of mesh analysis in electrical networks?
-The primary purpose of mesh analysis is to determine the unknown currents in an electrical network, which is essential for calculating the power delivered or absorbed by different electrical elements.
What is a mesh in the context of electrical networks?
-A mesh is a loop in an electrical network that does not contain any other loops within it. It is characterized by having the same first and last node.
How does mesh analysis help in obtaining the values of unknown currents?
-Mesh analysis provides a systematic approach to set up equations based on Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) for each mesh, which when solved, yield the values of the unknown currents flowing through the network.
What are the steps involved in performing mesh analysis?
-The steps involved in performing mesh analysis are: 1) Identify the total number of meshes in the network, 2) Assign mesh currents to each mesh, 3) Develop KVL equations for each mesh, and 4) Solve the KVL equations to find the mesh currents.
Why is mesh analysis only applicable to planar networks?
-Mesh analysis is only applicable to planar networks because it relies on the ability to draw the network without any branches crossing each other. Non-planar networks, where branches cross, cannot be analyzed using mesh analysis due to the complexity introduced by the crossings.
Can the direction of mesh current be chosen arbitrarily?
-Yes, the direction of mesh current can be chosen arbitrarily, but it is conventionally chosen as clockwise for convenience and to align with the typical current flow from the source on the left in the network.
What is the relationship between the number of meshes and the number of equations required in mesh analysis?
-The number of equations required to solve an electrical network using mesh analysis is equal to the number of meshes, which can be calculated using the formula: number of meshes = number of branches - number of nodes + 1.
How do you handle the situation where multiple mesh currents pass through the same resistor?
-When multiple mesh currents pass through the same resistor, the net current through the resistor is represented as the difference of the mesh currents, with the priority given to the mesh current for which the KVL equation is being written.
What is the significance of assigning clockwise direction to mesh currents?
-Assigning a clockwise direction to mesh currents is significant because it typically aligns with the direction of current flow from the source, which helps in obtaining positive values for the currents and simplifies the analysis.
How can mesh analysis be used to calculate power loss in a resistor?
-Once the mesh currents are determined through mesh analysis, the power loss in a resistor can be calculated using the formula: power loss = (current^2) * resistance, where 'current' is the current flowing through the resistor.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)