Difference between Analog and Digital Signals | AddOhms #6
Summary
TLDRThe script explores the distinction between analog and digital signals using clocks as a metaphor. Analog signals, like the hands of an analog clock, offer continuous and infinite precision, akin to the smooth change in AC voltage. Digital signals, however, operate with fixed levels, similar to digital clocks that jump from one number to the next. The script further explains the practical application in electronics, emphasizing the need to convert analog signals to digital for systems like Arduino. It concludes by highlighting that digital signals are a specialized form of analog, with specific voltage levels representing data.
Takeaways
- 🕰️ Analog and digital are terms used to describe different types of signals, with analog being continuous and digital being discrete.
- 📱 The transition from analog to digital is evident in various technologies, including cell phones and television transmissions.
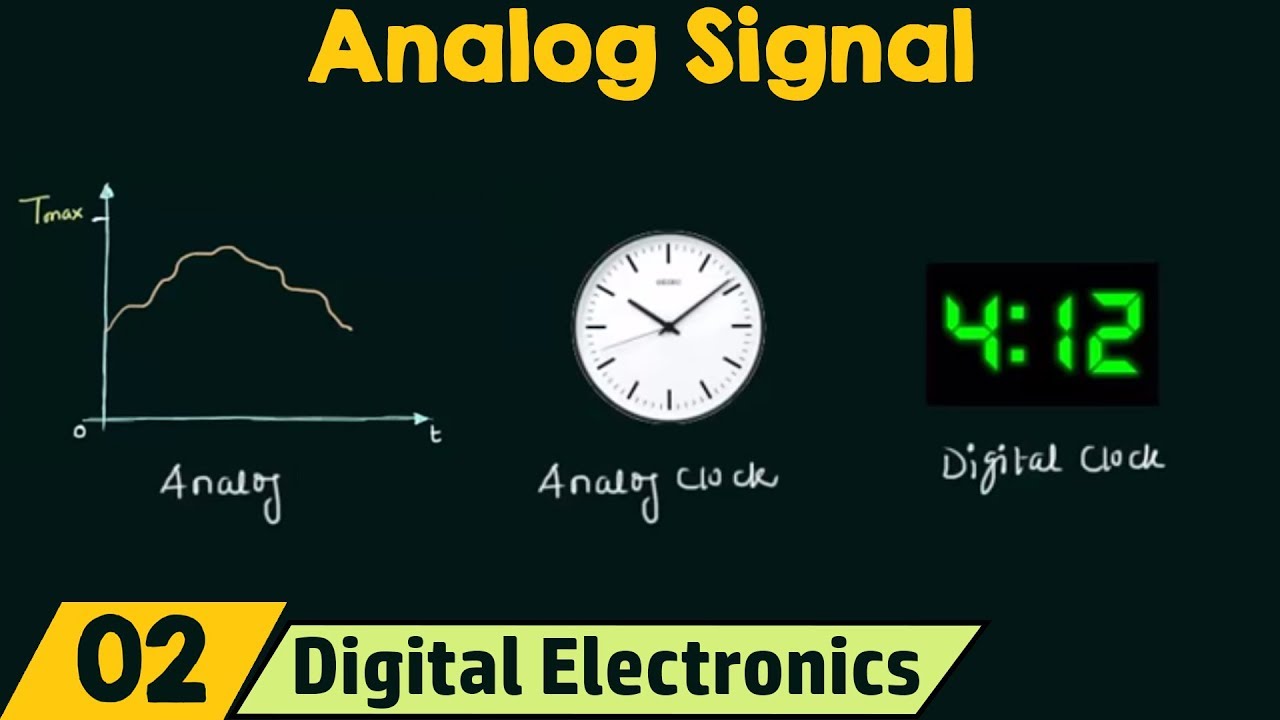
- ⏱ Analog clocks provide a visual example of continuous time representation, unlike digital clocks which show time in discrete increments.
- 🔋 Analog signals are continuously variable, like the hands of a clock or the voltage in an AC circuit, which changes continuously.
- 📊 Digital signals are represented by fixed symbols, typically 0s and 1s, which correspond to specific voltage levels.
- 🛠️ Sensors, like accelerometers, provide analog outputs that vary continuously and need to be converted to digital for digital systems.
- 💡 Digital signals have defined voltage levels for 0s and 1s, with an undefined zone in between that can cause uncertainty in signal interpretation.
- 🔌 The concept of analog and digital extends beyond clocks and includes electronic systems, where signals are processed and transmitted.
- 🔄 Understanding the difference between analog and digital is crucial for comprehending how electronic devices function and interact with each other.
- 🌐 The script highlights that digital signals are a form of analog signals where specific voltage levels are assigned special meanings.
Q & A
What is the primary difference between analog and digital signals?
-The primary difference is that analog signals are continuously variable and change, while digital signals have defined levels or symbols, typically represented by 0s and 1s.
How does the minute hand on an analog clock represent time?
-The minute hand on an analog clock represents time by continuously moving between the numbers on the clock face, allowing one to estimate the elapsed minutes by observing its position.
Why do we need to convert analog signals to digital before using them with digital systems?
-We need to convert analog signals to digital because digital systems can only process signals with fixed symbols like 0 and 1, and analog signals are continuously variable.
What is an example of an analog electronic device mentioned in the script?
-An example of an analog electronic device mentioned is an accelerometer, which provides an analog output that varies its voltage depending on the acceleration it measures.
How does the voltage in an AC system relate to the concept of analog signals?
-The voltage in an AC system continuously changes at a rate of 50 to 60 Hertz, which is an example of an analog signal because it is continuously variable.
What is the significance of the undefined area in digital signals?
-The undefined area in digital signals is significant because it represents voltage levels where the signal could be interpreted as either a 0 or a 1, which can cause unpredictability in digital logic.
How are digital signals formed in terms of voltage levels?
-Digital signals are formed with voltage levels where 0 volts represent a digital 0, and a high voltage, such as 5 volts, represents a digital 1.
What is the range of voltages considered as a digital 0 and 1 on an Arduino Uno?
-On an Arduino Uno, a digital 0 is considered from 0 volts up to 0.5 volts, while a digital 1 is from 3.5 volts up to 5 volts.
Why do digital clocks only show numbers 0 through 9?
-Digital clocks only show numbers 0 through 9 because digital signals are represented with fixed symbols, and these numbers represent the states of the signal.
How does the concept of analog and digital signals apply to modern technology like cell phones and television transmissions?
-Modern technology like cell phones and television transmissions have shifted from analog to digital to take advantage of the precision and efficiency of digital signals, which are less prone to interference and allow for more data to be transmitted.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)