Physics - Waves - Analogue and Digital Signals
Summary
TLDRThe video script explores the distinction between analog and digital signals, highlighting how analog signals vary continuously and can take on numerous values, while digital signals are binary, represented by ones and zeros. It demonstrates the superiority of digital signals in long-distance transmission, as they are resistant to noise and interference, allowing for clearer signal recovery. Additionally, digital signals can carry more information and are easily processed by computers, showcasing their higher quality and versatility compared to analog signals.
Takeaways
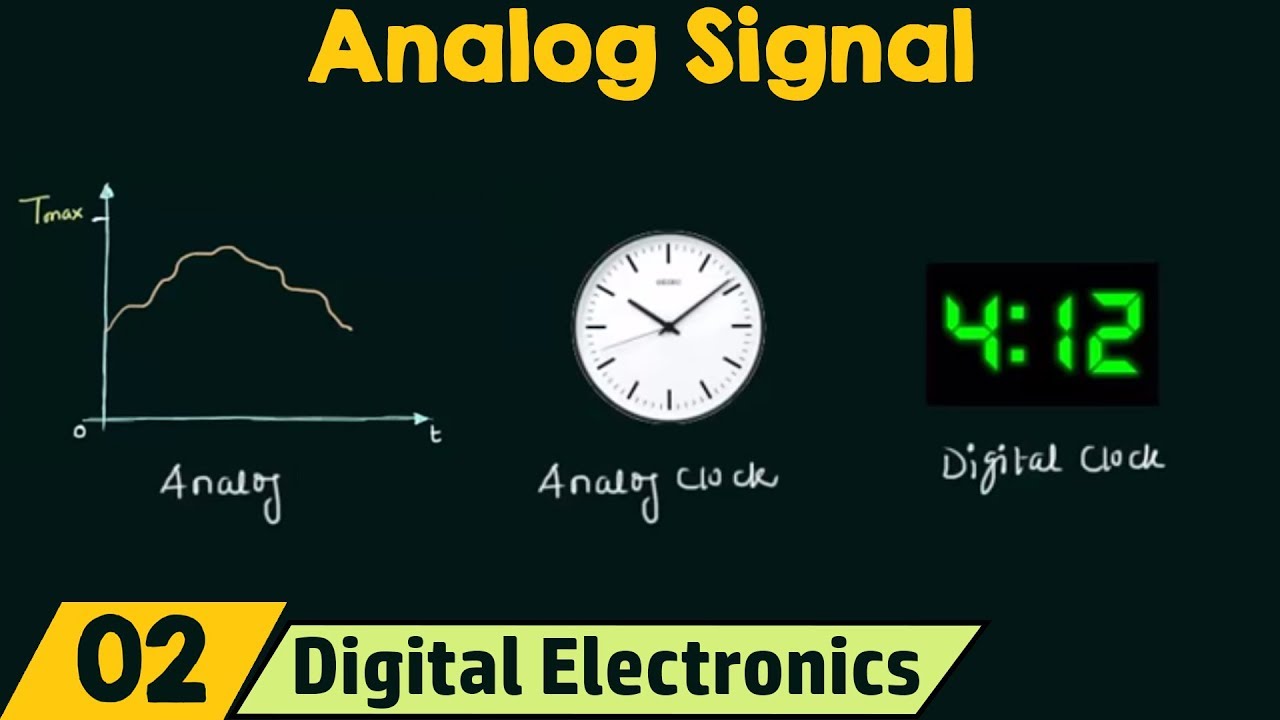
- 📶 **Analog Signal Characteristics**: Analog signals vary continuously in amplitude and frequency, taking on many different values.
- 🔢 **Digital Signal Characteristics**: Digital signals are binary, taking only two values, one or zero, represented as on or off.
- 🌐 **Signal Transmission**: Digital signals are more efficient for long-distance transmission compared to analog signals.
- 📱 **Phone Signal Conversion**: In phone calls, the analog voice signal is converted to digital before transmission.
- 🛰️ **Signal Path**: Digital signals can be sent via a series of transmitters like microwaves, phones, satellites, and then to the receiver.
- 📉 **Noise Impact on Analog**: Analog signals are susceptible to noise and interference, which degrade the signal quality over distance.
- 📈 **Noise Impact on Digital**: Digital signals maintain their integrity despite noise, allowing for clear reception and conversion back to the original signal.
- 🔍 **Signal Quality**: Digital signals provide higher quality due to their resistance to noise and interference.
- 📚 **Information Capacity**: Digital signals can carry more information and multiple signals simultaneously.
- 💻 **Computer Compatibility**: Digital signals are more easily interpreted and processed by computers.
Q & A
What are the two main ways of sending information mentioned in the script?
-The two main ways of sending information mentioned are analog and digital signals.
How does an analog signal differ from a digital signal in terms of its characteristics?
-An analog signal varies continuously in amplitude and frequency, taking on many different values, whereas a digital signal can only take two values, typically represented as 1 or 0.
What are the two values that a digital signal can take, and what are they sometimes called?
-A digital signal can take two values, which are either a one or a zero, and these are sometimes referred to as on or off.
Why is digital a better way of sending information over long distances according to the script?
-Digital is a better way of sending information over long distances because it is less susceptible to noise and interference, maintaining higher signal quality.
How is the process of converting an analog signal to a digital signal described in the script?
-The process is described as the analog sound entering the phone, being converted to a digital signal, and then sent out via microwaves.
What happens to the signal received by a phone in the case of digital transmission?
-In digital transmission, the signal received by the phone may pick up noise or interference, but it is still clear enough for the phone to convert it back perfectly to the original signal.
What is the main issue with analog signals when they are transmitted over long distances?
-The main issue with analog signals is that they pick up noise and interference, and their amplitude is reduced as they travel, leading to a degraded signal quality.
Why does amplifying an analog signal also amplify the noise along with the signal?
-Amplifying an analog signal also amplifies the noise because the process does not differentiate between the original signal and the noise picked up during transmission.
What are some benefits of digital signals over analog signals as mentioned in the script?
-Benefits of digital signals include resistance to noise and interference, the ability to carry more information, the capacity to send multiple different signals simultaneously, and ease of interpretation by computers.
How does the script illustrate the difference in signal quality between digital and analog transmissions?
-The script illustrates this by showing that a digital signal, despite noise, can be easily converted back to the original signal, while an analog signal becomes almost unrecognizable and requires amplification that also amplifies the noise.
What role do computers play in the context of digital signals as described in the script?
-Computers play a role in easily interpreting digital signals, which is one of the benefits of using digital signals over analog ones.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)