2.4 Overview of the Audit Process Audit Planning Audit Strategy vs Plan vs Program
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the intricacies of audit planning, contrasting the concepts of audit strategy, plan, and program. It uses the analogy of organizing a Filipino-themed party to clarify these distinctions. The script highlights the importance of developing an audit strategy to set scope and direction, an audit plan for a detailed engagement outline, and an audit program for specific step-by-step audit procedures. It also touches on considering the work of others, including predecessor auditors, internal auditors, and experts, emphasizing the auditor's responsibility and the need for objectivity and competence in these collaborations.
Takeaways
- 📘 The difference between audit strategy, audit plan, and audit program is essential for audit planning. The strategy is the broadest, the plan is more detailed but still broad, and the program contains specific, step-by-step procedures.
- 🎉 An analogy of planning a social event, like a Filipino-themed party, helps to illustrate the concepts of strategy, plan, and program in the context of audit planning.
- 🔍 Audit strategy is the required output of audit planning, which involves designing approaches to achieve necessary audit assurance at the lowest cost within available information constraints.
- 📝 The audit plan is more detailed than the strategy and includes an overview of the engagement, objectives, services, timetable, staff assignments, and preliminary evaluations.
- 🍗 The audit program provides a set of detailed instructions for auditors, including audit objectives for each area and time budgets, to ensure proper execution of work.
- 🛠️ Developing audit programs for initial engagements typically occurs in three stages, starting with broad phases and becoming more detailed as the audit progresses.
- 🔄 The audit program is not fixed and can be revised as work progresses, similar to materiality considerations that can be reviewed and adjusted during the audit.
- 🤝 Considering the work of others involves initiating contact with predecessor auditors and evaluating the involvement and objectivity of other professionals, such as internal auditors and experts.
- 👥 Internal auditors can assist external auditors but cannot take over or share the responsibility of the audit, which remains solely with the external auditor.
- 🏢 The objectivity of experts and internal auditors can be assessed through their organizational reporting structure, while their competence can be evaluated through academic background and certifications.
- 📑 Client-prepared working papers should not be accepted at face value and must be corroborated as part of the audit process.
- 🔚 The completion of audit planning phase sets the stage for the next phase, which is risk response, to be discussed in the subsequent video.
Q & A
What is the main difference between an audit strategy, an audit plan, and an audit program?
-An audit strategy is the broadest, setting the scope, timing, and direction of the audit. An audit plan is more detailed than a strategy but still contains broad strokes, outlining the nature and characteristics of the client's business and audit objectives. An audit program is the most detailed, containing specific audit procedures and instructions for each audit.
Why is it important to establish an audit strategy during audit planning?
-Establishing an audit strategy is crucial as it involves designing optimized approaches to achieve the necessary audit assurance at the lowest cost within the constraints of available information. It guides the development of a more detailed audit plan.
What are the key elements included in an audit plan?
-An audit plan includes the description of the client company, audit objectives, services to be performed, timetable of audit work, estimated start and end dates, work to be done by the client, assignment of audit staff, target completion dates, preliminary evaluation and judgment about materiality levels, special problems to be resolved, and conditions that may require changes in audit tests.
How is an audit program developed for initial engagements?
-For initial engagements, the audit program typically develops in three stages. The broad phases of the program can be outlined at the time of engagement, more details can be identified after the review of internal control structure and accounting procedures, and specific audit phase procedures can be further challenged and revised as work progresses.
What is the purpose of considering the work of others during audit planning?
-Considering the work of others allows the auditor to evaluate the competence and objectivity of other professionals involved, such as the predecessor auditor, internal auditors, and external experts. This helps the auditor to determine the extent to which they can rely on the work of these individuals.
Why is it necessary for an auditor to initiate contact with a predecessor auditor?
-Initiating contact with a predecessor auditor is necessary to gain insights into the client's previous audit experiences and to understand any potential issues or concerns. However, the extent of information shared is dependent on the client's permission.
How can an auditor assess the objectivity of an expert involved in the audit?
-An auditor can assess the objectivity of an expert by examining their organizational position, lines of communication, and to whom they directly report. This helps determine if the expert is influenced by parties that could compromise their objectivity.
What is the role of internal auditors in协助 an external audit?
-Internal auditors can assist external auditors by performing specific audit procedures and enhancing internal control. However, the responsibility for the audit cannot be transferred or shared with internal auditors; they are there in an assisting capacity only.
How can an auditor ensure that the audit program is adaptable to changes during the audit process?
-An auditor ensures adaptability by regularly reviewing and revising the audit program as the work progresses and as new information becomes available. This allows the program to reflect the current audit context and address emerging risks or issues.
What are some factors that could require changes in audit tests as outlined in an audit plan?
-Factors that could require changes in audit tests include changes in the client's business operations, new regulations, identification of material misstatements, or the discovery of new risks during the audit process.
Why is it important for an auditor to corroborate information provided by client staff or internal auditors?
-Corroborating information is important to ensure its accuracy and reliability. It helps the auditor to verify that the information provided is not misleading and to maintain the integrity of the audit process.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

2.2 Overview of the Audit Process Auditing Planning Knowledge, Analytics, Materiality

2.3 Overview of the Audit Process Audit Planning Risk Assessment

FASE DE LA AUDITORIA PLANIFICACION ESPECIFICA
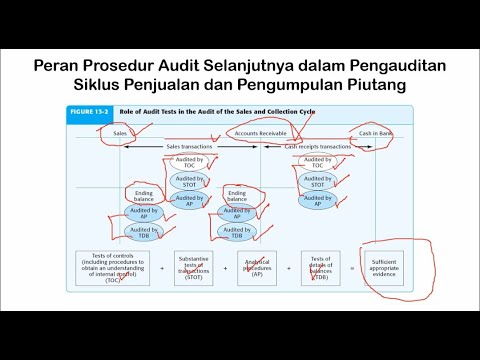
PERENCANAAN AUDIT - Strategi Audit Keseluruhan dan Program Audit

Tahapan Audit

Getting Started With: Developing an Audit Program
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
