Belajar If Conditional #english #belajarbahasainggris #ifcondition #fyp #materikelas
Summary
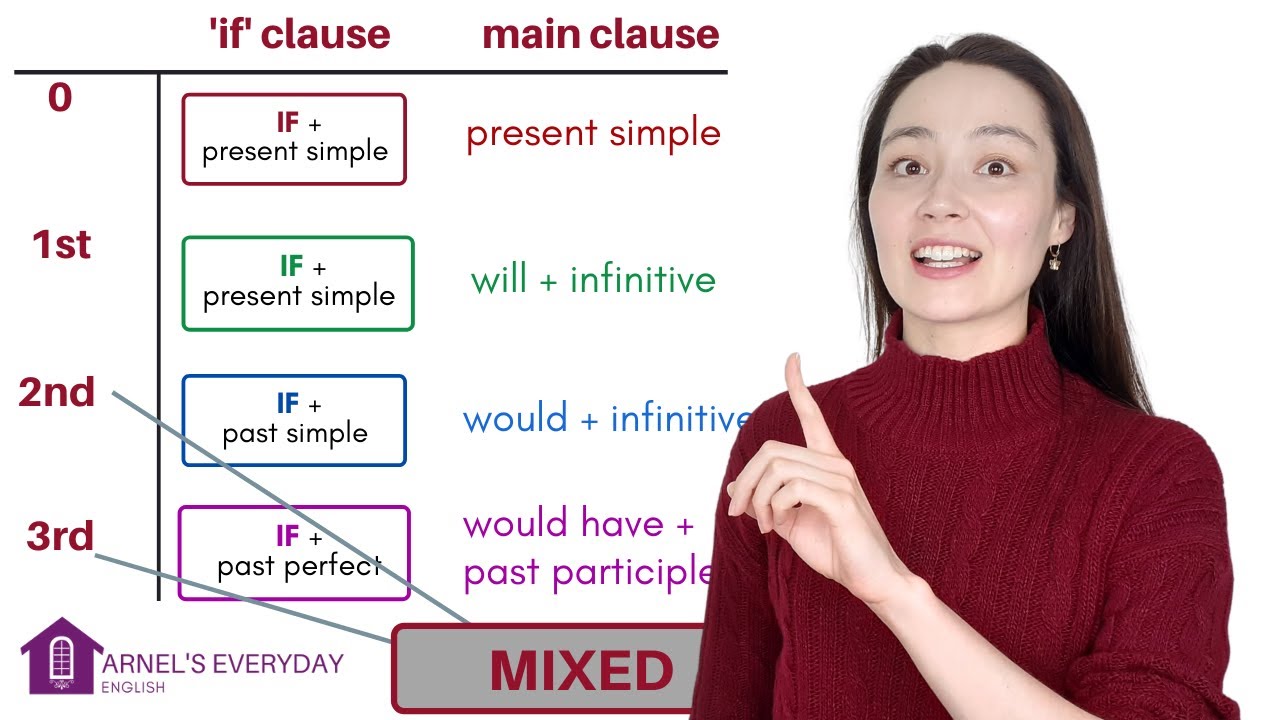
TLDRThis video explains the use of conditionals in English, focusing on zero, first, and second conditionals. The zero conditional describes general facts or situations that always happen, using the present simple tense. The first conditional deals with specific, likely future events, combining the present simple in the condition with 'will' in the result. The second conditional expresses hypothetical or highly unlikely situations, using the past simple in the condition and 'would' in the result. Through clear examples, the video highlights sentence structure, word order flexibility, and common mistakes, making it easier for learners to understand and apply conditional sentences effectively.
Takeaways
- 😀 Zero conditional is used to talk about general facts, things that always happen, or scientific truths.
- 😀 Both parts of a zero conditional sentence use the present simple tense.
- 😀 The word 'when' can replace 'if' in zero conditional sentences without changing the meaning.
- 😀 Questions in zero conditional usually start with 'do' or 'does' and often place the condition at the end.
- 😀 First conditional talks about specific situations that are very likely to happen.
- 😀 In first conditional, the 'if' part uses present simple, while the result uses 'will' + verb.
- 😀 'Will' should not be used in the condition part of the first conditional.
- 😀 Second conditional is used for hypothetical, very unlikely, or impossible situations.
- 😀 In second conditional, the 'if' part uses past simple, and the result uses 'would' + verb.
- 😀 The order of 'if' clause and result clause can usually be switched without changing meaning.
- 😀 Examples of zero conditional: 'If water reaches 0°, it freezes.' or 'Ice melts when you heat it.'
- 😀 Examples of first conditional: 'If it is sunny, we will go to the beach.' or 'If I hear any news, I will call you.'
- 😀 Examples of second conditional: 'If I won the lottery, I would buy a rocket.' or 'If I were a wild animal, I would be a lion.'
Q & A
What is the zero conditional used for?
-The zero conditional is used to talk about general facts, things that happen all the time, or scientific truths.
What is the structure of a zero conditional sentence?
-A zero conditional sentence has two parts: 'if' plus the present simple tense for the condition, and the present simple tense for the result. For example, 'If water reaches 0°C, it freezes.'
Can the word 'when' be used in place of 'if' in zero conditional sentences?
-Yes, 'when' can be used instead of 'if' in zero conditional sentences without changing the meaning. For example, 'When you heat ice, it melts.'
How do you form questions in the zero conditional?
-Questions in the zero conditional usually start with 'do' or 'does,' and the 'if' part often comes at the end. For example, 'Does rain turn to snow if it's 3°C?'
What distinguishes the first conditional from the zero conditional?
-The first conditional talks about specific situations that are likely to happen, using 'if' plus present simple for the condition and 'will' plus verb for the result.
Give an example of a correct first conditional sentence.
-If you study hard, you will pass the exam.
Why shouldn't 'will' be used in the 'if' part of the first conditional?
-Because the condition must be in the present simple tense. Using 'will' in the condition is incorrect and not grammatically accepted.
When is the second conditional used?
-The second conditional is used for hypothetical, very unlikely, or impossible situations.
What is the structure of a second conditional sentence?
-A second conditional sentence uses 'if' plus the past simple for the condition, and 'would' plus the verb for the result. For example, 'If I won the lottery, I would buy a rocket.'
Can the order of the 'if' clause and the result clause be changed in any conditional?
-Yes, the order is flexible in all conditionals. For example, 'I will call you if I hear any news' is equivalent to 'If I hear any news, I will call you.'
What is the key difference between the zero, first, and second conditionals?
-The zero conditional expresses general truths, the first conditional expresses likely future events, and the second conditional expresses hypothetical or unlikely situations.
Provide an example where the second conditional is used for an impossible situation.
-If I were a wild animal, I would be a lion.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

CONDITIONALS | Learn all the conditionals | English grammar

CONDITIONALS in Expressing Arguments | GRADE 9 || MELC-based VIDEO LESSON | QUARTER 1| MODULE 2
ALL CONDITIONALS | 0,1,2,3 and MIXED CONDITIONALS - English Grammar | if....

The 4 Conditionals (Stop Confusing Them)

APRENDA TODAS AS CONDICIONAIS EM INGLÊS | Do Zero à Fluência

Mixed Conditionals | English Grammar | Examples & Practice
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
