Animal Tissues - Class 9 Tutorial
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the four basic types of animal tissues: epithelial, nervous, muscle, and connective. Epithelial tissue serves as a protective covering for body surfaces, with subtypes including squamous, columnar, and cuboidal. Nervous tissue, made up of neurons, transmits signals throughout the body, enabling movement and reflexes. Muscle tissue, consisting of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles, facilitates bodily movement, both voluntary and involuntary. Finally, connective tissue supports and connects various body parts, with subtypes like blood, bone, cartilage, and adipose tissue. The video concludes with a review of the functions and classifications of each tissue type.
Takeaways
- 😀 Animal tissues are made up of groups of similar cells working together for a specific function.
- 😀 There are four main types of animal tissues: epithelial, nervous, muscle, and connective tissues.
- 😀 Epithelial tissue covers and protects internal and external body surfaces. It is subdivided into simple squamous, stratified squamous, columnar, and cuboidal types.
- 😀 Simple squamous epithelium is thin and flat, found in the alveoli for small molecule transport.
- 😀 Stratified squamous epithelium is multi-layered and protects areas like the skin from abrasion.
- 😀 Columnar epithelium acts as a barrier against bacteria and is permeable to necessary ions, found in the digestive system.
- 😀 Cuboidal epithelium aids in absorption and mechanical support, like in kidney tubules.
- 😀 Nervous tissue consists of neurons, with dendrites bringing signals to the cell body and axons transmitting them to other cells.
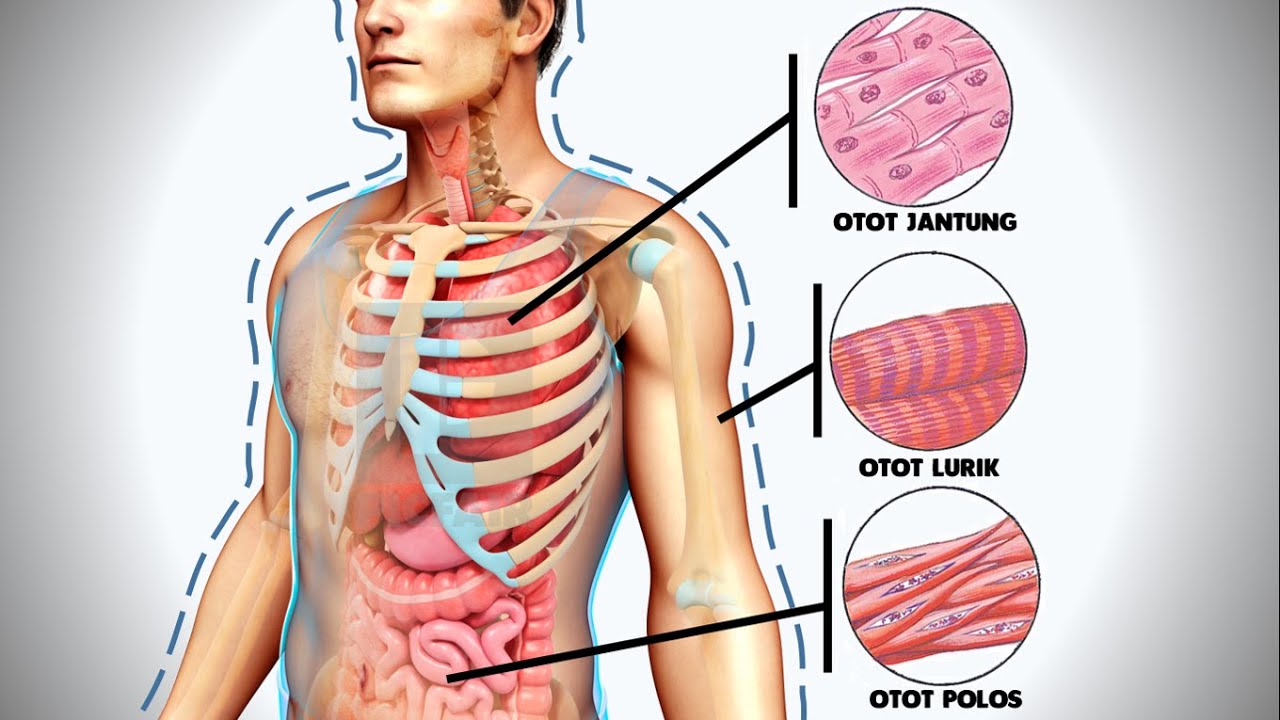
- 😀 Muscle tissue allows movement and is divided into three types: skeletal (voluntary), smooth (involuntary), and cardiac (involuntary).
- 😀 Connective tissue binds, supports, and transports materials, and includes blood, bone, ligament, cartilage, areolar, and adipose tissues.
- 😀 Blood is a connective tissue with a fluid matrix containing red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, essential for gas and material transport.
Q & A
What are the four basic types of animal tissues?
-The four basic types of animal tissues are epithelial tissue, nervous tissue, muscle tissue, and connective tissue.
What is the function of epithelial tissue?
-Epithelial tissue covers and protects the internal and external surfaces of the body, acting as a barrier and facilitating absorption, secretion, and filtration.
What are the different types of epithelial tissue?
-Epithelial tissue is subdivided into simple squamous, stratified squamous, columnar, and cuboidal epithelium, each categorized based on the shape and function of the cells.
Where is simple squamous epithelium found, and what is its function?
-Simple squamous epithelium is found in the lining of alveoli and allows for the transport of small molecules across the membrane due to its thin, flat, and single-layered structure.
What is the function of stratified squamous epithelium?
-Stratified squamous epithelium protects areas of the body that are subject to abrasion, such as the skin, due to its multi-layered structure.
What is the role of columnar epithelium in the body?
-Columnar epithelium acts as an impermeable barrier to bacteria while being permeable to essential ions. It is typically tall and column-shaped.
What is the purpose of cuboidal epithelium?
-Cuboidal epithelium aids in absorption and provides mechanical support. It is found lining the kidney tubules and is shaped like a cube.
How do nervous tissue cells work to send signals?
-Nervous tissue consists of neurons, which have dendrites that receive signals and an axon that transmits the signals to other neurons, allowing for communication within the body.
What are the three types of muscle tissues, and what are their functions?
-The three types of muscle tissues are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscle facilitates voluntary body movements, smooth muscle controls involuntary movements like those in the intestines and blood vessels, and cardiac muscle is responsible for the involuntary contractions of the heart.
What are the functions of connective tissue?
-Connective tissue binds and supports body parts, and also transports materials. Types of connective tissue include blood, bone, ligament, cartilage, areolar, and adipose tissue.
How does blood function as a connective tissue?
-Blood, as a connective tissue, contains red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets that transport gases and other materials throughout the body. It has a fluid matrix that supports circulation.
What is the role of bone in the body?
-Bone is a connective tissue that provides structural support to the body. Bone cells secrete calcium, which hardens the bone and helps protect vital organs.
What is the function of ligaments?
-Ligaments are fibrous and stretchy connective tissues that connect bones to each other, providing stability to joints and allowing for movement.
What is the purpose of cartilage in the body?
-Cartilage is a tough but flexible tissue that protects bones by preventing them from rubbing against each other, cushioning joints, and aiding in smooth movement.
What is the function of adipose tissue?
-Adipose tissue stores fat molecules, providing energy reserves, insulation, and cushioning for organs in the body.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)