Mekanika Fluida FM01 (Lecture3: 6/8). Venturimeter - Aplikasi persamaan Bernoulli
Summary
TLDRIn this lesson, the concept of the Venturi meter is introduced as a device used to measure fluid velocity within pipes. The script discusses how changes in pipe diameter affect fluid velocity and pressure, applying Bernoulli’s equation to calculate these changes. The Venturi meter allows the measurement of fluid velocity by observing differences in static pressure at different points in the pipe. The lesson emphasizes the practical application of Bernoulli’s principle and provides a detailed explanation of how measurements, such as pressure differences and pipe dimensions, are used to determine velocity using simple formulas.
Takeaways
- 😀 Venturi meter is an apparatus used to measure the speed of fluid flowing through a pipe.
- 😀 The shape of the pipe can vary, and the Venturi meter helps assess the flow rate despite the pipe's opacity.
- 😀 The principle behind the Venturi meter involves changes in fluid velocity as the diameter of the pipe changes.
- 😀 Bernoulli’s equation can be applied between two points (1 and 2) to analyze fluid behavior in a Venturi meter.
- 😀 Static pressure changes when the fluid's velocity changes as it passes through different diameters of the pipe.
- 😀 If the pressure in the pipe is greater than the atmospheric pressure, the fluid will rise within the pipe.
- 😀 If the pressure inside the pipe is lower than atmospheric pressure, air will enter the pipe.
- 😀 The flow velocity increases when the pipe diameter decreases, and this relationship can be quantified using Bernoulli’s equation.
- 😀 The pressure difference between two points in the pipe is related to the change in fluid velocity and can be calculated with Bernoulli's principle.
- 😀 Key formula: Velocity at Point 2 (U2) can be determined by the relationship U2 = U1 * (A1 / A2), where A1 and A2 are the areas at points 1 and 2.
- 😀 By measuring the difference in fluid height between two tubes and the pipe dimensions, the fluid velocity (U1) can be calculated using Bernoulli’s equation.
Q & A
What is the purpose of a Venturi meter?
-A Venturi meter is used to measure the velocity of a fluid flowing through a pipe. It works by utilizing the changes in fluid pressure and velocity as the fluid flows through a constricted section of the pipe.
How does the Venturi meter work?
-The Venturi meter has a pipe with a varying cross-sectional area. As the fluid enters a narrower section of the pipe, its velocity increases, and the pressure decreases. This change in velocity and pressure can be used to calculate the fluid's speed.
What is Bernoulli’s equation, and how is it related to the Venturi meter?
-Bernoulli’s equation relates the pressure, velocity, and height of a fluid at different points along its flow. In the case of the Venturi meter, the equation helps explain the relationship between changes in fluid velocity and pressure, which is essential for measuring flow speed.
What happens to the fluid when the diameter of the pipe decreases in a Venturi meter?
-When the diameter of the pipe decreases, the fluid velocity increases due to the continuity equation, which states that the flow rate must remain constant. At the same time, the pressure in the narrower section of the pipe decreases.
What variables are used in the Bernoulli equation for the Venturi meter?
-The variables used in the Bernoulli equation include pressure (P), fluid density (ρ), velocity (v), gravitational acceleration (g), and height (z). These variables are essential in calculating the pressure and velocity changes between two points in the fluid flow.
How do you calculate the velocity of the fluid in a Venturi meter?
-The velocity of the fluid in the narrower section of the pipe (Point 2) can be calculated using the following formula derived from Bernoulli’s principle: v2 = √(2g ΔH / ((A1 / A2)² - 1)), where ΔH is the height difference between the two points, and A1 and A2 are the cross-sectional areas at the two points.
What is the significance of the height difference (ΔH) in a Venturi meter?
-The height difference (ΔH) between the two points in the Venturi meter represents the pressure difference. This height difference can be measured physically, and it is used in the calculation of the fluid's velocity using Bernoulli's equation.
How is the pressure difference between two points in a Venturi meter related to velocity changes?
-The pressure difference between two points in the Venturi meter is inversely related to the velocity change. As the fluid accelerates in the narrower section of the pipe, the pressure decreases. This relationship is explained by Bernoulli’s equation, where an increase in velocity results in a decrease in pressure.
What role does the cross-sectional area (A1 and A2) play in the operation of a Venturi meter?
-The cross-sectional areas (A1 and A2) at two points in the Venturi meter determine how the fluid's velocity will change. According to the continuity equation, if the area decreases, the velocity increases. The ratio of A1 to A2 is crucial for calculating the fluid's speed using Bernoulli's equation.
What practical applications can the Venturi meter be used for?
-The Venturi meter is used in various applications where measuring the flow rate of fluids is necessary. It is commonly applied in industrial systems, water treatment plants, and in scientific experiments to measure fluid velocity in pipes.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
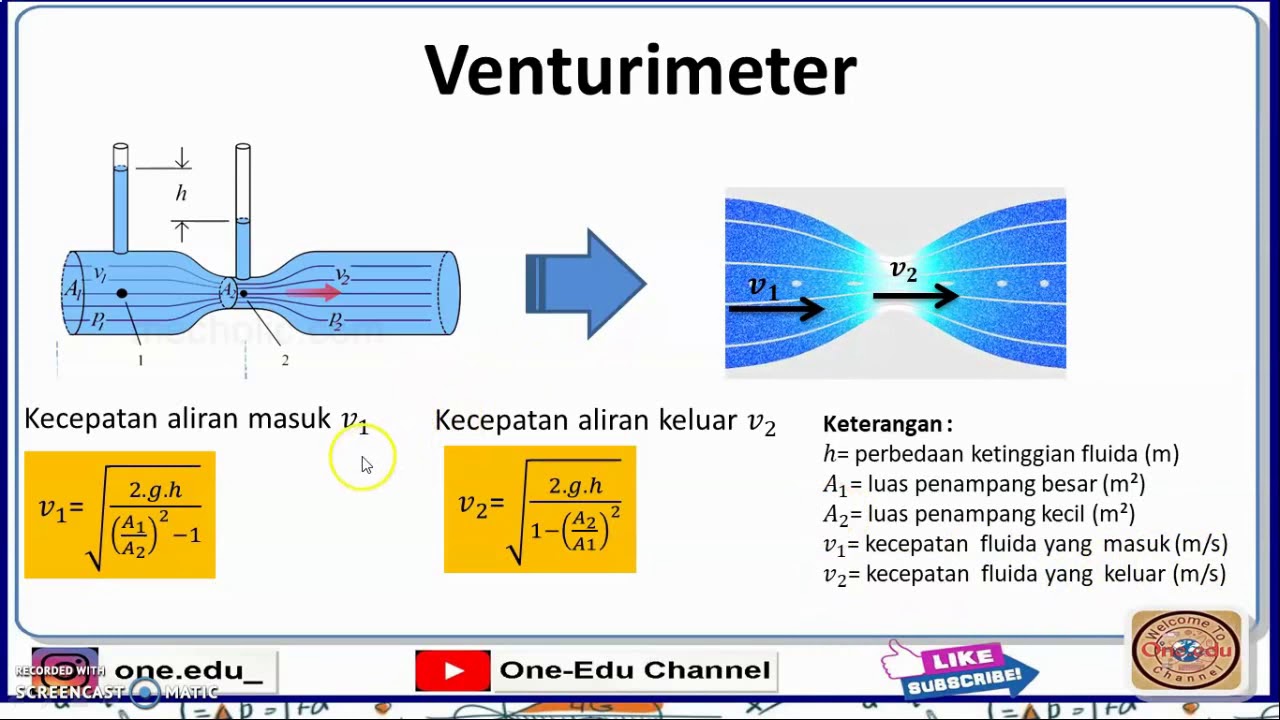
FISIKA KELAS XI: PENERAPAN HUKUM BERNOULLI PADA PIPA VENTURIMETER
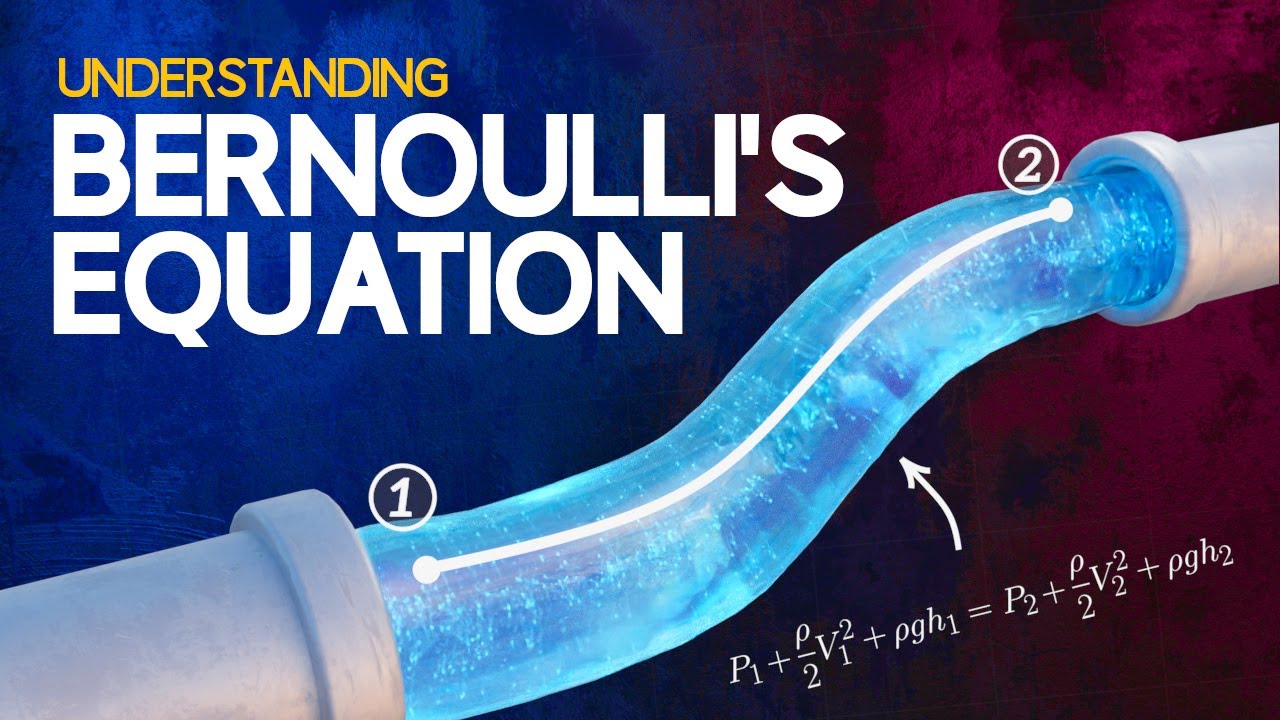
Understanding Bernoulli's Equation
Fluida Dinamis - Konsep Bernoulli - Simple Konsep - Fisika Kelas 11

Mekanika Fluida FM01 (Lecture3: 5/8). Kontinuitas (Continuity)

What is orifice plate & its types | Instrumentation Technician

FISIKA KELAS XI - VENTURIMETER TANPA MANOMETER || FLUIDA DINAMIS
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
