Blood Brain Barrier
Summary
TLDRThis video discusses the blood-brain barrier (BBB), highlighting its critical role in maintaining brain integrity. The BBB consists of endothelial cells tightly bound by junctions, supported by surrounding astrocytes. It controls the flow of nutrients, waste products, hormones, and neurotransmitters while limiting drug penetration. Only lipophilic molecules under 500 Daltons can pass through. The video also touches on ongoing research into BBB function and the challenges of drug delivery, with specialists gathering in February 2013 to explore the structure, function, and potential therapeutic applications of the BBB and related barriers.
Takeaways
- 😀 The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is an important anatomical feature that protects the brain.
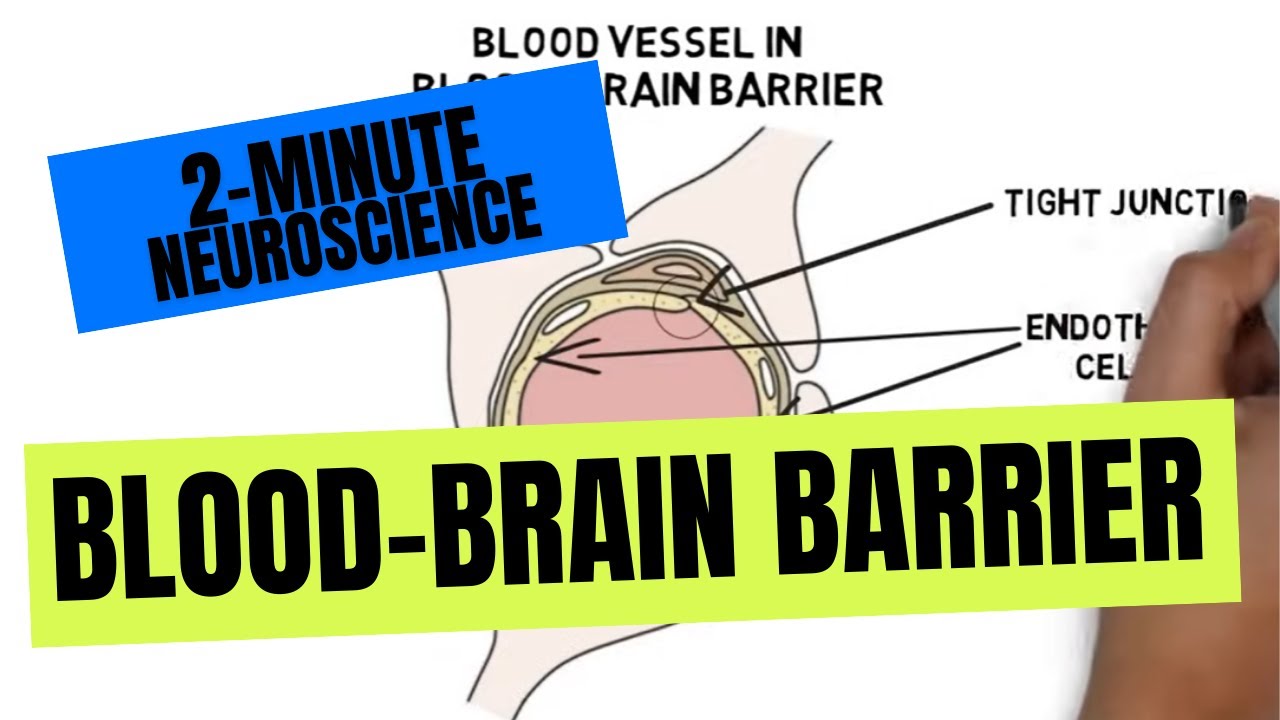
- 😀 The structural uniqueness of the BBB is due to endothelial cells connected by tight and gap junctions.
- 😀 Key proteins involved in maintaining the BBB's integrity include kexin, claudin 5, and Z1.
- 😀 Astrocytes, a type of glial cell, support the blood-brain barrier through their foot processes.
- 😀 The capillary bed in the human brain has a total length of about 600 km and covers a surface area of 20 square meters.
- 😀 The blood-brain barrier is selectively permeable, allowing nutrients in and waste products out, while restricting most molecules.
- 😀 Molecules that can cross the BBB must be lipophilic, smaller than 500 Daltons, and avoid active extrusion mechanisms.
- 😀 Few drugs are able to cross the blood-brain barrier effectively, making drug delivery a significant challenge.
- 😀 A workshop on the blood-brain barrier, held in February 2013, aimed to address questions about its structure and function.
- 😀 The workshop featured four main sessions focusing on different types of blood barriers and drug development strategies.
Q & A
What is the primary structural feature of the blood-brain barrier?
-The blood-brain barrier's most striking structural feature is the endothelial cells that are tightly joined by tight and gap junctions, which bind the cells side by side through several proteins, including kexin, claudin-5, and Z1, maintaining the barrier's integrity.
What role do astrocytes play in the blood-brain barrier?
-Astrocytes surround the blood-brain barrier's capillaries with their foot processes, providing support to these capillaries.
What is the total length and surface area of the capillary bed in the human brain?
-The total length of the capillary bed in the human brain is approximately 600 kilometers, with a surface area of about 20 square meters.
Which molecules are able to pass through the blood-brain barrier?
-The blood-brain barrier is permeable to certain molecules such as nutrients entering the brain, waste products, hormones, and excess neurotransmitters leaving the brain.
What properties do molecules need to cross the blood-brain barrier?
-Molecules need to be lipophilic, smaller than 500 Daltons, and capable of evading mechanisms of active extrusion to cross the blood-brain barrier.
How many drugs are able to translocate across the blood-brain barrier?
-Only a small number of drugs are able to translocate across the blood-brain barrier due to its selective permeability.
What is the focus of the 'Beating the Blood-Brain Barrier' workshop?
-The 'Beating the Blood-Brain Barrier' workshop, held in February 2013, focuses on discussing the structure and function of the blood-brain barrier, as well as the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier, the blood-retinal barrier, and strategies for overcoming the blood-brain barrier in drug development.
What are the four main sessions of the 'Beating the Blood-Brain Barrier' workshop?
-The four main sessions of the workshop are: the structure and function of the blood-brain barrier, the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier, the blood-retinal barrier, and strategies for overcoming the blood-brain barrier in drug development.
Why is the blood-brain barrier so important for drug delivery?
-The blood-brain barrier is important for drug delivery because it selectively allows certain molecules, like nutrients and waste products, to pass, while preventing the entry of many potentially harmful substances, including most drugs. Overcoming this barrier is a key challenge in drug development.
What are the potential challenges in delivering drugs across the blood-brain barrier?
-Challenges in delivering drugs across the blood-brain barrier include the barrier's selective permeability, which requires drugs to be lipophilic, smaller than 500 Daltons, and able to bypass active extrusion mechanisms. These factors make drug delivery to the brain difficult.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)