What is the Blood Brain Barrier?
Summary
TLDRThe blood-brain barrier serves as a critical defense mechanism for the brain, formed by tightly packed endothelial cells that limit the passage of substances from blood to brain tissue. While essential molecules like water, oxygen, and some fat-soluble compounds can cross, the barrier largely restricts most drugs. This poses significant challenges for developing effective treatments for neurological conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, and brain cancer, highlighting the need for innovative solutions in medicine.
Takeaways
- 🧠 The blood-brain barrier (BBB) protects the brain from foreign invaders.
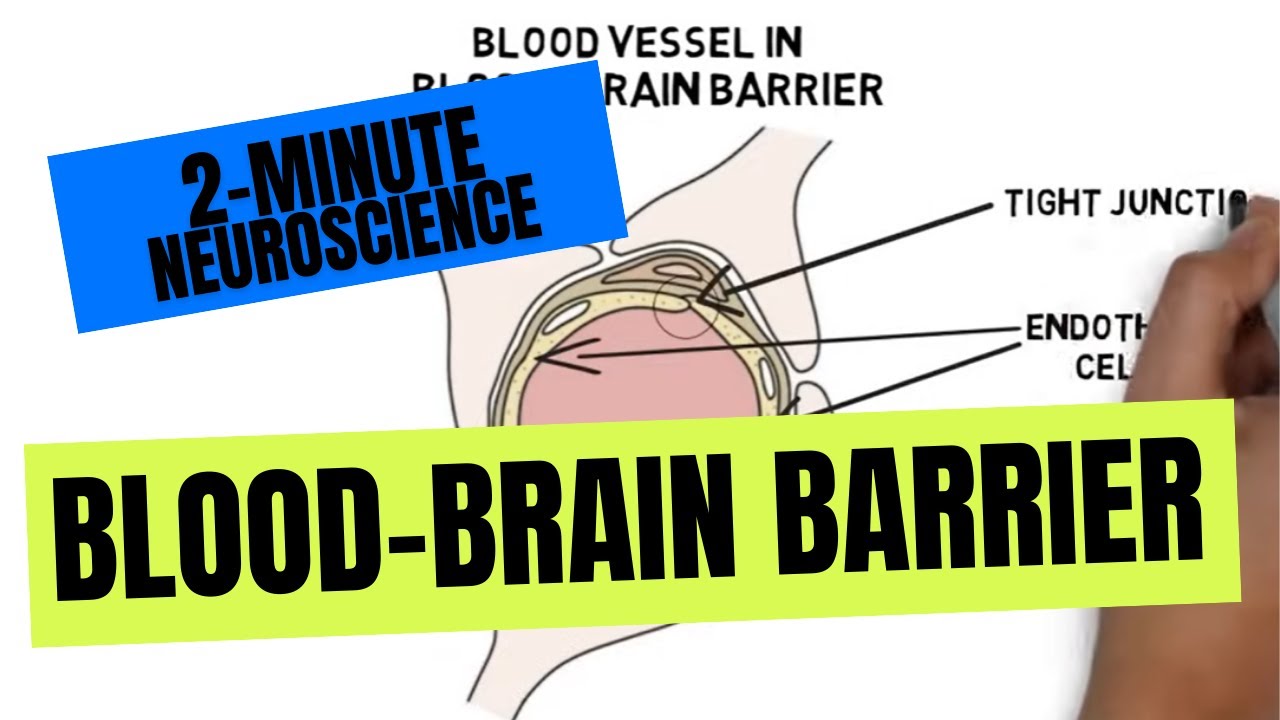
- 🔬 Endothelial cells line all blood vessels, but in the brain, they are tightly packed.
- 🌊 Only specific molecules, like water and oxygen, can easily cross the BBB.
- ☕ Fat-soluble substances such as caffeine and alcohol can also penetrate the barrier.
- 🍭 Glucose is essential for brain function and requires special transport proteins to cross the BBB.
- 💊 The BBB poses a significant challenge for drug delivery in treating neurological diseases.
- 🧪 Many drugs cannot effectively cross the BBB, complicating treatment options.
- 🧬 Conditions like Alzheimer's, stroke, and brain cancer are particularly affected by this barrier.
- 🔍 Understanding the BBB is crucial for developing new therapies for neurological conditions.
- 🚀 Innovative strategies are needed to enhance drug delivery across the blood-brain barrier.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the blood-brain barrier?
-The primary function of the blood-brain barrier is to protect the brain from foreign invaders by regulating which substances can pass from the bloodstream into brain tissue.
How do the endothelial cells in the brain's blood vessels differ from those in other parts of the body?
-The endothelial cells in the brain's blood vessels are tightly packed, creating fewer gaps and allowing only certain molecules to pass through compared to endothelial cells elsewhere in the body.
Which molecules can easily cross the blood-brain barrier?
-Water, oxygen, and some fat-soluble substances, such as caffeine and alcohol, can easily cross the blood-brain barrier.
How does glucose enter the brain?
-Glucose enters the brain with the help of specific proteins that facilitate its transport across the blood-brain barrier.
What challenges does the blood-brain barrier pose for medical treatments?
-The blood-brain barrier presents challenges for medical treatments because it prevents most drugs from reaching the brain, making it difficult to treat neurological conditions effectively.
Why is the blood-brain barrier considered a 'big problem' in medicine?
-It is considered a big problem in medicine because its selective permeability hinders the development of effective treatments for conditions like Alzheimer's, stroke, and brain cancer.
What role do fat-soluble substances play regarding the blood-brain barrier?
-Fat-soluble substances can easily cross the blood-brain barrier, which is important for understanding how certain drugs and compounds can affect brain function.
Can all types of drugs penetrate the blood-brain barrier?
-No, most drugs cannot penetrate the blood-brain barrier due to its selective nature, which restricts many therapeutic agents.
What implications does the blood-brain barrier have for neurological research?
-The blood-brain barrier complicates neurological research by limiting the effectiveness of drug delivery systems aimed at treating brain-related diseases.
What types of conditions are particularly affected by the challenges posed by the blood-brain barrier?
-Neurological conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, stroke, and brain cancer are particularly affected by the challenges posed by the blood-brain barrier.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)