The Blood Brain Barrier's Role in Neurodegeneration
Summary
TLDRThe blood-brain barrier is a protective filter that regulates which substances can pass from the blood into the brain. Composed of tight junctions, astrocyte projections, and endothelial cells, it safeguards brain function by blocking harmful substances. In Alzheimer's disease, this barrier breaks down, leading to the infiltration of neurotoxic proteins like beta and tau, which contribute to neurodegeneration. This degradation of the blood-brain barrier is linked to memory loss, behavioral changes, and cognitive decline over time, highlighting its crucial role in brain health and disease progression.
Takeaways
- 😀 The blood-brain barrier is a highly selective filter that controls which substances pass from the blood into the brain.
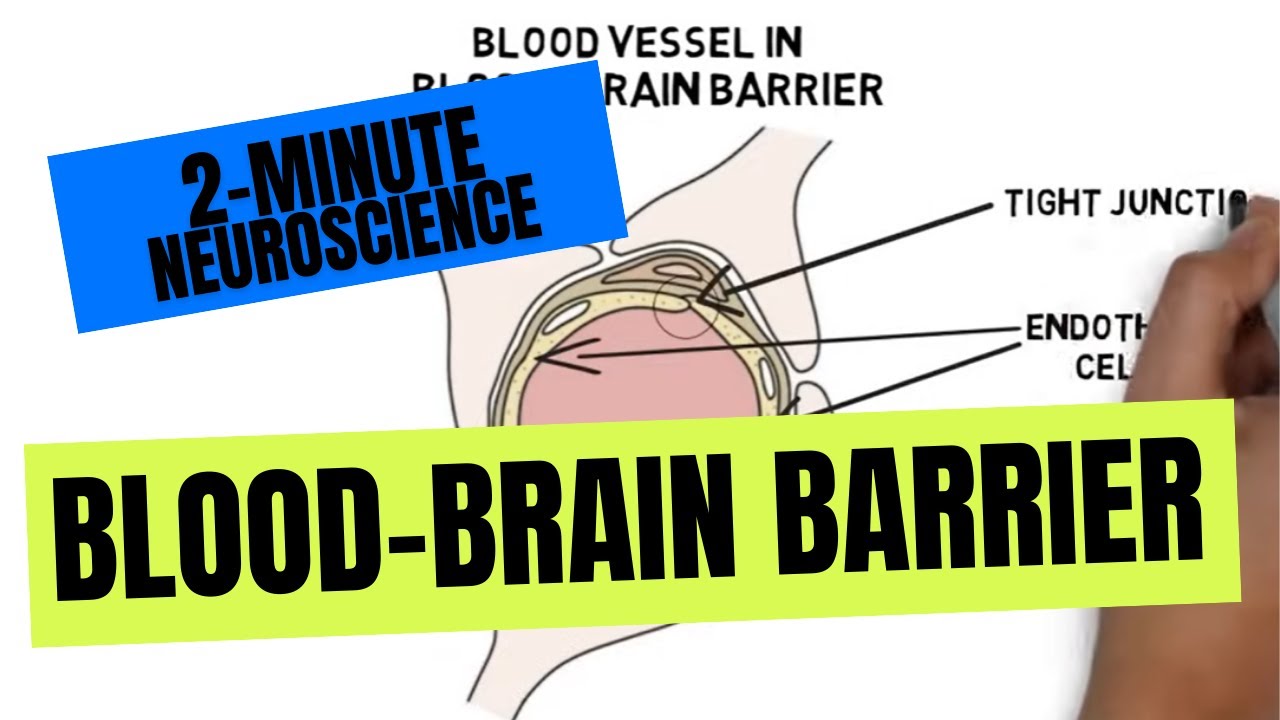
- 😀 The blood-brain barrier is made up of tight junctions between endothelial cells that restrict the passage of substances.
- 😀 Endothelial cells are wrapped in a layer of parasite cells, and a fibrous basement membrane surrounds them.
- 😀 Astrocytes, a type of glial cell, have projections called feet that further surround blood vessels, assisting in nutrient transport to neurons.
- 😀 The blood-brain barrier plays a crucial role in supporting neural activity by regulating nutrient flow to the brain.
- 😀 In conditions like Alzheimer's disease, the blood-brain barrier becomes compromised, leading to a breakdown in its structural integrity.
- 😀 Dysregulation of the blood-brain barrier is linked to the degradation of endothelial cells and parasite cells.
- 😀 The breakdown of the blood-brain barrier allows neurotoxic proteins, such as beta-amyloid and tau, to infiltrate the brain.
- 😀 Accumulation of beta-amyloid and tau is strongly associated with Alzheimer's disease and contributes to neurodegeneration.
- 😀 Over time, the accumulation of neurotoxic proteins and the failure of the brain's custodial system lead to memory loss, cognitive decline, and behavioral changes.
Q & A
What is the blood-brain barrier and what is its function?
-The blood-brain barrier is a selective filter that controls the passage of substances into the brain. It allows essential nutrients to pass through while keeping harmful substances in the blood vessels, thus protecting the brain from potential toxins.
What are the components of the blood-brain barrier?
-The blood-brain barrier is composed of tight junctions between endothelial cells, pericyte cells wrapped in a basement membrane, and astrocyte cells which form projections called 'feet' around the blood vessels.
How do endothelial cells contribute to the blood-brain barrier?
-Endothelial cells in the blood-brain barrier are tightly connected through junctions that restrict the movement of substances between them, ensuring that only select molecules can pass into the brain.
What role do pericytes play in the blood-brain barrier?
-Pericytes surround the endothelial cells in the blood-brain barrier and help to maintain the structural integrity of the barrier, ensuring proper function and preventing unwanted substances from passing through.
How do astrocytes support the function of the blood-brain barrier?
-Astrocyte cells extend projections known as 'feet' that surround the blood vessels. These feet help transport nutrients from the blood to the neurons, thus supporting neural activity.
What happens to the blood-brain barrier in Alzheimer's disease?
-In Alzheimer's disease, the blood-brain barrier begins to break down. The endothelial cells degrade, compromising tight junctions, and the pericytes also degrade, leading to a loss of the barrier's structural integrity.
What are the consequences of a broken blood-brain barrier in Alzheimer's disease?
-When the blood-brain barrier breaks down, it leads to the infiltration of neurotoxic proteins, such as beta-amyloid and tau, which build up and contribute to neurodegeneration, altering memory, behavior, and cognition.
How do beta-amyloid and tau contribute to Alzheimer's disease pathology?
-Beta-amyloid and tau are proteins that accumulate in the brain when the blood-brain barrier is compromised. Their buildup is strongly associated with Alzheimer's disease, leading to neurodegeneration and cognitive decline.
What is the role of the blood-brain barrier in maintaining brain health?
-The blood-brain barrier maintains brain health by regulating the passage of substances into the brain, ensuring that harmful substances are kept out while delivering necessary nutrients for proper neural function.
Why is the breakdown of the blood-brain barrier significant in the context of Alzheimer's disease?
-The breakdown of the blood-brain barrier is significant in Alzheimer's disease because it allows neurotoxic proteins to infiltrate the brain, which accelerates the accumulation of pathological proteins and contributes to the neurodegeneration observed in Alzheimer's.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)