健康A 4週目Part2
Summary
TLDRThis lecture delves into the science of muscle fibers, categorizing them into slow-twitch (ST) and fast-twitch (FT) fibers, explaining their roles in endurance versus explosive strength activities. It compares the fiber composition of different animals, highlighting how certain fish species are adapted for endurance or rapid movements. The transcript also discusses the genetic basis of muscle fiber composition, showing that it is largely inherited but can be influenced by training. Athletes are encouraged to reflect on their own muscle fiber types to optimize their training, and genetic testing is presented as a tool for personalized athletic development.
Takeaways
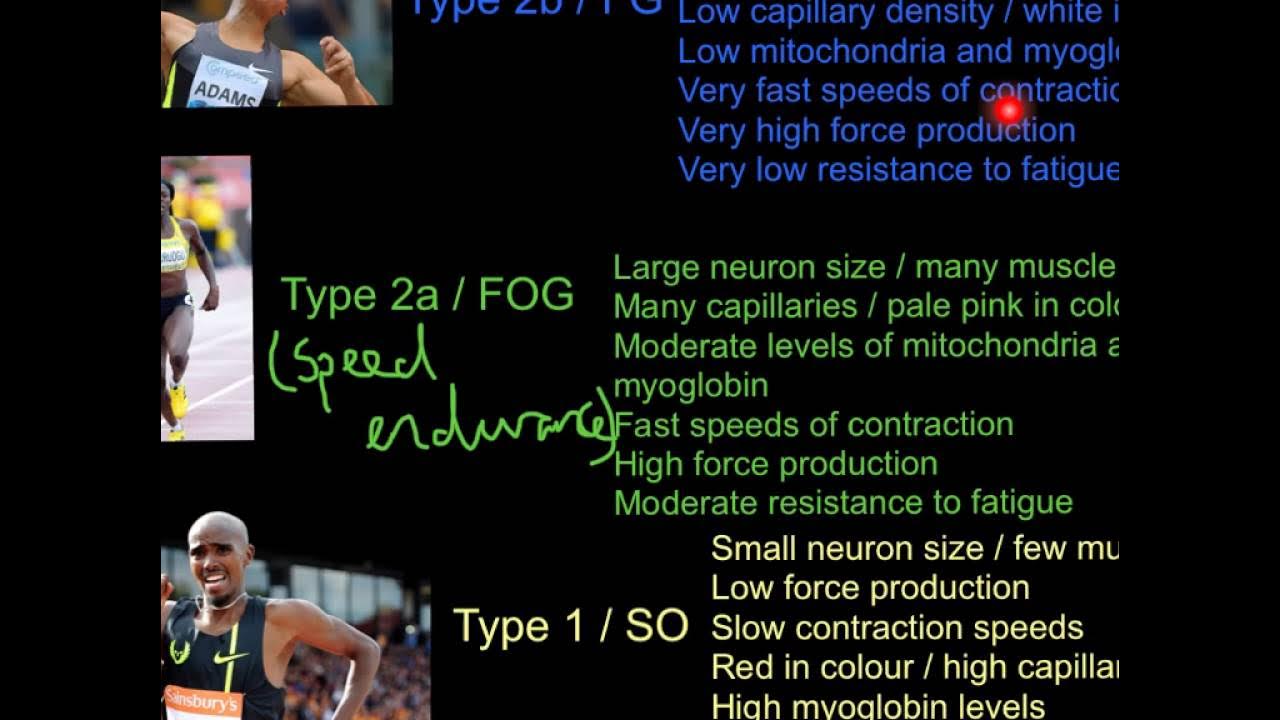
- 😀 Slow-twitch (ST) fibers are used for endurance activities, supporting long-lasting physical efforts like marathons.
- 😀 Fast-twitch (FT) fibers are responsible for quick, explosive movements, such as those needed for sprints or weightlifting.
- 😀 ST fibers are rich in myoglobin, which helps store oxygen, making them ideal for endurance activities and giving them a reddish appearance.
- 😀 FT fibers, particularly FTB, are fast and provide explosive power, making them essential for short-duration, high-intensity activities.
- 😀 Muscle fiber composition varies across species: animals like tuna and bonito rely more on ST fibers due to their migratory nature, while flounder rely more on FT fibers for quick bursts.
- 😀 Humans generally have a mix of ST and FT fibers, with athletes’ proportions differing based on their specialized sports performance (e.g., sprinters vs. marathon runners).
- 😀 Training can shift the properties of fibers (like FTB to FTA), but the overall proportion of ST vs. FT fibers does not significantly change with long-term training.
- 😀 Muscle fiber composition is largely determined by genetics, as seen in studies comparing identical and fraternal twins, where identical twins have similar fiber compositions.
- 😀 Studies show that the muscle fiber composition of athletes differs based on their sport: sprinters have more FT fibers, while marathoners have more ST fibers.
- 😀 Genetic testing is becoming more common in sports to tailor training to an athlete's muscle fiber composition, helping them maximize their performance potential.
- 😀 Even though training affects muscle fiber characteristics, genetic predisposition plays a crucial role in determining whether someone excels in endurance or explosive power sports.
Q & A
What are the two main types of muscle fibers mentioned in the script?
-The two main types of muscle fibers mentioned are 'chicken fibers' (ST fibers) and 'planting fibers' (FT fibers).
What characteristics differentiate ST fibers from FT fibers?
-ST fibers (chicken fibers) are slow-twitch fibers, which are more endurance-oriented, while FT fibers (planting fibers) are fast-twitch fibers, providing quick, powerful bursts of energy suitable for short-distance movements.
Why is the meat of tuna and bonito considered to be more similar to chicken rather than white fish?
-Tuna and bonito, being migratory fish, have a higher proportion of chicken fibers (ST fibers), which support endurance activities. The red color of their meat comes from myoglobin, which helps transport oxygen to the muscles, similar to the role of hemoglobin in red blood cells.
How does the muscle fiber composition of fish differ from that of other animals?
-Fish, depending on their lifestyle (e.g., migratory or sedentary), have a clear distinction in muscle fiber composition, with migratory fish like tuna and bonito having a higher percentage of ST fibers, while sedentary fish like flounder possess more FT fibers.
What is the role of myoglobin in muscle fibers?
-Myoglobin is a protein in muscles that binds and stores oxygen, making it essential for muscle endurance. Its presence in muscle fibers contributes to the red coloration of certain fish and meats, like tuna and bonito.
How does muscle fiber composition influence athletic performance?
-Muscle fiber composition significantly affects athletic performance. Endurance athletes, like marathon runners, typically have a higher proportion of ST fibers, while sprinters or athletes in explosive power sports have more FT fibers.
Can muscle fiber composition be altered through training?
-While muscle fiber composition is largely determined by genetics, certain fibers, like FTB (fast-twitch B) fibers, can convert into FTA (fast-twitch A) fibers through specific training. However, ST and FT fibers themselves cannot significantly change in type due to training.
How does muscle fiber composition vary between individuals?
-Muscle fiber composition can vary significantly between individuals, even among those with similar athletic goals. Some may have a higher proportion of ST fibers, while others may lean more toward FT fibers, influencing their natural aptitude for endurance or explosive power activities.
What role does genetics play in determining muscle fiber composition?
-Genetics plays a major role in determining muscle fiber composition. Studies with identical twins have shown that muscle fiber characteristics are highly similar in those with the same genetic makeup, indicating that muscle fiber composition is largely inherited.
How does the training of fast-twitch fibers differ from slow-twitch fibers?
-Training for fast-twitch fibers (FT) typically involves short bursts of intense activity, such as sprinting or weightlifting, focusing on explosive power. In contrast, slow-twitch fibers (ST) benefit from longer, sustained exercises like long-distance running or cycling, which emphasize endurance.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)