GCSE Chemistry - Addition Reactions of Alkenes
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the reactions of alkenes, which are unsaturated hydrocarbons with at least one carbon-carbon double bond. Alkenes undergo addition reactions, allowing other molecules to bond to them. The video covers three types of addition reactions: with hydrogen, water, and halogens. It demonstrates the process using examples like propene (hydrogenation to form propane), ethene (hydration to form ethanol), and ethene reacting with bromine (decolorizing bromine water). The video also touches on industrial processes such as fractional distillation to separate ethanol from water, concluding with a test to distinguish alkenes from alkanes based on their reactivity.
Takeaways
- 😀 Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons containing at least one carbon-carbon double bond.
- 😀 The presence of the double bond in alkenes allows them to undergo addition reactions.
- 😀 Addition reactions occur when the double bond opens up and bonds with atoms from another molecule.
- 😀 Alkenes can undergo addition reactions with hydrogen, water, and halogens.
- 😀 When alkenes react with hydrogen, the product is an alkane, as the double bond is broken.
- 😀 The reaction of alkenes with water, in the presence of a catalyst at high temperatures, produces alcohols like ethanol.
- 😀 Ethanol produced from ethene via reaction with water is used in alcoholic drinks and industrial processes.
- 😀 To separate ethanol from unreacted ethene and water, fractional distillation is used.
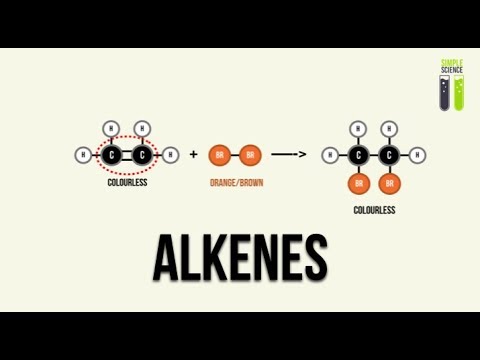
- 😀 In the reaction of alkenes with halogens like bromine, the double bond opens up to form a dibromo compound, decolorizing the bromine.
- 😀 The reaction of bromine with alkenes is used as a test to distinguish them from alkanes, as alkenes react with bromine to decolorize it, while alkanes do not.
Q & A
What are alkenes and what makes them unsaturated hydrocarbons?
-Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons because they contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. This double bond is what makes them unsaturated, as they can bond with additional atoms or molecules.
What is the significance of the carbon-carbon double bond in alkenes?
-The carbon-carbon double bond in alkenes is significant because it allows them to undergo addition reactions, where the double bond can break and allow other atoms to bond with the carbons, forming new compounds.
What are addition reactions, and why are they important for alkenes?
-Addition reactions are chemical reactions where atoms or molecules are added to a compound, such as an alkene. They are important because the double bond in alkenes opens up, allowing them to react with hydrogen, water, or halogens, leading to the formation of new compounds.
How does hydrogen react with an alkene, and what is the result?
-When hydrogen gas reacts with an alkene in the presence of a catalyst, the carbon-carbon double bond breaks, allowing hydrogen atoms to bond with the carbons. The result is an alkane, which is a saturated hydrocarbon without a double bond.
What are the conditions for the reaction of alkenes with water, and what does it produce?
-For alkenes to react with water, the presence of a catalyst and high temperatures are required so that water is in the form of vapor. The reaction produces an alcohol, specifically ethanol in the case of ethene, by splitting the water molecule into a hydrogen atom and a hydroxyl group.
What is fractional distillation, and how is it used in the production of ethanol from ethene?
-Fractional distillation is a technique used to separate liquids based on their boiling points. In the case of ethanol production from ethene, this method is used to separate ethanol from water and unreacted ethene after the reaction has taken place.
What is the test to distinguish alkenes from alkanes, and how does it work?
-The test to distinguish alkenes from alkanes involves adding bromine water to the solution. Alkenes, being more reactive due to the double bond, will decolorize the bromine water. In contrast, alkanes, which are saturated, will not react and the solution will remain orange.
What is the product of the reaction between an alkene and bromine, and what happens to the color of the solution?
-When an alkene reacts with bromine, a dibromoalkane is formed, and the orange color of the bromine solution disappears. This occurs because the bromine is added to the double bond, making the solution colorless.
Why do alkenes react more readily with bromine compared to alkanes?
-Alkenes react more readily with bromine because of the carbon-carbon double bond, which is a site of higher electron density and is more reactive. Alkanes, on the other hand, have single bonds and are saturated, making them less reactive.
What industrial applications rely on the reaction of alkenes with water to form ethanol?
-The reaction of alkenes with water to form ethanol is widely used in the chemical industry, especially in the production of ethanol for alcoholic beverages and as a solvent or fuel additive in industrial processes.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
GCSE/IGCSE Organic Chemistry - Part 3 - Alkenes

Aula #05 - Prof. Pavanelli - Alcenos e Alcinos

Hydrocarbons | #aumsum #kids #science #education #children

A Level Chemistry Revision "The Structure and Reactivity of Alkenes"

Yuk, mengenal HIDROKARBON ! materi kimia kelas 11 semester 1

Halogenation | Organic Chemistry | Chemistry | FuseSchool
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
