Halogenation | Organic Chemistry | Chemistry | FuseSchool
Summary
TLDRThis video explains how halogens react with alkenes through addition reactions, where the halogen is added across the carbon-carbon double bond. It highlights the reaction of chlorine, bromine, and iodine with alkenes, noting that reactivity decreases as you move down the halogen group. The video also explores how bromine, as an orange-brown reagent, turns colorless when reacting with alkenes, making it a simple test to detect the presence of a carbon-carbon double bond. The content aims to provide a clear understanding of these reactions and their practical applications.
Takeaways
- 😀 Alkenes contain a carbon-carbon double bond, which is key to their reactivity.
- 😀 Halogens like chlorine, bromine, and iodine react with alkenes in an addition reaction.
- 😀 In an addition reaction, the halogen is added across the carbon-carbon double bond of the alkene.
- 😀 Fluorine reacts violently with alkenes to form carbon and hydrogen fluoride, but this is not a useful reaction.
- 😀 Chlorine, bromine, and iodine react more slowly as you move down Group 7 of the periodic table.
- 😀 Chlorine reacts quickly with alkenes, while iodine reacts the slowest.
- 😀 The same reaction mechanism applies to both small and large alkenes.
- 😀 The products of halogen addition to alkenes are always halogenoalkanes.
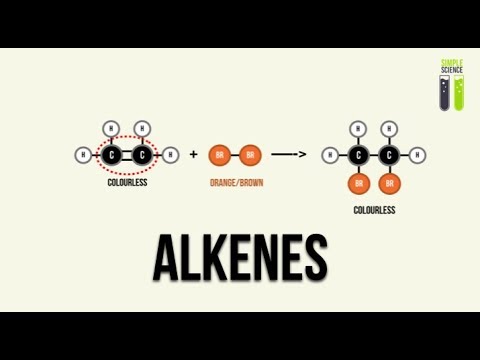
- 😀 Bromine’s reaction with alkenes is commonly used as a test for the presence of a carbon-carbon double bond.
- 😀 Bromine is orange-brown, and when it reacts with an alkene, it turns colorless, indicating the presence of the double bond.
Q & A
What type of reaction occurs when a halogen reacts with an alkene?
-An addition reaction occurs when a halogen reacts with an alkene. In this reaction, the halogen is added across the carbon-carbon double bond.
What are some examples of alkenes mentioned in the script?
-Examples of alkenes mentioned in the script include ethene, propene, and butene.
Which halogens are mentioned in the script as reacting with alkenes?
-The halogens mentioned in the script are chlorine, bromine, and iodine.
What happens when fluorine reacts with ethene?
-When fluorine reacts with ethene, the reaction is violent, forming carbon and hydrogen fluoride. This reaction is not particularly useful.
How do the reactions of halogens with alkenes change as you move down the group of halogens?
-As you move down the group of halogens, the reactions become slower. Chlorine reacts quickly with alkenes, bromine reacts slower, and iodine reacts the slowest.
What is the result of the addition reaction of a halogen with an alkene?
-The result is the formation of a halogenoalkane, where the halogen is added across the carbon-carbon double bond.
What is the purpose of the addition reaction of bromine with an alkene?
-The addition reaction of bromine with an alkene is used as a test for the presence of a carbon-carbon double bond. Bromine is orange-brown, and when it reacts with an alkene, it becomes colorless, indicating the presence of the double bond.
Why is fluorine not a useful halogen in reactions with alkenes?
-Fluorine is not useful in reactions with alkenes because it reacts too violently, forming carbon and hydrogen fluoride, which is not a desirable outcome for most chemical processes.
What products are formed when a halogen reacts with an alkene?
-The products formed are halogenoalkanes, where the halogen is added across the carbon-carbon double bond of the alkene.
How can the reaction of bromine with an alkene be further explored?
-It would be a good extension task to research the naming of the halogenoalkanes formed in the reaction of bromine with alkenes, as naming these molecules provides more detailed insights into their structure and properties.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

GCSE Chemistry - Addition Reactions of Alkenes
GCSE/IGCSE Organic Chemistry - Part 3 - Alkenes

REAKSI HIDROKARBON (OKSIDASI, SUBTITUSI, ADISI DAN ELIMINASI)

Halogen Displacement Reactions | 14–16 Practicals

GCSE Chemistry - Addition Polymers & Polymerisation #56

Detection of Halogens in an Organic Compound - MeitY OLabs
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)