Pertemuan 1 Statistika sosial
Summary
TLDRThis lecture on statistics covers a wide range of topics, starting with the definition and history of statistics, including the shift from using large population data to sample data. It explains key concepts like population, sample, and statistical inference, emphasizing the importance of confidence levels in predictions. The speaker discusses both descriptive and inferential statistics, detailing their roles in summarizing and drawing conclusions from data. The session introduces various statistical methods, including hypothesis testing, correlation, regression, and the differences between parametric and non-parametric tests, preparing students for deeper analysis after midterms.
Takeaways
- 😀 Introduction to statistics covers definitions, data collection techniques, tables, graphs, central tendency, data spread, probability, hypothesis testing, and regression.
- 😀 The history of statistics development: Before 1900, data was large-scale (population data), and analysis was simpler. After 1900, the use of smaller sample data and more complex analysis methods developed.
- 😀 The difference between population and sample data is critical in research. Population refers to the whole group, while a sample is a subset representing the population.
- 😀 Sampling is important when population data is impractical to collect due to size, cost, or time constraints.
- 😀 Estimation or inference is used to make predictions about a population based on sample data. The accuracy of these predictions is quantified using confidence levels.
- 😀 A distinction is made between parameters (values derived from population data) and statistics (values derived from sample data). Both represent measures like mean, median, and mode.
- 😀 Understanding variables in statistics: A variable is a characteristic being studied, such as behavior in a study on students.
- 😀 Data can be collected through existing sources (secondary data) or by generating new data (primary data) through experiments or simulations.
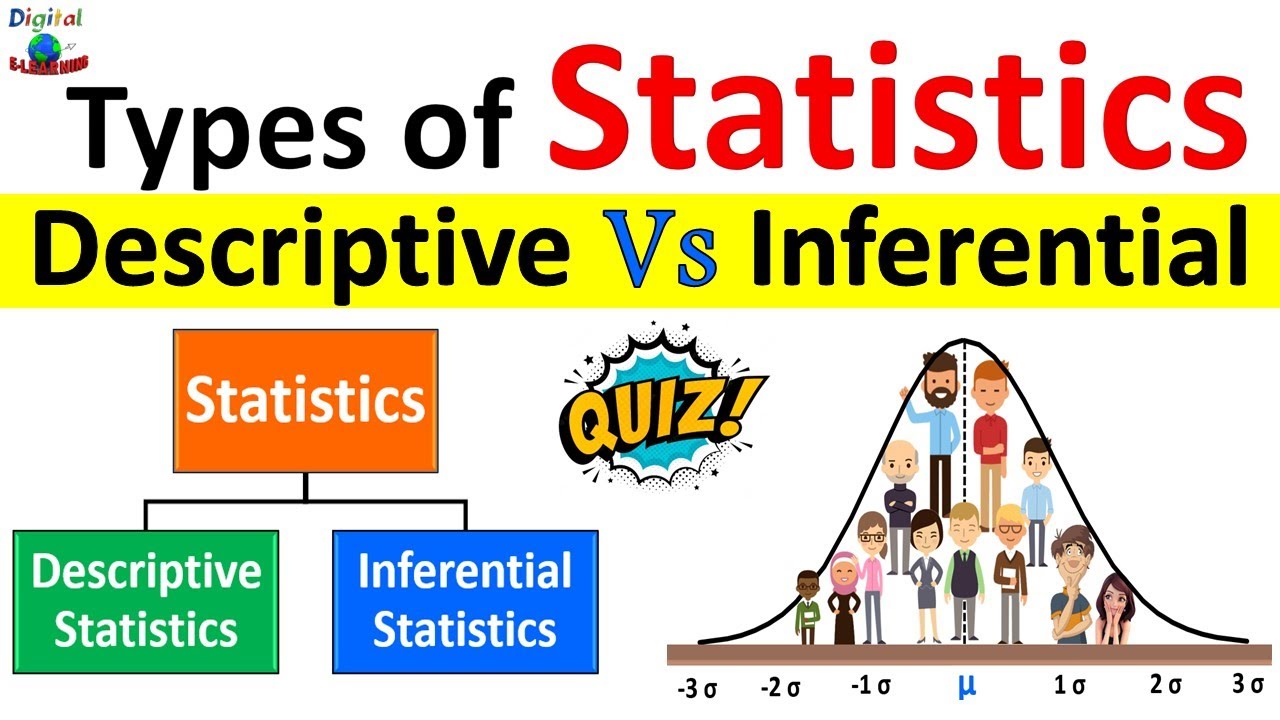
- 😀 Statistics can be categorized into two main types: Descriptive statistics (describes data) and inferential statistics (makes predictions or tests hypotheses).
- 😀 Inferential statistics often involves hypothesis testing to determine if relationships between variables are statistically significant, such as testing the impact of motivation on learning outcomes.
- 😀 Understanding the difference between parametric and non-parametric tests is crucial for choosing the appropriate statistical method based on data characteristics (e.g., normality of distribution and scale of measurement).
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the lecture discussed in the transcript?
-The primary focus of the lecture is an introduction to statistics, including the history, concepts, methods, and different types of statistical analysis, as well as distinctions between population and sample data.
What are the key differences between statistics and statistika as mentioned in the transcript?
-Statistics refers to methods of analyzing and interpreting data, while statistika refers to the broader science of data collection and analysis. The distinction lies in terminology, but both concepts deal with interpreting data, with statistics applying to sample data and statistika to population data.
How did the field of statistics evolve after 1900?
-After 1900, statistics evolved with the development of more complex analytical methods. It shifted from using large population data to utilizing smaller sample data, making analysis more manageable and efficient.
Why is it sometimes difficult to use data from the entire population?
-Using data from the entire population can be challenging because it is often large, time-consuming, and costly to collect and analyze. This can lead to biases and inefficiencies, prompting the use of sample data instead.
What is the purpose of sampling in statistics?
-Sampling is used to select a subset of data from the population to make statistical inferences. It helps overcome practical limitations like time, cost, and resource constraints that make working with an entire population impractical.
What is the significance of estimation in statistics?
-Estimation in statistics allows us to make predictions about a population based on sample data. For example, it helps to estimate the characteristics of the entire population with a certain degree of confidence, often expressed as a percentage probability.
How are descriptive statistics different from inferential statistics?
-Descriptive statistics focus on summarizing and presenting the data (e.g., through charts and averages), while inferential statistics involve making predictions or generalizations about a population based on sample data, often through hypothesis testing.
What are some common statistical methods mentioned in the transcript?
-Some common statistical methods include t-tests, ANOVA (Analysis of Variance), correlation, regression analysis, and hypothesis testing. These methods help in comparing groups, finding relationships, and drawing conclusions from data.
Why is it important to understand the type of data being analyzed in statistical research?
-Understanding the type of data is crucial because it determines which statistical methods and tests are appropriate for analysis. For example, the choice between parametric or non-parametric tests depends on whether the data meets certain assumptions, such as normal distribution.
What is the difference between population data and sample data in statistical analysis?
-Population data refers to the complete set of observations or measurements from the entire group being studied, while sample data refers to a smaller subset of the population. Statistical inferences are often drawn from samples rather than populations due to practical constraints.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)