video 5.1. inferential statistics logic
Summary
TLDRThe class has covered fundamental topics like distributions and descriptive statistics, and now shifts to inferential statistics. Inferential statistics enable researchers to make decisions about populations based on sample data. The process involves four main steps: caring about the state of the world (population), collecting sample data, calculating the likelihood of an outcome (e.g., flipping a coin), and making a decision based on the data. The logic behind inferential statistics is to infer the fairness of a scenario, like whether a coin is fair, using sample observations.
Takeaways
- 📊 We have covered fundamental topics like distributions and descriptive statistics in class.
- 🔄 Now we are shifting focus to inferential statistics, which will be the main topic for the rest of the class.
- 🧠 Inferential statistics allow researchers to make decisions about populations based on sample data.
- 🗺️ The first step is caring about the state of the world, focusing on the population, not just a sample.
- 🪙 An example given is determining whether a coin is fair or not, by observing and analyzing data from coin flips.
- 📈 Step two is making observations, such as flipping the coin and collecting data about the outcomes.
- 🤔 Step three involves calculating how likely the coin is fair based on the observations, using probability.
- 🧮 For instance, if a coin comes up heads 100 out of 100 times, you'd likely conclude it's not a fair coin.
- 📉 The fourth step is making a decision about the population (e.g., deciding if the coin is fair or not).
- 🔑 This logic behind inferential statistics will be applied throughout the semester to make decisions based on data.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the class so far?
-The class has primarily focused on distributions and descriptive statistics.
What is the next topic the class will cover?
-The class will now switch to inferential statistics for the rest of the semester.
What is the purpose of inferential statistics?
-Inferential statistics allow researchers to make inferences or decisions about a population based on sample data.
What is the first step in the process of inferential statistics?
-The first step is caring about the state of the world, which refers to the population, not just a sample.
How does the instructor use the coin example to explain inferential statistics?
-The instructor uses a coin-flipping scenario to demonstrate how observations from a sample (coin flips) can help determine if the coin is fair, representing the population.
What is meant by 'collecting your sample data' in the example?
-In the coin example, collecting sample data refers to flipping the coin and recording the results.
What would you expect if a coin is fair based on probability?
-If a coin is fair, it should come up heads about half the time, meaning 50 out of 100 flips would be heads.
What conclusion could you make if the coin lands heads 100 times out of 100 flips?
-If the coin lands heads 100 times, you would likely conclude that the coin is not fair.
How do you calculate the likelihood of the coin being fair based on observations?
-You calculate the probability of the observed data (e.g., the number of heads) given the assumption that the coin is fair.
What is the overall logic behind inferential statistics as discussed in class?
-The logic is to use sample data to calculate probabilities and make decisions about the state of the world (i.e., the population).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

STATISTIKA PENDIDIKAN PERTEMUAN 1-PENGANTAR STATISTIKA DAN STATISTIK

SEB1 Pengantar Statistika / Konsep Dasar Statistika - Statistika Ekonomi dan Bisnis bab 1 (Part 1)
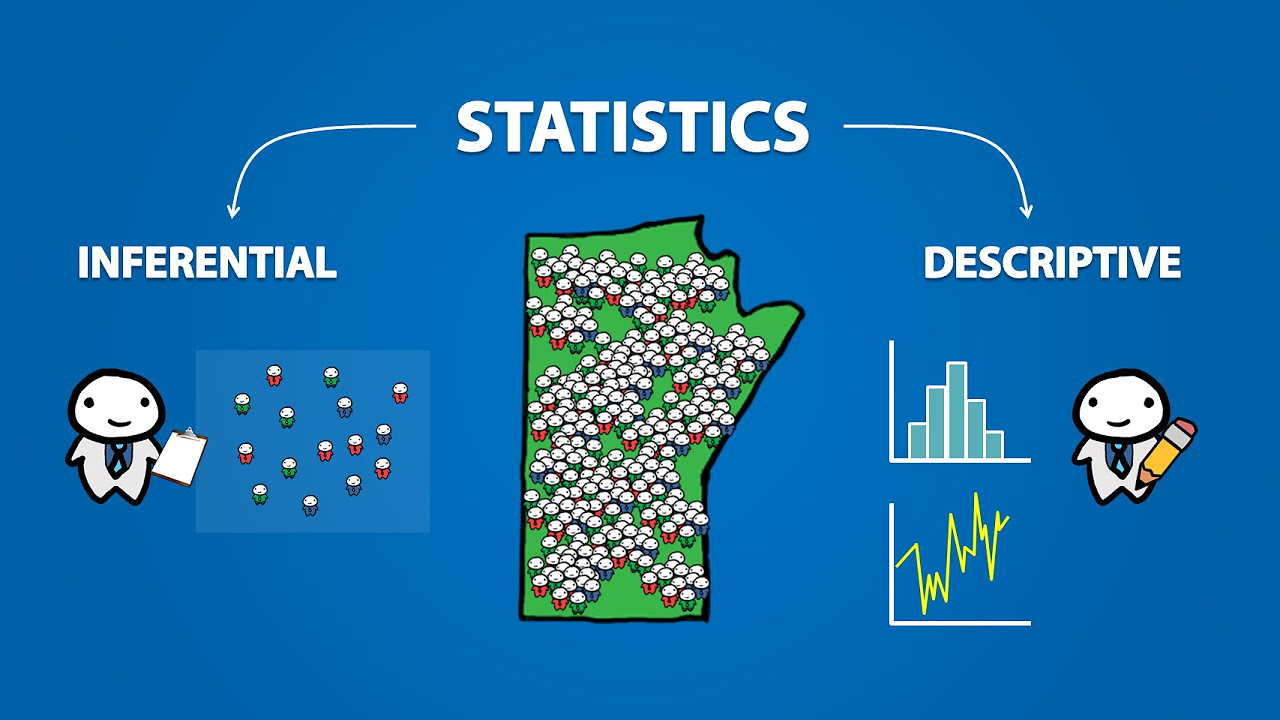
Introduction to Statistics (1.1)
Statistics For Data Analytics | Complete Syllabus | Data Science | Statistics Tutorial | Part 1

Statistik Inferensial

KUPAS TUNTAS: Apakah Perbedaan Statistik Inferensial dengan Statistik Deskriptif ?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)