Aplikasi Model Regresi dan Pengembangan
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the presenter discusses the application of regression models and their development, focusing on multiple regression analysis. The session covers various specifications, including multiple, log, quadratic, and translog models, as well as their practical application in economic analysis. Using examples like the determinants of consumption in Jambi Province, the presenter demonstrates how to evaluate and diagnose econometric models through software like EViews. Key topics include assessing significance using p-values, testing for heteroskedasticity, multicollinearity, and autocorrelation, and interpreting regression results to improve model accuracy.
Takeaways
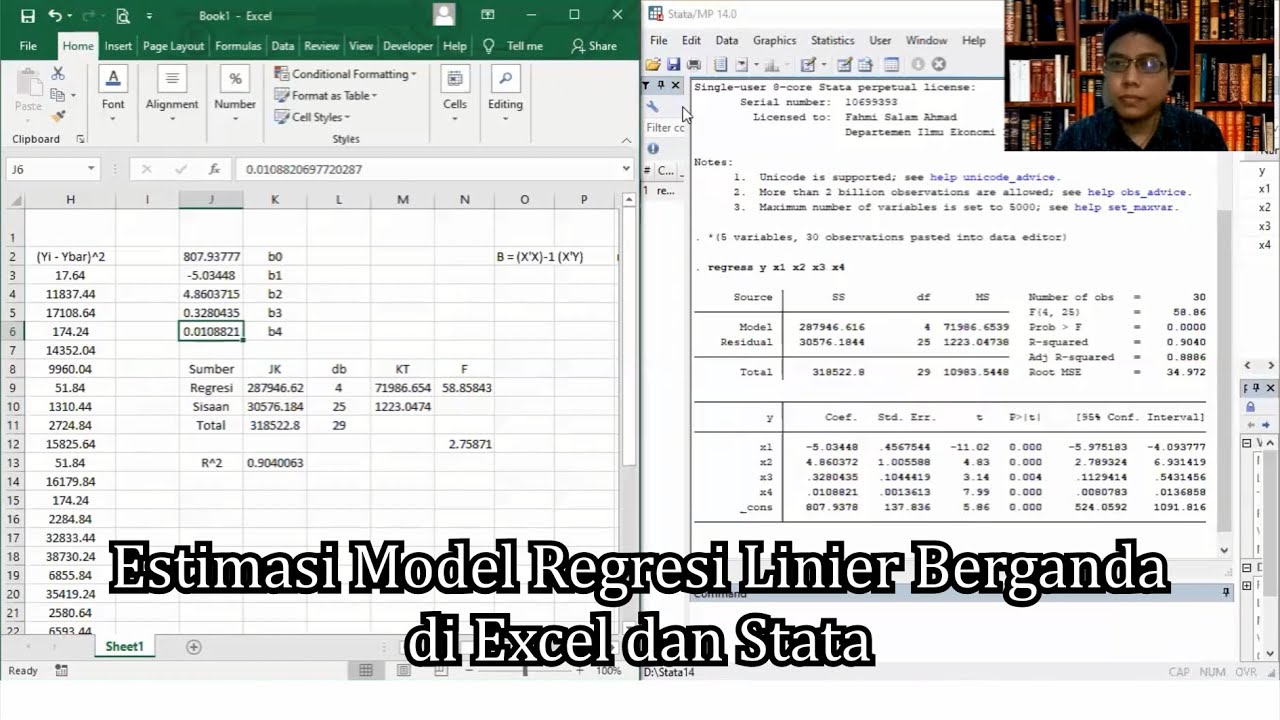
- 😀 Multiple regression models are used to analyze the relationship between a dependent variable and more than one independent variable. For example, the production of farmers is influenced by the amount of labor and urea fertilizer used.
- 😀 The script discusses different types of regression models, including multiple regression, quadratic regression, and log models like Cobb-Douglas production functions.
- 😀 Logistic regression, particularly binary and multinomial logit models, is introduced as a method for analyzing categorical dependent variables like loan repayment behavior.
- 😀 The concept of limited dependent variables is emphasized, and examples are given where regression models can analyze factors such as credit repayment or consumer behavior.
- 😀 In practical applications, like the consumption model of Jambi Province, econometrics tools (like EViews, Stata, or RStudio) are used to estimate the relationships between consumption and factors like PDRB (Gross Regional Domestic Product), investment, and interest rates.
- 😀 The importance of evaluating statistical and economic criteria, such as the p-value (probability value) and the sign of coefficients (positive or negative), is highlighted when interpreting regression results.
- 😀 The regression analysis of consumption in Jambi Province revealed that only investment significantly influenced consumption, while other variables like PDRB and interest rates did not.
- 😀 Diagnostic tests for multicollinearity, heteroskedasticity, and autocorrelation are necessary to ensure valid regression results. If issues are detected, corrective measures like using Generalized Least Squares (GLS) can be applied.
- 😀 The significance of performing diagnostic tests on residuals is discussed, with examples of using LM tests for autocorrelation and White’s test for heteroskedasticity.
- 😀 The script concludes that, based on the analysis, keeping PDRB in the model and removing investment was the best choice for a more reliable regression result due to the multicollinearity issue in the initial model.
Q & A
What is multiple regression, and how is it applied in the lecture?
-Multiple regression is a statistical technique where a dependent variable is explained by more than one independent variable. In the lecture, the example provided was the production of rice by farmers, which is regressed against two independent variables: labor usage and fertilizer usage. A squared term of fertilizer is also included to account for non-linear effects.
What is the Cobb-Douglas production function and how is it used in the lecture?
-The Cobb-Douglas production function is a log-linear model used to describe the relationship between output and inputs. In the lecture, the production of rice was analyzed using a log-transformed version of the model, where variables like labor and fertilizer usage were logged before regression to estimate the elasticity of production.
What is a log-linear regression model, and why is it useful?
-A log-linear regression model involves transforming the data by taking the natural logarithm of the variables before performing the regression. It is useful because it simplifies the interpretation of elasticities and allows for capturing proportional relationships, as demonstrated with the Cobb-Douglas function in the lecture.
What is the difference between logistic regression and Tobit models?
-Logistic regression is used for categorical dependent variables, particularly binary outcomes (0/1), whereas Tobit models are used for censored data, where the dependent variable is limited or truncated, such as consumption data that can only take values between 0 and 1.
How does the concept of limited dependent variables apply in the lecture?
-The lecture highlighted how models like logistic regression and Tobit are used to analyze situations with limited dependent variables, such as predicting whether a person will repay a loan (binary outcome) or analyzing censored consumption data where values are restricted to a certain range.
What were the key diagnostic tests discussed in the lecture for model evaluation?
-The lecture covered diagnostic tests like multicollinearity, heteroscedasticity, and autocorrelation. Multicollinearity was tested using variance inflation factors (VIF), heteroscedasticity was tested using the White test, and autocorrelation was checked using the LM test.
What is multicollinearity, and how does it affect regression models?
-Multicollinearity occurs when independent variables in a regression model are highly correlated with each other, which can lead to unreliable estimates of the coefficients. The lecture demonstrated how to detect multicollinearity using VIF values, and if it is present, one of the correlated variables may need to be removed.
What is heteroscedasticity, and how was it addressed in the lecture?
-Heteroscedasticity refers to the condition where the variance of the residuals in a regression model is not constant. In the lecture, it was detected using the White test, and if heteroscedasticity was present, Generalized Least Squares (GLS) was used to correct for it.
How is GLS (Generalized Least Squares) different from OLS (Ordinary Least Squares)?
-GLS is an estimation technique used when there is heteroscedasticity or autocorrelation in the residuals of a regression model. Unlike OLS, which assumes homoscedasticity and no autocorrelation, GLS adjusts for these issues to provide more efficient estimates of the regression coefficients.
How did the speaker address the issue of model specification in the lecture?
-The speaker discussed the process of model specification, where multiple models could be tested, and emphasized that no single model is universally correct. They demonstrated how different model specifications, such as transforming data or adjusting for heteroscedasticity, can lead to more accurate results.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)