Telecurso – Ensino Médio – Física – Aula 24
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, viewers learn about the three primary methods of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. Through relatable examples such as cooking, sunbathing, and environmental phenomena like sea breezes, the script illustrates how heat moves through different materials and mediums. The lesson also highlights conductors and insulators, explaining how some materials facilitate heat transfer while others prevent it. By connecting everyday experiences to fundamental physical concepts, the video provides an engaging and accessible understanding of thermodynamics, making it relevant and easy to grasp for students.
Takeaways
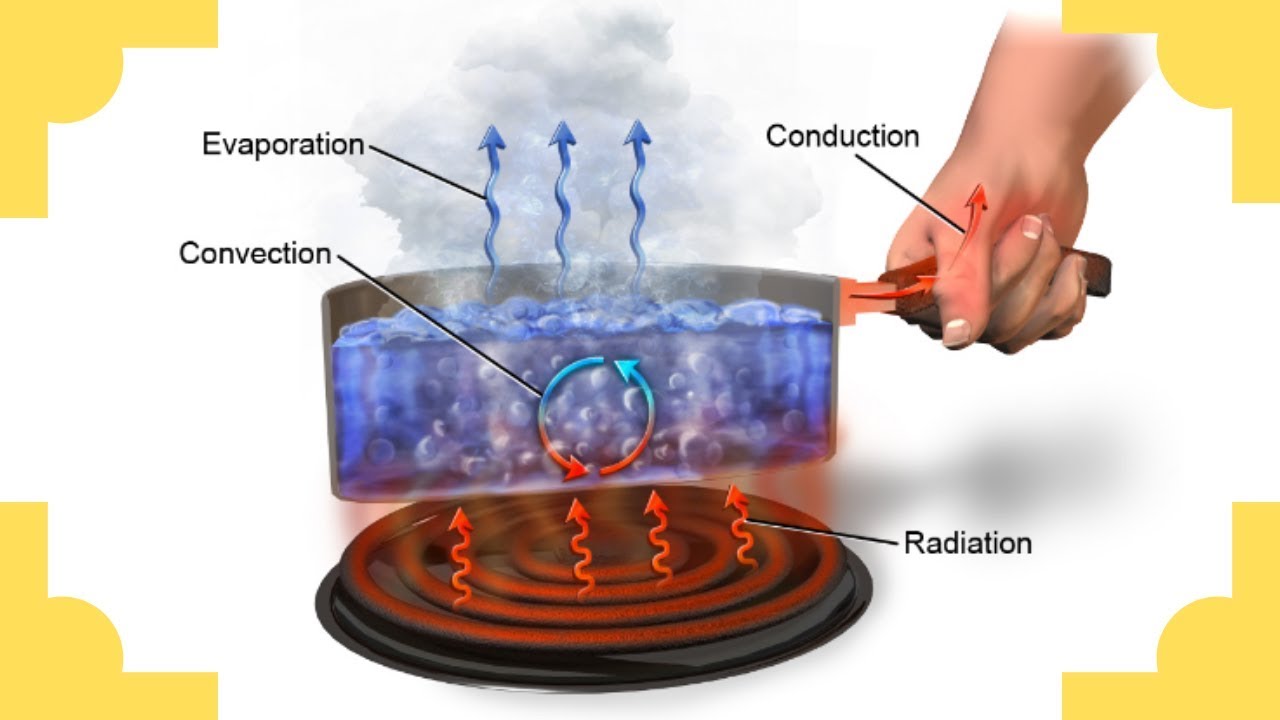
- 😀 Heat transfer occurs in three main forms: conduction, convection, and radiation.
- 😀 Conduction happens when two objects with different temperatures come into contact, transferring heat from the hotter object to the cooler one.
- 😀 Metals are examples of good heat conductors, allowing thermal energy to pass through them easily.
- 😀 Insulating materials like Styrofoam reduce the transfer of heat and help maintain temperature stability inside containers.
- 😀 Radiation does not require a medium to transfer heat; for example, the Sun's rays can travel through space and heat objects like sand.
- 😀 Convection occurs when heated air rises and cooler air sinks, forming a continuous cycle of air movement.
- 😀 The specific heat capacity of a material determines how much energy is needed to change its temperature; for example, sand heats up faster than water.
- 😀 Thermal equilibrium is reached when two objects in contact have the same temperature, causing no further heat transfer between them.
- 😀 A thermos bottle works by preventing heat transfer through conduction, radiation, and convection, using a double-walled structure and vacuum.
- 😀 Real-life examples, such as the difference between how quickly sand and water heat up, help illustrate the principles of heat transfer in everyday situations.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the teleclass discussed in the script?
-The primary focus of the teleclass is to explain the different forms of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation.
How does conduction work in heat transfer?
-Conduction occurs when two bodies at different temperatures are in direct contact, transferring heat through the vibration of atoms from the hotter object to the cooler one.
What are conductors and insulators?
-Conductors are materials that allow the passage of heat, such as metals, while insulators are materials that hinder the transfer of heat, like Styrofoam or wool.
Why does the sand at the beach heat up faster than the water?
-Sand heats up faster than water because it has a lower specific heat, meaning it requires less energy to increase its temperature.
What is the significance of a material's specific heat in heat transfer?
-A material's specific heat determines how much heat is required to raise its temperature. Materials with lower specific heat, like sand, heat up more quickly than those with higher specific heat, like water.
What is convection and how does it occur?
-Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids (liquids or gases). It happens when hot, less dense air or liquid rises, and cooler, denser air or liquid sinks, forming a circulating current.
How does radiation differ from conduction and convection in terms of heat transfer?
-Radiation transfers heat without needing a medium, as it can occur through the vacuum of space. Unlike conduction and convection, which require a material to transfer heat, radiation relies on electromagnetic waves.
What real-world example illustrates the concept of radiation?
-A real-world example of radiation is the Sun's rays transferring energy to the Earth, even though space is a vacuum.
Why does the teacher emphasize the use of conductors and insulators in daily life?
-The teacher emphasizes this because conductors and insulators are key to understanding how heat is managed in real-world applications, such as cooking, cooling systems, and maintaining temperature in objects like thermoses.
What phenomenon explains the cool breeze felt at the beach when the sun sets?
-This phenomenon is called the 'terrestrial breeze,' and it occurs because the sand cools down faster than the water, causing the air above the sand to become denser and sink, while the air over the water remains warmer and rises, creating a circulating breeze.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)