Scales of Measurement - Nominal, Ordinal, Interval, Ratio (Part 1) - Introductory Statistics
Summary
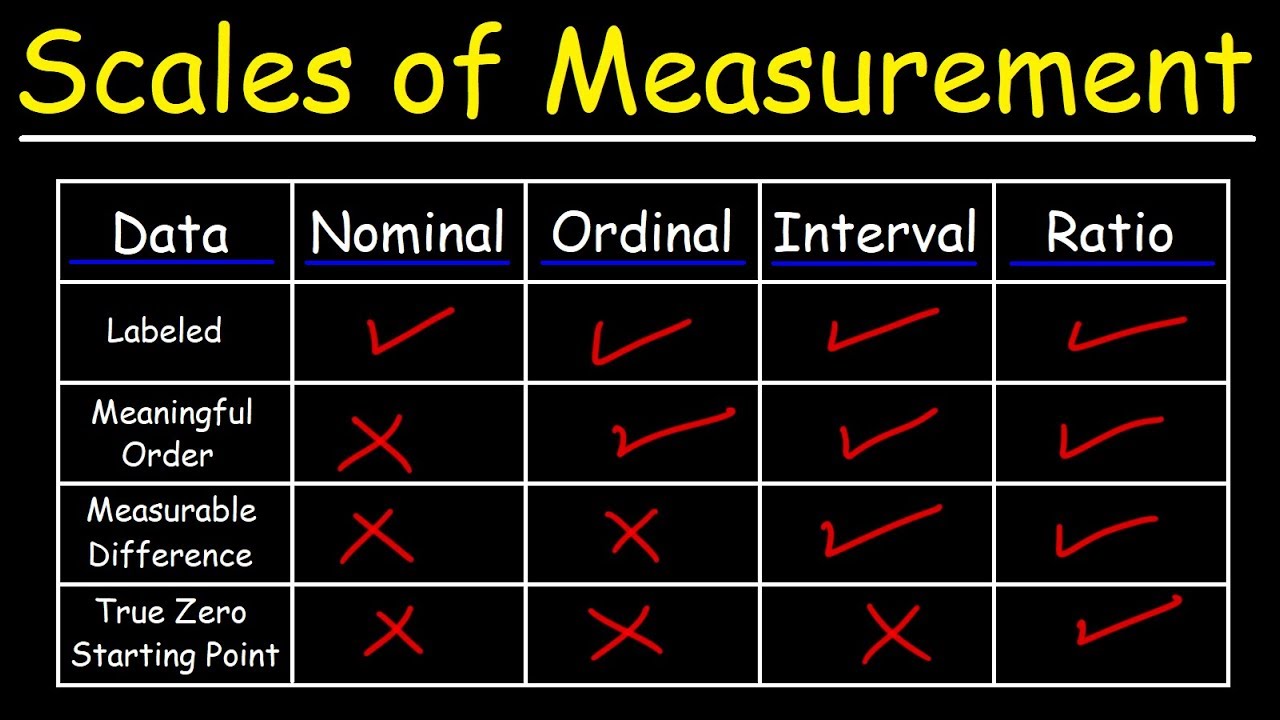
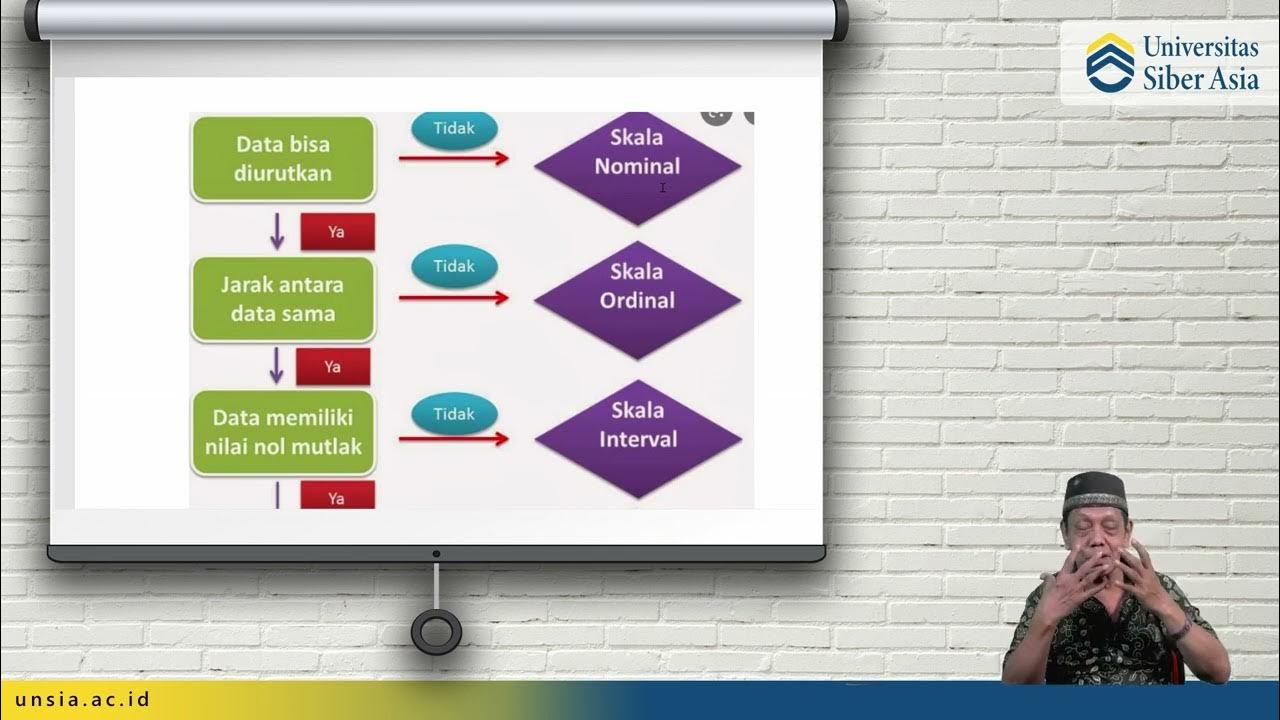
TLDRThis video explains the four scales of measurement in statistics: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. It begins by defining measurement as assigning numbers to objects according to specific rules. The nominal scale assigns numbers to differentiate objects without implying any order, such as in gender or sports uniform numbers. The ordinal scale assigns numbers to show order, such as race placements. The interval scale has both order and equal intervals, illustrated with temperature differences. The video concludes with a look at the ratio scale, which builds on the others by having a true zero point.
Takeaways
- 😀 Measurement is the process of applying numbers to objects according to a set of rules.
- 😀 When measuring, numbers are assigned to objects based on specific rules, such as using a tape measure to determine height.
- 😀 There are four scales of measurement in statistics: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio.
- 😀 Nominal scale assigns numbers to objects to differentiate between them without implying any order or value.
- 😀 An example of a nominal scale is gender, where males are assigned a 1 and females a 2 (the numbers have no inherent meaning).
- 😀 In baseball, uniform numbers are a nominal scale as they simply differentiate players without indicating skill or position.
- 😀 Ordinal scale assigns numbers to objects that have a meaningful order or ranking, such as race placements (1st, 2nd, 3rd).
- 😀 Ordinal data can rank objects, indicating relative performance, such as in a race or election results.
- 😀 Interval scale builds upon ordinal by having equal intervals between categories, such as temperature measured in degrees Fahrenheit.
- 😀 In the interval scale, the difference between any two adjacent numbers (like 78 and 79 degrees) is always the same.
- 😀 Ratio scale, the highest level of measurement, includes all the properties of the other scales, but also features a true zero point, which indicates the absence of the quantity being measured.
Q & A
What is the definition of measurement in the context of the script?
-Measurement is the process of applying numbers to objects according to a set of rules.
Can you explain the process of measuring someone's height with a tape measure?
-To measure someone's height, you extend a tape measure vertically from the ground to the top of their head, reading off the number in feet and inches.
What are the four scales of measurement mentioned in the video?
-The four scales of measurement mentioned are nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio.
What does a nominal scale of measurement involve?
-In a nominal scale, numbers are assigned to objects where the numbers have no meaning beyond differentiating between different objects. For example, assigning 1 for males and 2 for females.
Why is gender an example of a nominal scale?
-Gender is an example of a nominal scale because the numbers assigned (1 for males, 2 for females) are used only to differentiate between the two groups, without implying any order or value.
How does the example of baseball uniform numbers illustrate the nominal scale?
-Baseball uniform numbers are a nominal scale because they simply differentiate between players, with no meaning about their skills or positions.
What is the key feature of an ordinal scale of measurement?
-An ordinal scale involves assigning numbers to objects where the numbers have meaningful order, such as ranking the positions in a race (first, second, third).
How does ordinal data differ from nominal data?
-Ordinal data differs from nominal data in that ordinal data has meaningful order or ranking, while nominal data only differentiates between categories without any hierarchy.
What makes the interval scale different from ordinal data?
-The interval scale has not only meaningful order but also equal intervals between adjacent categories, such as the consistent difference between temperature values (e.g., 1 degree difference is the same throughout the scale).
Can you give an example of an interval scale in the script?
-Temperature in degrees Fahrenheit is an example of an interval scale, where the difference between any two consecutive degrees is the same throughout the scale.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
Scales of Measurement - Nominal, Ordinal, Interval, & Ratio Scale Data
Scales of Measurement: Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and Ratio Scale

02 Klasifikasi data statistika
Pertemuan 5 - Statistik - Prof. DR. H. Budi Santoso, MSc, APU

Levels of Measurement in Statistics: Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and Ratio

STATPROB Levels or Scales of Measurement
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
