Scales of Measurement: Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and Ratio Scale
Summary
TLDRIn this tutorial, Professor Matius Berto explains the four levels of measurement in statistics: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio scales. Using the example of apples, he demonstrates how data can be compared in various ways, from simple equality (nominal) to the ability to calculate meaningful differences and ratios (interval and ratio). Understanding these scales is crucial for choosing the appropriate statistical methods, as different methods require different types of data measurement. This foundational knowledge helps ensure accurate analysis and is essential for making informed statistical decisions across disciplines.
Takeaways
- 😀 Statistics is versatile and applies to many fields, including medicine, criminology, and economics.
- 🍏 The apple example is used to demonstrate how we perceive and describe objects through attributes like color, weight, harvest date, and sweetness.
- 📊 Data is organized in a table to compare apples based on various attributes, illustrating the importance of categorizing information.
- ⚖️ Weights of the apples can be mathematically manipulated (e.g., calculating differences and averages), while attributes like color and sweetness cannot.
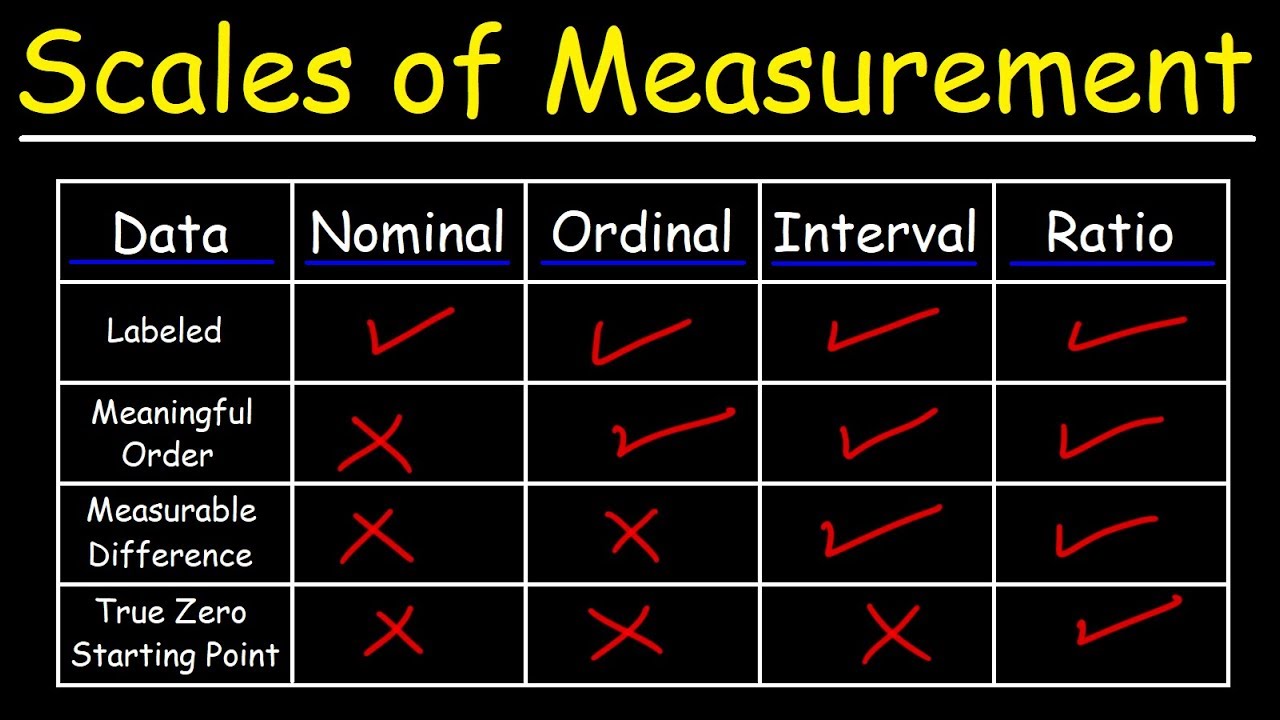
- 🔢 The four levels of measurement are: nominal scale, ordinal scale, interval scale, and ratio scale.
- 🏷️ Nominal scale involves only 'same' or 'different' comparisons, as seen with the apple's color.
- 🔼 Ordinal scale allows for ordering values, such as ranking the sweetness of apples from sour to sweet.
- 📅 Interval scale lets us determine the distance between values, like the number of days between apple harvest dates.
- 🔗 Ratio scale allows for ratios between values, such as comparing the weight of apples and saying one is 1.4 times heavier than another.
- 🧰 Understanding scales of measurement is crucial in statistics because it determines which mathematical operations can be applied to a data set.
Q & A
What are the four levels of measurement discussed in the video?
-The four levels of measurement are nominal scale, ordinal scale, interval scale, and ratio scale.
What is a nominal scale, and what kind of operations can be performed on it?
-A nominal scale is the simplest level of measurement where values can only be compared for equality or inequality. No mathematical operations such as addition or subtraction can be performed on it.
Can you provide an example of an attribute measured on a nominal scale from the video?
-In the video, the color of the apples is measured on a nominal scale, where the apples can only be classified as being the same or different in color.
How does an ordinal scale differ from a nominal scale?
-An ordinal scale allows for comparisons of equality or inequality, as well as the ability to rank or order the values. In contrast, a nominal scale only allows for equality or inequality comparisons without any sense of order.
What attribute from the video is an example of an ordinal scale?
-The sweetness of the apples is an example of an ordinal scale, as it allows the apples to be ordered from sour to sweet.
What operations can be performed on an interval scale?
-On an interval scale, in addition to equality and inequality comparisons, values can also be ordered, and the distance between values can be measured. However, ratios are not meaningful.
Which attribute in the video is measured on an interval scale?
-The harvest dates of the apples are measured on an interval scale, where the dates can be compared, ordered, and the distance between them can be calculated.
What is a ratio scale, and what kind of operations are possible with it?
-A ratio scale is the highest level of measurement, where all types of comparisons—equality, inequality, order, distance, and ratios—are possible. This scale allows for meaningful ratios between values.
What is an example of an attribute measured on a ratio scale from the video?
-The weight of the apples is measured on a ratio scale, where operations such as addition, subtraction, and meaningful ratios (e.g., one apple weighing 1.4 times more than another) are possible.
Why is understanding scales of measurement important in statistics?
-Understanding scales of measurement is crucial because different statistical methods require different types of data. Some methods involve sums, others involve ratios or order, and knowing which scale the data belongs to helps determine the appropriate statistical technique.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Scales of Measurement - Nominal, Ordinal, Interval, & Ratio Scale Data
Scales of Measurement - Nominal, Ordinal, Interval, Ratio (Part 1) - Introductory Statistics

Nominal, Ordinal, Interval & Ratio Data: Simple Explanation With Examples

Levels of Measurement in Statistics: Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and Ratio

STATPROB Levels or Scales of Measurement

02 Klasifikasi data statistika
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)