Menentukan Mean, Median, dan Modus Data Kelompok
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial explains how to calculate the mean, median, and mode for grouped data using a frequency distribution table. The presenter walks through the step-by-step process for determining each measure of central tendency, including formulas for mean (ψ = Σfx / Σf), median, and mode. The video demonstrates how to compute midpoints, cumulative frequencies, and class widths, followed by detailed calculations for each measure. This content is aimed at helping viewers understand and apply statistical methods for analyzing grouped data effectively.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video explains how to calculate statistical measures of central tendency (mean, median, and mode) for grouped data.
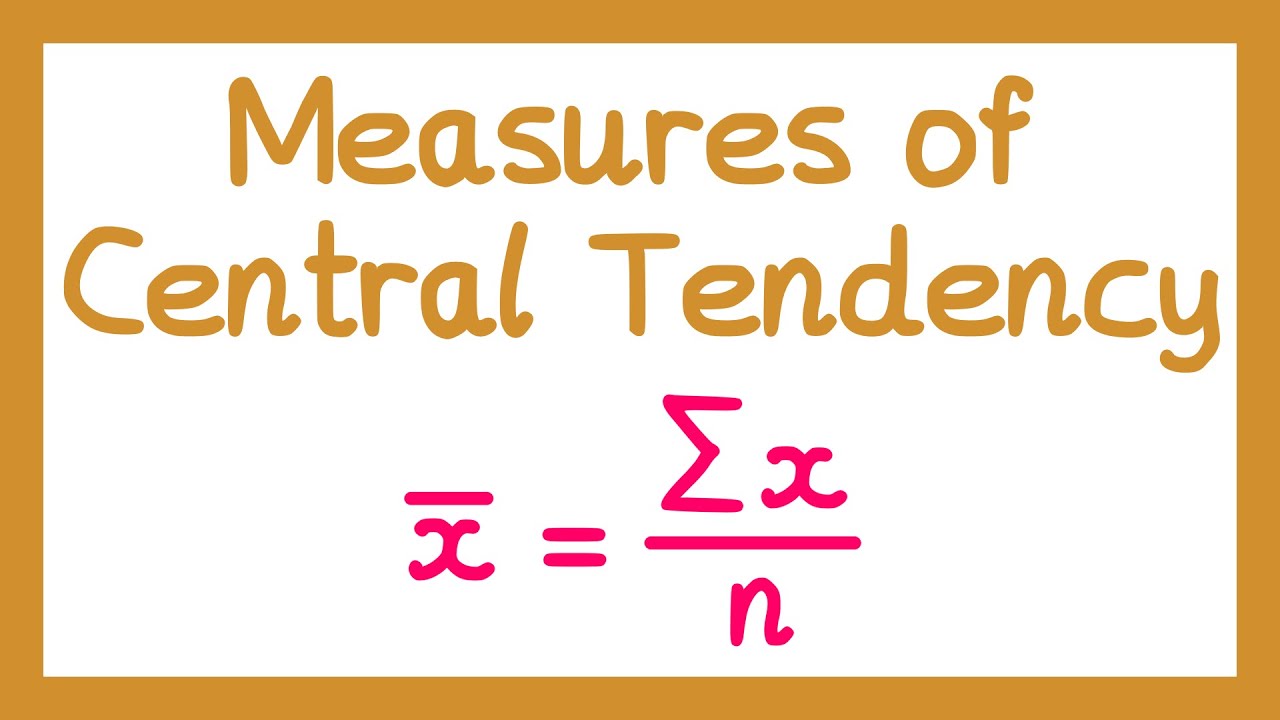
- 😀 The formula for calculating the mean (rata-rata) is: X̄ = Σ(f * x) / Σf, where 'f' is frequency and 'x' is the class midpoint.
- 😀 To find the class midpoint, add the lower and upper bounds of a class interval, then divide by two.
- 😀 The cumulative frequency is essential for identifying the median class when calculating the median for grouped data.
- 😀 The formula for calculating the median is: Median = L + [(N/2 - F) / f_m] * h, where L is the lower boundary, F is the cumulative frequency before the median class, f_m is the frequency of the median class, and h is the class width.
- 😀 The mode is determined using the formula: Mode = L + [(D1 / (D1 + D2)) * h], where D1 and D2 are the frequency differences between the mode class and its neighbors.
- 😀 The mode class is the one with the highest frequency in a frequency distribution table.
- 😀 For calculating the median, it is important to identify the correct median class based on cumulative frequencies and the total number of observations.
- 😀 In calculating the mode, pay attention to the differences in frequency (D1 and D2) between the mode class and its preceding and succeeding classes.
- 😀 The video includes step-by-step examples for calculating the mean, median, and mode using grouped data, ensuring clear understanding of the process.
Q & A
What is the formula for calculating the mean (average) of grouped data?
-The formula for calculating the mean (average) of grouped data is: X̄ = Σ(f * x) / Σf, where f is the frequency and x is the midpoint of the class interval.
How do you determine the midpoint of a class interval in grouped data?
-To determine the midpoint of a class interval, you add the lower limit and upper limit of the interval and divide the sum by 2. For example, for the class interval 20-24, the midpoint is (20 + 24) / 2 = 22.
What is the process for calculating the mean of grouped data?
-To calculate the mean, first find the midpoint of each class interval, then multiply each midpoint by the corresponding frequency. After that, sum all the frequency-midpoint products (Σ(f * x)) and divide it by the total frequency (Σf).
How is the median of grouped data determined?
-The median is determined using the formula: Median = L + ((N/2 - F) / f) * h, where L is the lower boundary of the median class, N is the total frequency, F is the cumulative frequency before the median class, f is the frequency of the median class, and h is the class width.
What steps are involved in calculating the median for grouped data?
-To calculate the median for grouped data, first find the cumulative frequency, then determine the median class by identifying the class where the cumulative frequency reaches or exceeds half of the total frequency. Next, apply the median formula to calculate the exact value.
How is the cumulative frequency calculated?
-Cumulative frequency is calculated by summing the frequencies of all previous classes up to the current class. For example, if the frequencies are 4, 8, 12, the cumulative frequencies would be 4, 12, and 24 respectively.
What is the formula for calculating the mode of grouped data?
-The formula for calculating the mode is: Mode = L + ((D1 / (D1 + D2)) * h), where L is the lower boundary of the mode class, D1 is the difference between the frequency of the mode class and the previous class, D2 is the difference between the frequency of the mode class and the next class, and h is the class width.
How do you determine the mode for grouped data?
-To determine the mode, first identify the class with the highest frequency (the mode class). Then, calculate the differences (D1 and D2) between the mode class frequency and the frequencies of the classes before and after it. Use these values in the mode formula.
What is the role of the class width when calculating the mode?
-The class width (h) plays a crucial role in the mode formula as it helps to scale the differences (D1 and D2) in frequency relative to the width of the class intervals. This ensures that the mode calculation reflects the actual distribution of the data.
Why is it important to find the class interval for the median or mode?
-It is important to find the correct class interval for the median or mode because the position of these measures of central tendency depends on the cumulative frequencies and the frequency distribution within each class interval. The correct interval ensures an accurate calculation.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Statistika - Ukuran Pemusatan Data (Mean, Median, Modus)
Measures of Central Tendency - Year 1 Statistics [A-level]

Statistika #3 Ukuran Pemusatan : Mean - Modus - Median | Kelas X Fase E Kurikulum Merdeka

Statistika Dasar Ukuran Pemusatan Data (Mean, Modus, Median) Data Tunggal dan Data Kelompok

STATISTIKA CARA MENCARI NILAI MEAN, MEDIAN, MODUS DATA KELOMPOK PART 1

MAT 152 SAS 8 Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
