What is FTIR Spectroscopy? – Technology Introduction – METTLER TOLEDO - EN
Summary
TLDRFourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) is a powerful analytical technique used in laboratories to analyze molecular structures and compositions. By utilizing modulated mid-infrared energy, FTIR detects specific bond vibrations in molecules, creating a unique spectral fingerprint. Coupling FTIR with Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) allows real-time monitoring of chemical reactions, providing crucial insights into reaction kinetics and mechanisms without the need for offline sampling. While primarily qualitative, FTIR can also yield quantitative data, following the Beer-Lambert law, to inform control variables during reactions. This capability enhances efficiency in chemical analysis and experimentation.
Takeaways
- 🔬 FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy) is an analytical technology used to analyze molecular structures and compositions.
- 💡 FTIR spectroscopy utilizes mid-infrared energy to probe samples, with infrared light being absorbed at specific frequencies related to molecular bond energies.
- 🔗 Different molecular bonds vibrate at different energies, allowing FTIR to absorb various wavelengths of infrared radiation.
- 🧪 The resulting spectrum from FTIR acts as a unique fingerprint for each molecule, based on the position, frequency, and intensity of absorption bands.
- ⏱ Coupling FTIR with Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) enhances its utility, enabling real-time monitoring of chemical reactions without the need for manual sampling.
- 📊 FTIR can measure key reaction characteristics such as initiation, endpoint, intermediates, kinetics, and mechanisms in real time.
- 📏 FTIR primarily provides qualitative data but can also yield quantitative measurements following the Beer-Lambert law.
- 🔍 The absorbance for specific vibrational frequencies is directly proportional to the concentration of those bonds once the instrument is calibrated.
- ⚙️ Real-time quantitative data obtained from FTIR can help control reaction conditions, such as reagent addition and reaction termination.
- 🌐 For further information on FTIR technology, resources are available at mt.com.
Q & A
What is Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)?
-FTIR is an analytical technology used to understand the structure of molecules and the composition of molecular mixtures by analyzing how they absorb mid-infrared light.
How does FTIR spectroscopy work?
-FTIR spectroscopy uses modulated mid-infrared energy to interrogate a sample. Molecules absorb infrared light at specific frequencies related to their atom-to-atom vibrational bond energies, creating a spectrum that serves as a characteristic fingerprint for the molecule.
What does the spectrum produced by FTIR represent?
-The spectrum produced by FTIR represents the position, frequency, and intensity of absorption bands, which correlate to different molecular bonds and functional groups in a sample.
Why is FTIR ideal for monitoring chemical reactions?
-FTIR is ideal for monitoring chemical reactions because it can detect changes in molecular bonds in real time, allowing for the measurement of reaction kinetics, intermediates, and endpoints.
What is Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) in FTIR?
-ATR is a technique that enhances FTIR by allowing for the examination of samples without the need for manual sampling. It enables real-time analysis of reactions as they occur.
What are some key reaction characteristics that can be monitored using FTIR?
-Key reaction characteristics that can be monitored include initiation, endpoint, reactive intermediates, reaction kinetics, and mechanistic information.
Can FTIR provide quantitative measurements?
-Yes, FTIR can provide quantitative measurements by following Beer-Lambert's law, which relates absorbance to the concentration of a specific bond in a sample once the system is calibrated.
What is Beer-Lambert's law?
-Beer-Lambert's law states that absorbance (A) is proportional to the product of molar absorptivity (a), the path length of the sample (b), and the concentration (c) of the absorbing species.
How can real-time quantitative data from FTIR be used in experiments?
-Real-time quantitative data can be used to control experimental conditions, such as deciding when to add reagents, adjusting temperature, or terminating the reaction based on observed changes.
Where can one find more information about FTIR spectroscopy?
-More information about FTIR spectroscopy can be found at mt.com.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
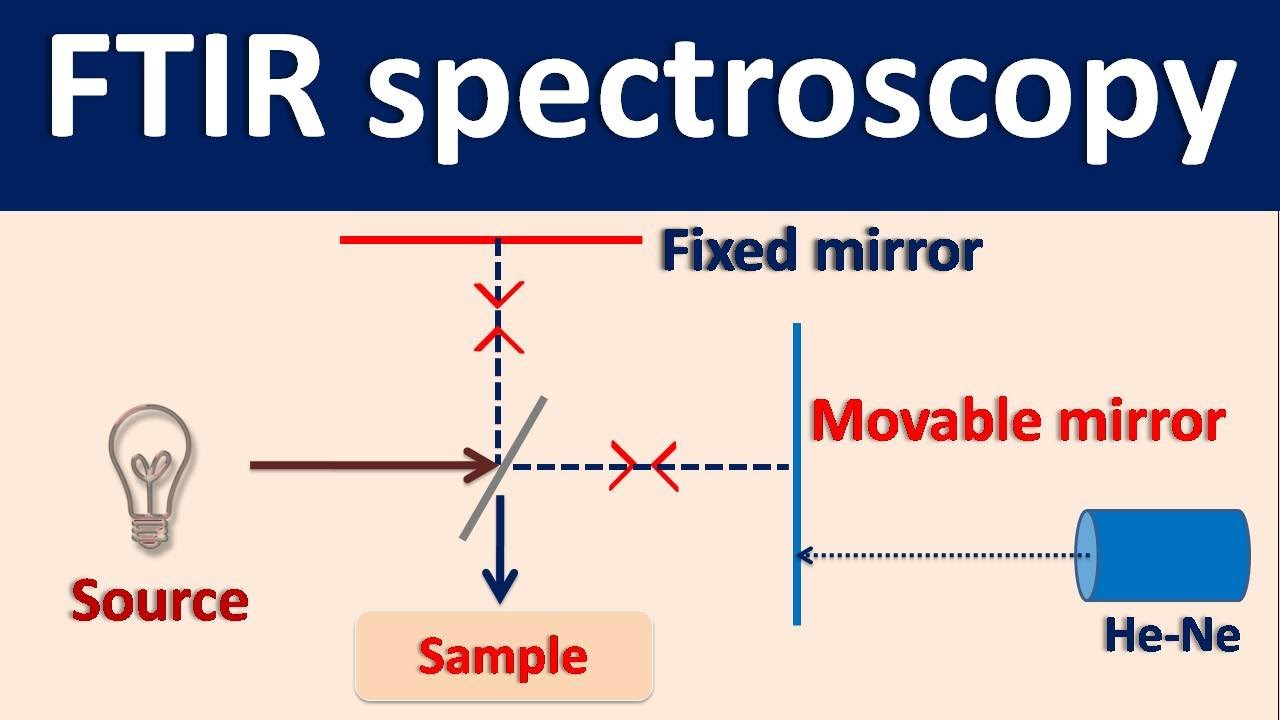
Fourier Transform IR spectroscopy (FTIR) - How it works?

Back to Basics: Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy

Introduction to Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
IR Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry: Crash Course Organic Chemistry #5

(16) IR Spectroscopy | Introduction to Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy | Instrumental Method of Analysis

Spektroskopi Raman
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
