Konfigurasi elektron mekanika kuantum (spdf) dan elektron valensi-Teori Atom mekanika kuantum
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explores electronic configuration and valence electrons based on quantum mechanics. It contrasts these concepts with Bohr's atomic theory, emphasizing the Aufbau principle, Hund's rule, and Pauli's exclusion principle. Viewers learn how to determine the maximum number of electrons in various orbitals and how to write electronic configurations accurately. The video also explains the significance of valence electrons in chemical bonding, differentiating between main group and transition elements. Through practical examples, such as sodium and argon, the video aims to reinforce understanding of these fundamental chemistry concepts.
Takeaways
- 😀 Electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons in an atom's orbitals and is essential for understanding chemical behavior.
- 🧑🔬 The Aufbau Principle states that electrons fill orbitals from the lowest to the highest energy level.
- ⚖️ Hund's Rule dictates that electrons must fill degenerate orbitals singly before pairing up.
- 🚫 The Pauli Exclusion Principle ensures that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers.
- 📊 Each orbital can hold a specific maximum number of electrons: 1s and 2s can hold 2 electrons, 2p can hold 6, 3s can hold 2, 3p can hold 6, and 3d can hold 10.
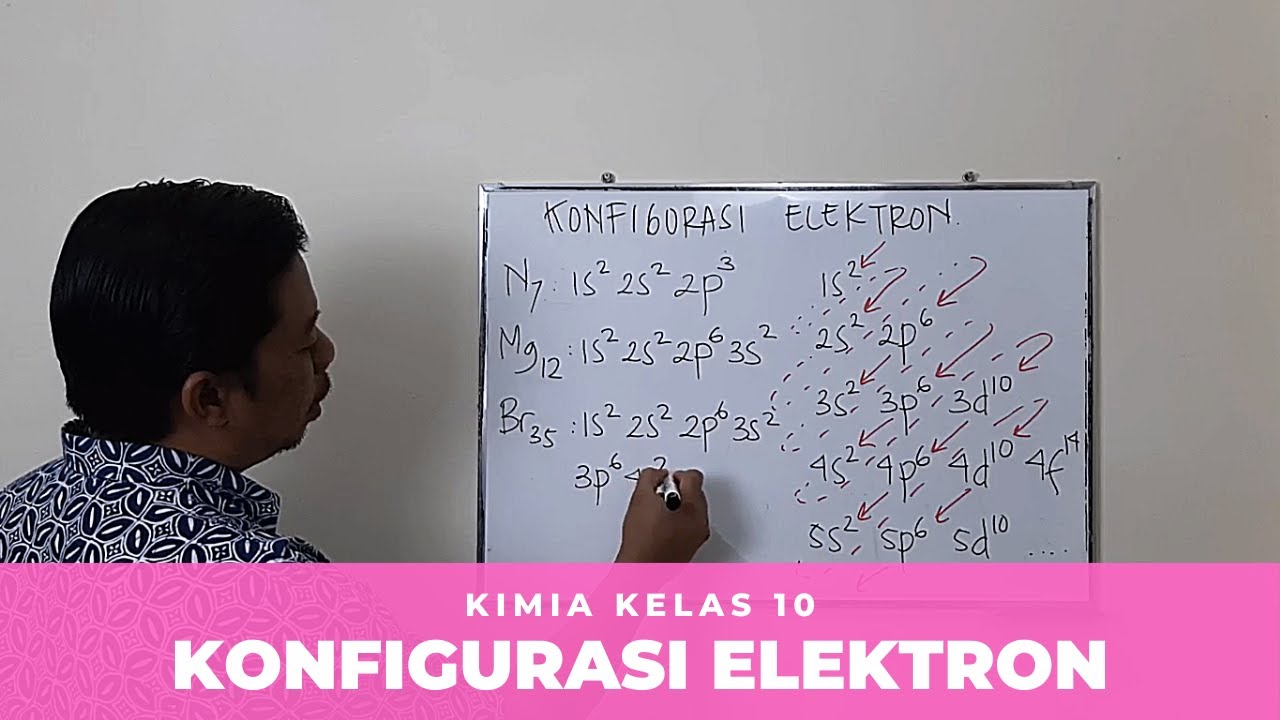
- ✍️ Writing electron configurations involves starting from the lowest energy orbitals and using the atomic number to fill them correctly.
- 🔬 Valence electrons are the outermost electrons involved in chemical bonding and can be identified from the electron configuration.
- 🧪 Main group elements have valence electron configurations represented as ns² npⁿ, while transition elements have configurations like ns²(n-1)dⁿ.
- 🔍 Examples provided in the script demonstrate how to determine electron configurations and valence electrons for various elements.
- 📚 Mastering electron configurations and valence electrons is crucial for further studies in chemistry and understanding chemical reactions.
Q & A
What is electron configuration?
-Electron configuration refers to the arrangement or distribution of electrons in each orbital of an atom.
What are the three main rules for writing electron configurations according to quantum mechanics?
-The three main rules are: the Aufbau principle (electrons fill orbitals from lowest to highest energy), Hund's rule (electrons fill degenerate orbitals singly before pairing), and the Pauli exclusion principle (no two electrons can have the same four quantum numbers).
How does the Aufbau principle guide the filling of electrons in orbitals?
-The Aufbau principle states that electrons occupy the lowest energy orbitals first before moving to higher energy levels.
What is Hund's rule and how does it apply to filling p and d orbitals?
-Hund's rule states that electrons will occupy degenerate orbitals singly and with the same spin before pairing up. This means that in p and d orbitals, each orbital will get one electron before any orbital gets a second electron.
What does the Pauli exclusion principle state?
-The Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers, which effectively means that no orbital can contain two electrons with the same spin.
How is the maximum number of electrons in an orbital determined?
-The maximum number of electrons in an orbital can be determined by the formula 2n², where n is the principal quantum number corresponding to the energy level.
What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy the 2p orbital?
-The maximum number of electrons that can occupy the 2p orbital is 6, as there are three degenerate p orbitals, each capable of holding 2 electrons.
Can you give an example of writing an electron configuration for an element?
-For carbon (atomic number 6), the electron configuration is 1s² 2s² 2p², indicating that there are two electrons in the 1s orbital, two in the 2s orbital, and two in the 2p orbital.
What are valence electrons and why are they important?
-Valence electrons are the outermost electrons involved in chemical bonding. They determine the chemical properties of an element and how it will react with other elements.
How can we differentiate between main group elements and transition metals based on their electron configurations?
-Main group elements (group A) have valence electron configurations that follow the pattern ns² np⁶, while transition metals (group B) have configurations that include d orbitals, following the pattern ns² (n-1)d.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

CONFIGURACIÓN ELECTRÓNICA del BROMO | Química desde cero
Konfigurasi Elektron | KIMIA KELAS 10

konfigurasi elektron

KONFIGURASI ELEKTRON MEKANIKA KUANTUM - MATERI KIMIA KELAS 10 | Edcent.id

Konfigurasi Elektron dan Elektron Valensi- Kimia SMA kelas 10 semester 1

Struktur Atom • Part 7: Konfigurasi Elektron Ion, Elektron Valensi, Elektron Terakhir
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
