What is TPM -Total Productive Maintenance ? | 8 TPM pillars Total Productive Maintenance
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces Total Productive Maintenance (TPM), a proactive approach aimed at achieving zero accidents, defects, and breakdowns in manufacturing. It highlights the origins of TPM in Japan, its evolution from preventive maintenance, and the eight foundational pillars, including autonomous maintenance and quality maintenance. The video also distinguishes between TPM and Total Quality Management (TQM), outlines types of maintenance, and discusses the significant benefits of implementing TPM, such as reduced unplanned maintenance, enhanced safety, and lower production costs. Overall, it emphasizes the importance of employee involvement and structured processes in optimizing production efficiency.
Takeaways
- 😀 TPM (Total Productive Maintenance) aims for zero accidents, breakdowns, and defects in manufacturing processes.
- 📅 The history of TPM traces back to 1951 in Japan, originating from preventive maintenance concepts introduced from the USA.
- 🏗️ TPM is built on eight pillars, starting with a foundation of 5S to maintain a clean and organized work environment.
- 🛠️ Autonomous Maintenance empowers operators to take ownership of equipment by performing basic maintenance tasks.
- 🔧 Planned Maintenance involves scheduled evaluations to prevent equipment breakdowns, minimizing unplanned downtime.
- ✅ Quality Maintenance focuses on achieving zero defects in production, enhancing customer satisfaction and reducing costs.
- 👥 Focused Improvement encourages small teams to work together for continuous, incremental improvements in equipment operations.
- 📚 Training and Education are essential for building employee competence, ensuring everyone contributes to overall productivity.
- 🏭 TPM is distinct from TQM (Total Quality Management), focusing more on equipment and maintenance while TQM targets overall quality.
- ⚙️ There are two main types of maintenance: Corrective Maintenance (fixing issues post-failure) and Preventive Maintenance (proactively avoiding issues).
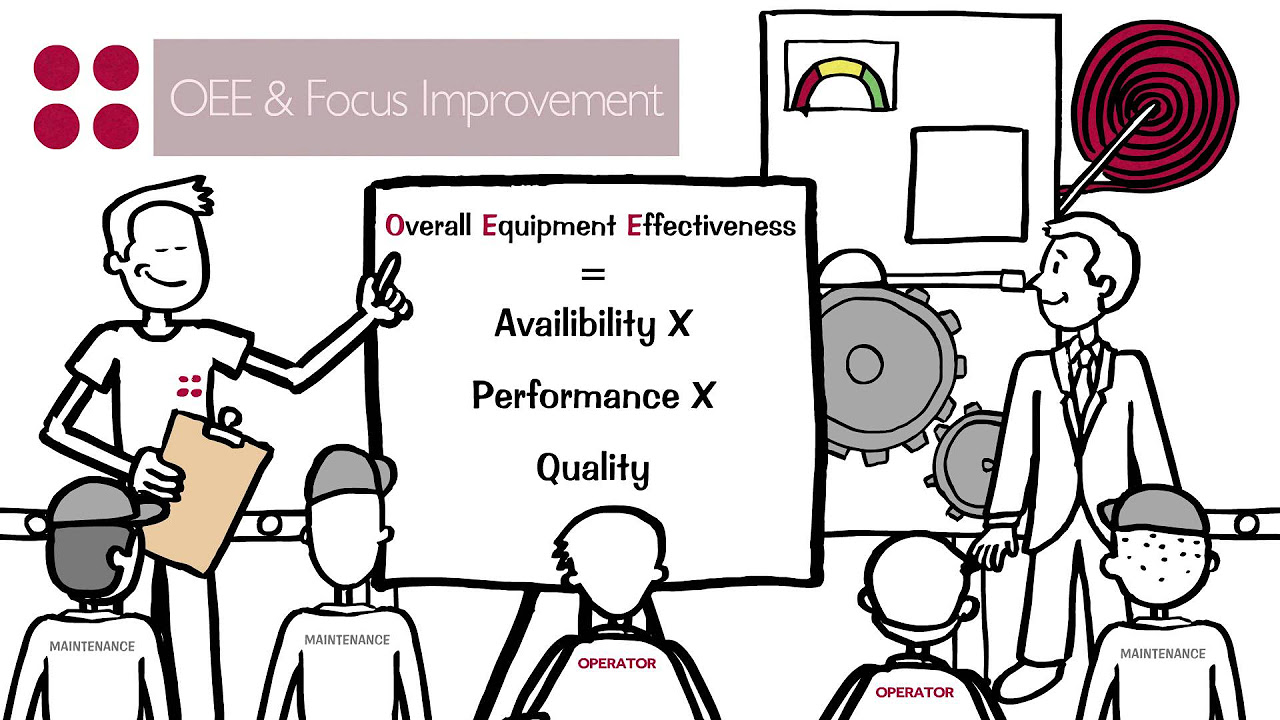
- 📊 Implementing TPM leads to measurable results through Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) and reduces workplace accidents.
Q & A
What is Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)?
-TPM is a maintenance strategy aimed at achieving zero accidents, zero breakdowns, and zero defects by involving all employees in the maintenance and production processes.
When and where did TPM originate?
-TPM originated in Japan in 1951, evolving from the concept of preventive maintenance influenced by practices from the United States.
What does the acronym TPM stand for?
-TPM stands for Total, Productive, and Maintenance. 'Total' refers to all individuals in the organization working towards a common goal, 'Productive' relates to producing goods that meet customer expectations, and 'Maintenance' involves keeping equipment in optimal condition.
What is the primary goal of TPM?
-The primary goal of TPM is to increase Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) and aim for zero waste in production.
What are the eight pillars of TPM?
-The eight pillars of TPM are: 1) Autonomous Maintenance, 2) Planned Maintenance, 3) Quality Maintenance, 4) Focused Improvement, 5) Early Equipment Management, 6) Training and Education, 7) Safety, Health, and Environment, and 8) TPM in Administration.
How does TPM differ from Total Quality Management (TQM)?
-TPM focuses on equipment and operational efficiency, while TQM emphasizes overall quality as an output. Both aim to reduce waste but approach it from different angles.
What are the two main types of maintenance discussed in the script?
-The two main types of maintenance are Corrective Maintenance, which is performed after a failure, and Preventive Maintenance, which aims to prevent problems before they occur.
What are the benefits of implementing TPM?
-The benefits of implementing TPM include reduced unplanned maintenance, less downtime, safer work environments, lower production costs, increased profitability, and measurable results through OEE.
What is the significance of the 5S foundation in TPM?
-The 5S foundation is essential for establishing a clean and organized work environment, which supports the effective implementation of the eight pillars of TPM.
What role does training and education play in TPM?
-Training and education are crucial in TPM as they empower employees to contribute to the productivity of the production process and enhance their competence in equipment maintenance.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Four Principles – Lean Manufacturing & TPM
Four Principles TPM

What is Total Productive Maintenance | 8 Pillars of TPM | 6 Big Losses | Type of Maintenance

How 7 Companies Mastered TPM (Total Productive Maintenance)

#22 Free Lean Six Sigma Green Belt | Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)

Understanding Quality Assurance - GCSE Business Studies Revision - OCR, Edexcel, AQA - BizzWizard
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
