The Menstrual Cycle Explained - 4 PHASES OF MENSTRUAL CYCLE MADE EASY!
Summary
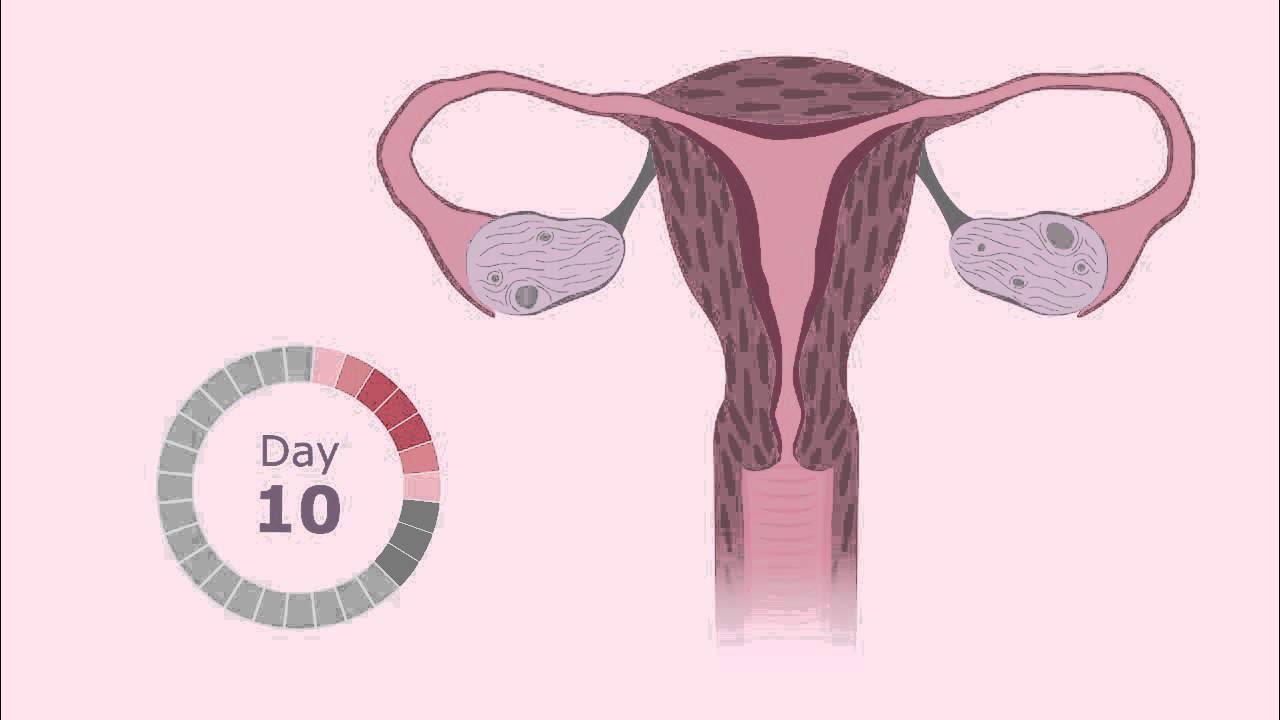
TLDRThe menstrual cycle is a monthly hormonal process experienced by women from puberty to menopause, consisting of four phases: the menstrual phase, where the uterine lining sheds; the follicular phase, starting on the first day of menstruation and preparing the body for ovulation; the ovulation phase, where a mature egg is released; and the luteal phase, which prepares the uterus for potential pregnancy. Hormonal fluctuations throughout these phases can cause various physical symptoms. Understanding this cycle is crucial for women's health and fertility awareness.
Takeaways
- 😀 Women experience a menstrual cycle monthly from puberty until menopause, driven by hormones.
- 😀 The menstrual cycle consists of four phases: menstrual phase, follicular phase, ovulation phase, and luteal phase.
- 😀 The menstrual phase begins when pregnancy does not occur, leading to a drop in estrogen and progesterone, causing the uterine lining to shed.
- 😀 Symptoms during the menstrual phase can include bloating, cramps, tiredness, lower back pain, tender breasts, and irritability.
- 😀 The follicular phase overlaps with the menstrual phase and is marked by the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) from the pituitary gland.
- 😀 FSH stimulates the ovaries to produce follicles, each containing an immature egg, with one follicle becoming dominant and maturing.
- 😀 The ovulation phase occurs when a surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) triggers the release of a mature egg from the ovary, typically around day 14 of the cycle.
- 😀 Signs of ovulation include a slight increase in body temperature and a thicker, egg-white-like vaginal discharge.
- 😀 The luteal phase follows ovulation and involves the formation of the corpus luteum, which releases progesterone to maintain the uterine lining.
- 😀 If fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum shrinks, leading to decreased hormone levels and the onset of menstruation.
Q & A
What is the menstrual cycle?
-The menstrual cycle is a hormone-driven process that occurs each month in women from puberty until menopause, involving the development and release of an egg from the ovaries and the shedding of the uterine lining if pregnancy does not occur.
What are the four phases of the menstrual cycle?
-The four phases of the menstrual cycle are the menstrual phase, follicular phase, ovulation phase, and luteal phase.
What happens during the menstrual phase?
-During the menstrual phase, the uterine lining sheds due to a drop in estrogen and progesterone levels, resulting in the release of blood, mucus, and tissues through the vagina.
How long does the menstrual phase usually last?
-The menstrual phase typically lasts around 3 to 7 days.
What occurs during the follicular phase?
-In the follicular phase, the hypothalamus signals the pituitary gland to release follicular stimulating hormone (FSH), which stimulates the ovaries to produce follicles containing immature eggs. This phase overlaps with the menstrual phase and lasts about 16 days.
What triggers ovulation?
-Ovulation is triggered by an increase in estrogen during the follicular phase, which causes the pituitary gland to release luteinizing hormone (LH), leading to the release of a mature egg from the ovary.
What are the symptoms of ovulation?
-Symptoms of ovulation may include a slight increase in body temperature and a thicker vaginal discharge, often described as having the texture of egg whites.
What happens during the luteal phase?
-During the luteal phase, the corpus luteum forms from the released follicle and secretes progesterone and some estrogen to maintain the thickened uterine lining for potential implantation of a fertilized egg.
What is human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG)?
-HCG is a hormone produced if pregnancy occurs; it is responsible for maintaining the corpus luteum and is the hormone detected by pregnancy tests.
What happens if pregnancy does not occur after ovulation?
-If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum shrinks, leading to decreased levels of estrogen and progesterone, which triggers the onset of the menstrual period as the uterine lining sheds.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)