Menstrual Cycle Phases Nursing | Follicular Phase & Luteal Phase Med Surg
Summary
TLDRThe menstrual cycle is a monthly process involving the ovaries, uterus, and hormones to prepare the body for potential pregnancy. It has two main phases: the follicular phase (before ovulation) and the luteal phase (after ovulation). Key hormones like GnRH, FSH, LH, estrogen, and progesterone control ovulation and the thickening of the uterine lining. If pregnancy doesn't occur, menstruation begins, shedding the lining. The cycle resets with rising FSH levels. Birth control and emergency contraception work by manipulating these hormones to prevent pregnancy, either by stopping ovulation or preventing embryo implantation.
Takeaways
- 😀 Menstrual cycle, also known as period or menstruation, is a monthly cycle that involves changes in the endometrium and ovaries.
- 😀 The menstrual cycle starts at puberty (menarche) and continues until menopause, around the age of 50-55.
- 😀 The endometrium is the uterine lining, which thickens to support a fertilized egg during pregnancy and sheds when the egg isn't fertilized.
- 😀 The menstrual cycle consists of two main cycles: the ovarian cycle (hormonal changes that trigger ovulation) and the uterine cycle (preparing the uterus for pregnancy).
- 😀 The ovarian cycle involves the release of an egg (ovulation), while the uterine cycle involves thickening the endometrial lining to catch a fertilized egg.
- 😀 The menstrual cycle has two phases: the follicular phase (before ovulation) and the luteal phase (after ovulation).
- 😀 The follicular phase is marked by hormonal activity that triggers ovulation, while the luteal phase prepares the uterus for possible pregnancy.
- 😀 If the egg is not fertilized, the corpus luteum dissolves, leading to a drop in estrogen and progesterone, which triggers menstruation (bleeding).
- 😀 A fertilized egg produces HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), which helps maintain high levels of estrogen and progesterone to prevent menstruation.
- 😀 Birth control methods, like oral contraceptives, work by maintaining high levels of estrogen and progesterone, which prevent ovulation and fertilization.
Q & A
What is the menstrual cycle?
-The menstrual cycle is a monthly series of changes that occur in the female reproductive system, specifically in the endometrium (the uterine lining) and the ovaries. It begins at puberty and continues until menopause, typically around age 50-55.
What is the endometrium, and what role does it play in the menstrual cycle?
-The endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus. It thickens during the menstrual cycle in preparation for a possible pregnancy, and if no fertilization occurs, it is shed as menstrual blood.
What are the two main phases of the menstrual cycle?
-The two main phases of the menstrual cycle are the follicular phase (before ovulation) and the luteal phase (after ovulation).
What happens during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle?
-During the follicular phase, hormones trigger the growth of ovarian follicles, and estrogen is released. Estrogen thickens the endometrial lining in preparation for a potential pregnancy.
What occurs during ovulation in the menstrual cycle?
-During ovulation, the ovary releases an egg, which travels to the uterus. The uterus, in turn, prepares by thickening its lining to catch and support the egg if it gets fertilized.
What happens in the luteal phase?
-In the luteal phase, the ovary releases both estrogen and progesterone. These hormones help maintain the thickened endometrial lining to support a fertilized egg. If fertilization doesn't occur, hormone levels drop, leading to menstruation.
What role do the hormones GnRH, FSH, and LH play in the menstrual cycle?
-GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone) is released by the hypothalamus, stimulating the anterior pituitary to release FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) and LH (luteinizing hormone). These hormones trigger the ovarian follicles to release an egg and increase estrogen production, leading to ovulation.
What happens if the egg is not fertilized during the menstrual cycle?
-If the egg is not fertilized, the corpus luteum in the ovary disintegrates, causing a drop in estrogen and progesterone. This leads to the shedding of the endometrial lining, resulting in menstrual bleeding.
How does pregnancy affect the menstrual cycle?
-If the egg is fertilized, the fertilized egg releases HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), which keeps estrogen and progesterone levels high, preventing the shedding of the uterine lining and stopping the menstrual cycle.
How do birth control methods like the pill and Plan B work?
-Birth control methods, such as the pill, maintain high levels of estrogen and progesterone to prevent ovulation. Plan B, or emergency contraception, works by causing the shedding of the uterine lining, preventing a fertilized egg from implanting in the uterus.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
The Menstrual Cycle

The Menstrual Cycle - GCSE Biology (9-1)
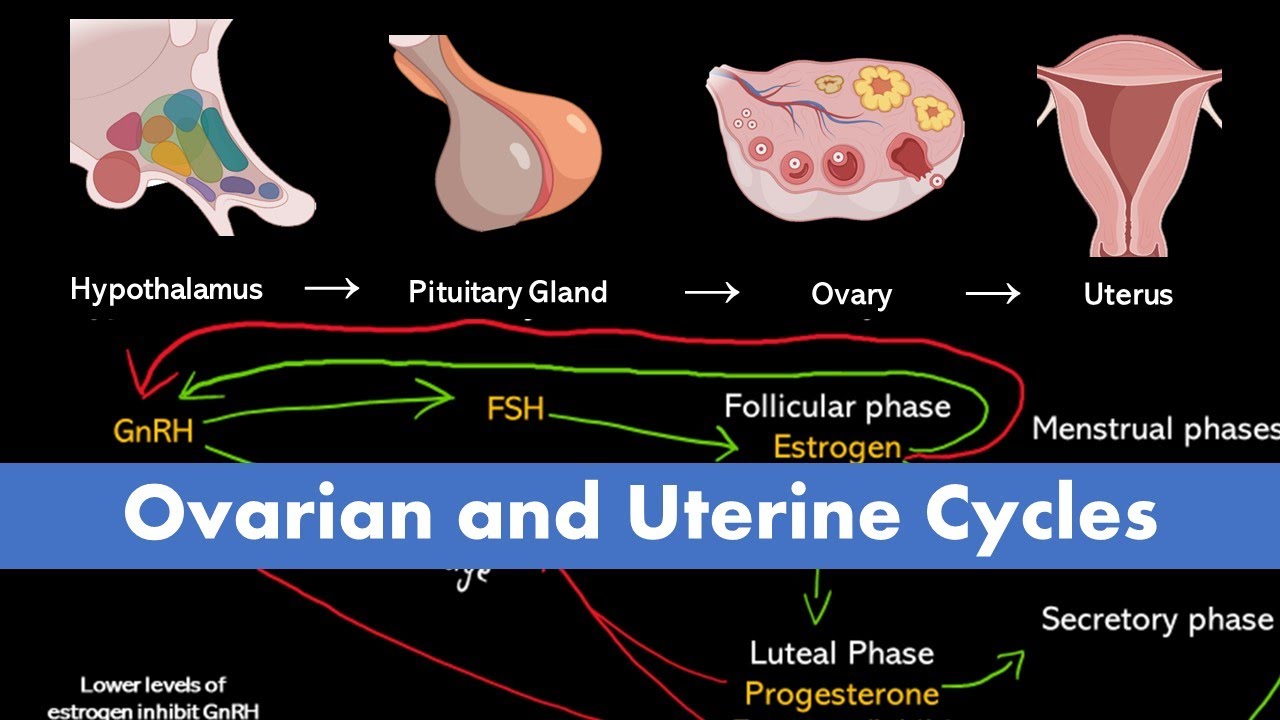
Ovarian and Uterine Cycle (Menstrual Cycle)

ovulation and menstrual cycle often called period|medical animationDandelionTeam #ovulation #period

Ovulation & the Menstrual Cycle

The Menstrual Cycle Explained - 4 PHASES OF MENSTRUAL CYCLE MADE EASY!
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)