Incoterms® 2020 Explained for Import Export Global Trade
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the importance of Incoterms® in international trade, detailing the 11 terms that outline the responsibilities of buyers and sellers when shipping goods globally. Incoterms® 2020, published by the International Chamber of Commerce, specify who is responsible for tasks, costs, and risks at each stage of the shipping process. The video covers key terms like EXW, FCA, FOB, CIF, and DDP, and emphasizes the need for clarity in sales contracts to avoid disputes. It also introduces IncoDocs, a platform for creating global trade documentation.
Takeaways
- 📦 Understanding Incoterms® is essential for international trade and outlines selling terms between buyer and seller.
- 📚 Incoterms® stands for International Commercial Terms and is published by the International Chamber of Commerce.
- 🌍 The latest version, Incoterms® 2020, came into effect on January 1, 2020, and is widely recognized by governments and legal authorities.
- 💼 Incoterms® define the responsibilities for tasks, costs, and risks between the buyer and seller of goods in international transactions.
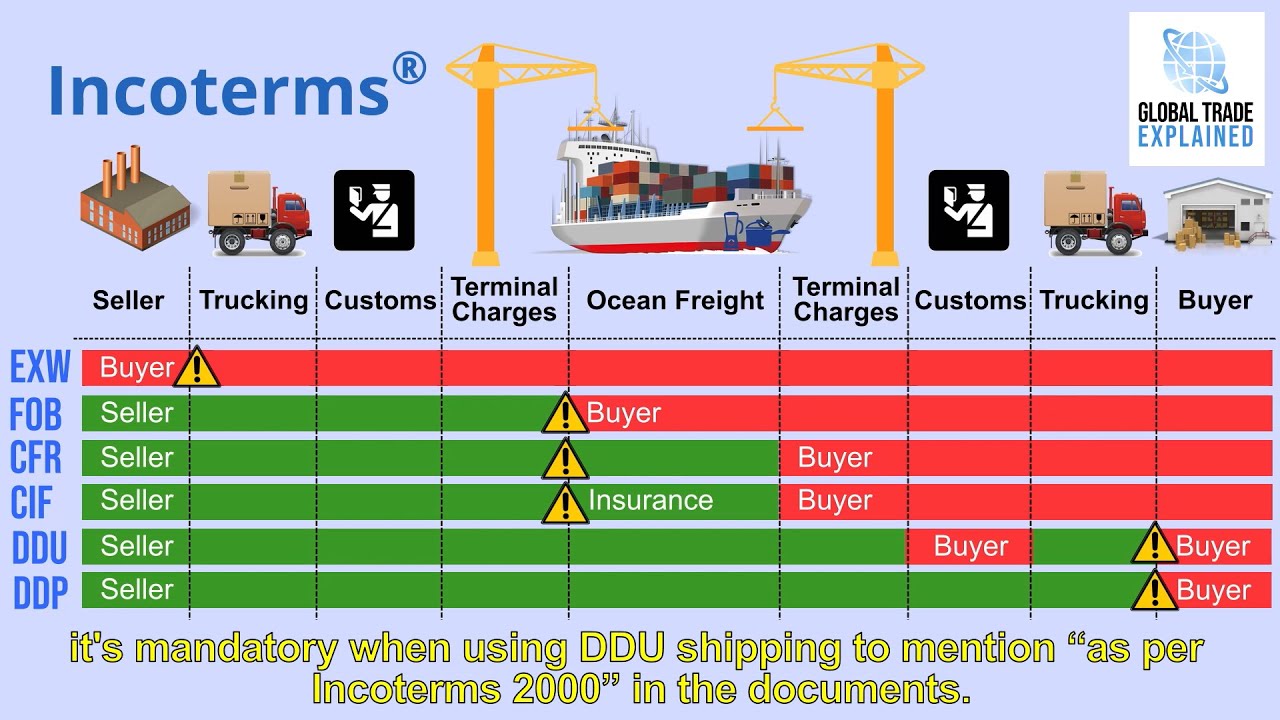
- 🚢 The chart explains different Incoterms®, showing which tasks are handled by the seller and which are passed to the buyer during the supply chain process.
- 🏭 EXW (Ex-Works) means the seller's responsibility ends once the goods are made and packaged, and all further costs are borne by the buyer.
- 🚚 FOB (Free-On-Board) is a common Incoterm® where the seller covers all costs up to the loading of goods on the export vessel, with risks and costs shifting to the buyer afterward.
- ⛴ CFR, CIF, CPT, and CIP Incoterms® require the seller to pay for transportation, with CIF and CIP including insurance for the goods.
- 📦 DAP, DPU, and DDP Incoterms® involve the seller covering costs and responsibilities up to the delivery and unloading of goods at the destination.
- 📝 It's critical that both parties agree on and document the chosen Incoterm® to prevent disputes, ensuring clear responsibilities.
Q & A
What are Incoterms® and why are they important in international trade?
-Incoterms® are International Commercial Terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). They are important because they define the responsibilities, risks, and costs for buyers and sellers during the international sale and transportation of goods, ensuring clear agreements and reducing the risk of disputes.
How many Incoterms® are there in total, and when was the latest version published?
-There are 11 Incoterms®, and the latest version, Incoterms® 2020, came into effect on January 1, 2020.
What does the Incoterm® EXW (Ex-Works) mean for the buyer and seller?
-Under EXW (Ex-Works), the seller's responsibility is limited to making the goods available at their warehouse. All costs and risks from that point onward, including transportation and export duties, are borne by the buyer.
What are the seller's obligations under FOB (Free-On-Board) Incoterm®?
-Under FOB, the seller covers all costs and risks associated with getting the goods to the port of loading and loading them onto the vessel. Once the goods are loaded, the buyer assumes all further risks and costs, including shipping and import duties.
What is the main difference between CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) and CFR (Cost and Freight) Incoterms®?
-The key difference between CIF and CFR is that under CIF, the seller must provide insurance for the goods during transport, whereas under CFR, the seller only covers the cost and freight, but not the insurance.
When would a seller choose to use the CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid To) Incoterm®?
-A seller would use CIP if they agree to cover the transportation costs and insurance for the goods to the destination. This Incoterm® is applicable to any mode or combination of modes of transport.
What does the DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) Incoterm® imply for the seller?
-Under DDP, the seller is responsible for delivering the goods to the buyer's location, including all transportation costs, import duties, taxes, and customs clearance at the destination country. The buyer has no obligations until the goods are delivered.
What is the difference between DAP (Delivered At Place) and DPU (Delivered at Place Unloaded) Incoterms®?
-The difference between DAP and DPU is that under DAP, the seller delivers the goods to the agreed place but does not handle unloading. In contrast, under DPU, the seller is responsible for both delivery and unloading of the goods at the destination.
Why is it important for buyers and sellers to clearly state the agreed Incoterm® in their sales contracts?
-Clearly stating the agreed Incoterm® in sales contracts is important because it ensures both parties are aware of their responsibilities and reduces the risk of misunderstandings or disputes over costs, risks, and responsibilities during the shipping process.
What kind of assistance can a freight forwarder provide regarding Incoterms®?
-A freight forwarder can offer guidance on choosing the most appropriate Incoterm® for a particular shipment, as well as assist with documentation, customs clearance, and managing logistics to ensure compliance with the agreed terms.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
Incoterms for beginners | Global Trade Explained

Incoterms 2020 detailed explanation

Lesson 1 - Introduction to the Incoterms® 2020 rules

Incoterms (International commercial Terms) 2020 #1 Ekspor Impor

INCOTERMS COMO NUNCA TE EXPLICARAM 😱 FOB CIF EXW FCA DAT

Explained about basic INCOTERMS for beginners! EXW/FOB/CFR/CIF/DAP/DDP.
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
