CORRELATIONAL RESEARCH
Summary
TLDRThis educational video discusses correlational research, a non-experimental method analyzing relationships between two variables without manipulating them. It covers the definition, purpose, and key aspects of correlation: direction (positive, negative, zero) and magnitude (strong, weak, none). The video clarifies that correlation does not imply causation, distinguishing it from experimental research.
Takeaways
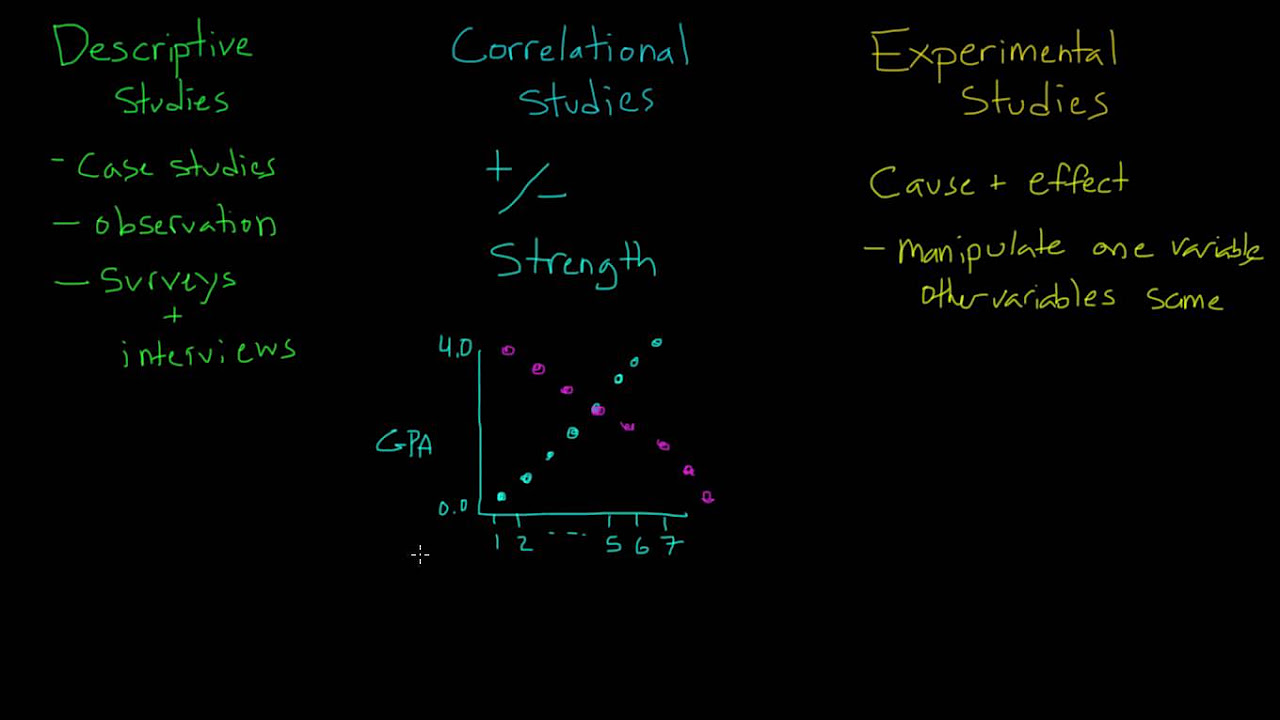
- 🔍 Correlational research is a non-experimental method that studies the relationship between two variables.
- 📊 It focuses on quantitative data to identify patterns, trends, or insights.
- 🔄 Correlational studies observe how changes in one variable might predict changes in another.
- 📈 The research design investigates both the direction and magnitude of relationships among variables.
- ➡️ Direction of correlation can be positive, negative, or zero, indicating the type of relationship between variables.
- 📉 Positive correlation means as one variable increases, the other also increases.
- 📈 Negative correlation indicates that as one variable increases, the other decreases.
- 🔄 Zero correlation suggests no relationship between the variables, with changes in one not affecting the other.
- 📌 Magnitude measures how strongly the variables are related, ranging from strong to weak or no correlation.
- ⚠️ Correlation does not imply causation; correlational research does not establish cause and effect.
- 🔬 Unlike experimental research, correlational research does not manipulate variables; it merely measures and observes them.
Q & A
What is correlational research?
-Correlational research is a non-experimental research method that studies the relationship between two variables by analyzing quantitative data to identify patterns, trends, or insights.
Why is correlational research conducted?
-Correlational research is conducted to establish a relationship between two variables and to observe how changes in one variable might correspond to changes in another.
What are the two aspects of correlation discussed in the script?
-The two aspects of correlation discussed are direction and magnitude. Direction refers to whether the relationship is positive, negative, or zero, while magnitude refers to the strength of the relationship.
What does a positive correlation indicate?
-A positive correlation indicates that as one variable increases, the other variable also increases.
Can you provide an example of a positive correlation from the script?
-An example of a positive correlation given in the script is that as the amount of money increases, the level of happiness also increases.
What is a negative correlation?
-A negative correlation indicates that as one variable increases, the other variable decreases.
Can you give an example of a negative correlation from the script?
-An example of a negative correlation provided in the script is that the more classes one skips, the lower the exam scores will be.
What is meant by zero correlation?
-Zero correlation means there is no relationship between the two variables, so changes in one variable do not lead to any changes in the other.
What is the difference between correlation and causation?
-Correlation refers to the relationship between two variables, while causation implies a cause-and-effect relationship. Correlational research does not deal with cause and effect.
How does correlational research differ from experimental research?
-In correlational research, none of the variables under study are manipulated or changed; they are simply measured and observed. In contrast, experimental research involves manipulating variables to observe the effects.
What is the purpose of studying the magnitude in correlational research?
-Studying the magnitude in correlational research helps to understand how strongly related the variables are, which can be categorized as strong, weak, or zero correlation.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)