The 4 Conditionals (Stop Confusing Them)
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Teacher Mike explains the four main types of conditional sentences in English: zero, first, second, and third conditionals. The zero conditional is used for general truths, while the first conditional talks about real possibilities in the future. The second conditional discusses unlikely or imaginary situations, and the third conditional refers to hypothetical past scenarios. Mike provides clear examples for each type and emphasizes how conditional sentences help describe different time periods and situations, offering additional tips on using modal verbs and mixed conditionals.
Takeaways
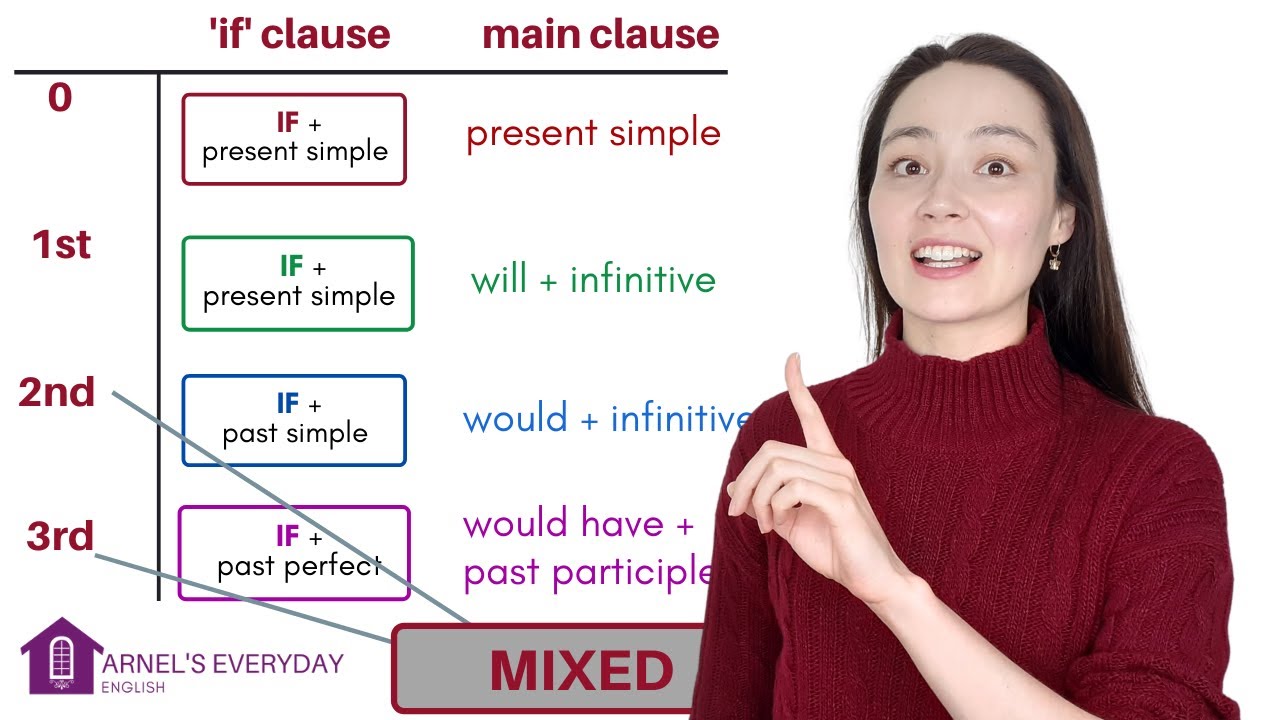
- 🔵 The first conditional is used for things that might realistically happen in the future. It follows the structure: 'If + present simple, will + verb.'
- 🟢 The second conditional is for unreal or unlikely situations, using 'If + past simple, would + verb.' It's used for imaginary scenarios.
- 🔴 The third conditional deals with imaginary situations in the past that didn’t happen, using 'If + past perfect, would have + past participle.'
- 🔵 The zero conditional expresses general truths or facts, following 'If + present simple, present simple.'
- 🟢 Conditionals can start with the 'If' clause or have the 'If' clause in the middle of the sentence, like 'If you mix red and yellow, you get orange,' or 'You get orange if you mix red and yellow.'
- 🔴 The past form 'were' is preferred over 'was' in the second conditional for formal grammar, like 'If I were you, I wouldn't do that.'
- 🔵 The first conditional often uses 'will,' but can also use other modal verbs like 'can,' 'could,' or 'should' depending on context.
- 🟢 Mixed conditionals describe how situations in different time periods influence each other, e.g., how something in the future affects the past.
- 🔴 The second conditional does not use 'will' because it’s meant for unreal situations. Instead, use 'would,' 'could,' or 'might.'
- 🔵 Verbs in conditionals can also use 'to be' with a noun, preposition, or adjective, e.g., 'If I call my mother, she will be happy.'
Q & A
What is the zero conditional used for?
-The zero conditional is used to talk about things that are always true or generally true, such as rules or facts.
How is the first conditional structured?
-The first conditional is structured as 'If + present simple, will + verb,' and is used to talk about things that might happen in the future.
Can other modal verbs be used in place of 'will' in the first conditional?
-Yes, other modal verbs like 'going to,' 'can,' 'could,' or 'should' can be used in the first conditional, depending on the context.
What is the main difference between the zero and first conditional?
-The zero conditional describes things that are always true, while the first conditional describes things that might happen in the future.
What is the second conditional used for?
-The second conditional is used to talk about unreal or very unlikely situations, often hypothetical or imaginary.
How do you structure a second conditional sentence?
-The second conditional is structured as 'If + past simple, would + verb,' and is used for unreal or unlikely situations.
Why shouldn't you use 'will' in the second conditional?
-'Will' is not used in the second conditional because it is for real situations, while the second conditional is for unreal or hypothetical scenarios.
What is an example of the third conditional?
-An example of the third conditional is, 'If you had invited me, I would have come,' meaning the invitation didn't happen, so the action didn't occur.
How do you structure a third conditional sentence?
-The third conditional is structured as 'If + past perfect, would have + past participle,' and is used for hypothetical situations in the past.
What are mixed conditionals used for?
-Mixed conditionals are used to talk about situations where one time period affects another, such as how something in the future impacts the past or vice versa.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

CONDITIONALS | Learn all the conditionals | English grammar

English Conditional Sentences (with examples!)

Conditional Sentence Dalam Bahasa Inggris
ALL CONDITIONALS | 0,1,2,3 and MIXED CONDITIONALS - English Grammar | if....

APRENDA TODAS AS CONDICIONAIS EM INGLÊS | Do Zero à Fluência

Conditional Sentences Type 0 1 2 3 | If Clause | Materi Bahasa Inggris Kelas 11 12
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
