Default Gateway Explained
Summary
TLDRThis video explains what a default gateway is and its role in network communication. The default gateway, usually a router, enables devices on one network to communicate with devices on another. Through a demonstration on Windows, the video shows how to check a network’s IP configuration. It also covers how devices use IP addresses and subnet masks to determine whether they are on the same or different networks, and when data needs to be forwarded through the default gateway. The video concludes with examples illustrating these concepts in action.
Takeaways
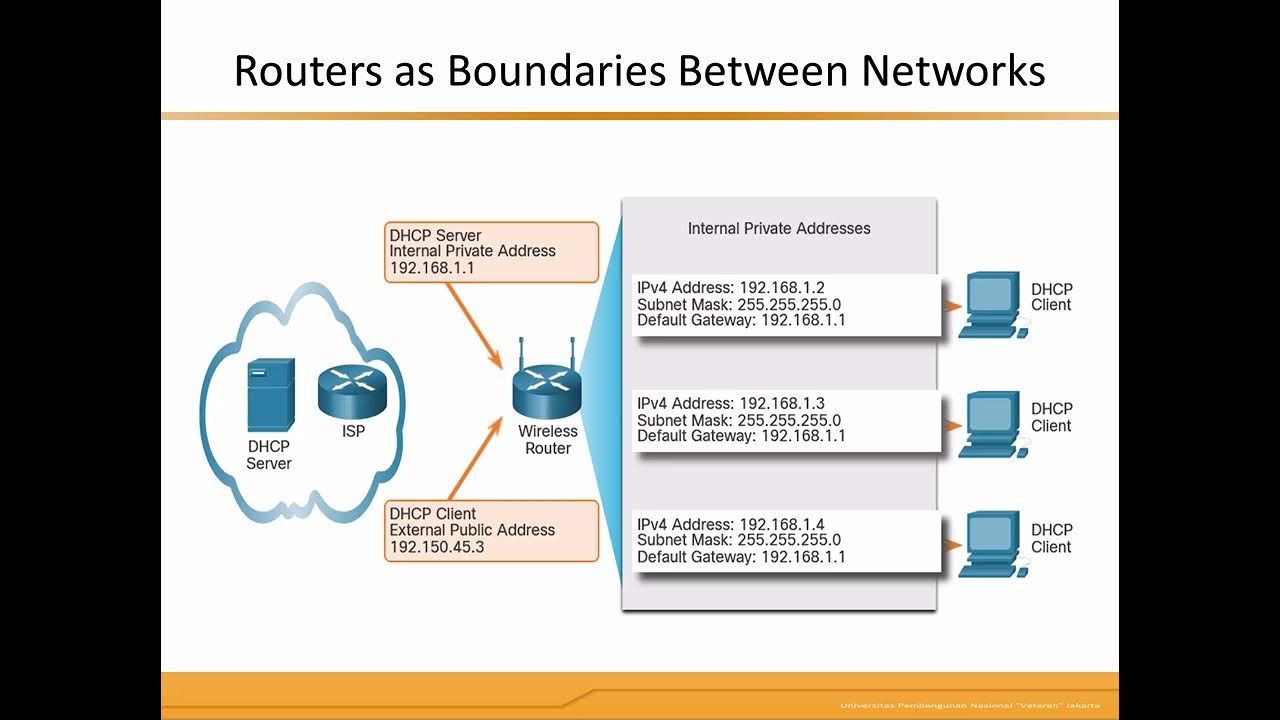
- 🌐 A default gateway is a device, typically a router, that forwards data from one network to another.
- 💻 On Windows, you can check the default gateway by opening a command prompt and typing 'ipconfig' to view network settings.
- 🚪 The default gateway acts as the doorway or first point of contact for devices on a network that need to communicate with devices on a different network.
- 🔀 Devices on the same network communicate directly through a switch, bypassing the default gateway.
- 🧭 To determine if another device is on the same network, computers use the IP address and subnet mask to identify the network and host portions.
- 🔢 The subnet mask helps distinguish the network portion of an IP address by aligning the '1's in the subnet mask with the corresponding bits in the IP address.
- 🤝 Computers on the same network communicate directly using their MAC addresses, found via ARP broadcasts.
- 🛑 ARP broadcasts are limited to the local network and cannot pass through a router, requiring the use of the default gateway for cross-network communication.
- 🔀 When two devices are on different networks, the default gateway routes the data between them.
- 🌍 Each subnet has its own default gateway, ensuring communication across separate networks through the appropriate routing.
Q & A
What is a default gateway?
-A default gateway is a device, typically a router, that forwards data from one network to another.
How do you check the default gateway on a Windows computer?
-Open a command prompt, type 'ipconfig', and the output will display the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
Why is a router usually the default gateway?
-A router acts as the doorway between networks, allowing data to travel between local networks and the internet.
Can computers on the same network communicate without using a default gateway?
-Yes, if the computers are on the same network, they can communicate directly through a switch without using the default gateway.
How do computers determine if another device is on the same or a different network?
-They check the IP address and subnet mask. If the network portion of the IP addresses matches, the devices are on the same network.
What role does the subnet mask play in networking?
-The subnet mask helps identify which part of the IP address is the network portion and which is the host portion.
What happens if two computers are on different networks?
-They must communicate through the default gateway, as devices on different networks cannot directly exchange data.
How does a computer find another device's MAC address on the same network?
-The computer sends out an ARP broadcast asking for the MAC address of the device it wants to communicate with.
Why can't ARP broadcasts go past a router?
-ARP broadcasts are limited to the local network and cannot cross the router, which separates different networks.
What is the purpose of the default gateway when computers are on different networks?
-The default gateway allows communication between devices on different networks by routing data between them.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Everything Hosts do to speak on the Internet - Part 2 - Networking Fundamentals - Lesson 3
Gateways to Other Network

BGP Explained in detail || BGP Overview, Message Types, States || CCNA & CCNP

Apa itu DHCP ?

Connect to Router (Determining Router's Address)

Implementation of DHCP using Cisco Packet Tracer
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
