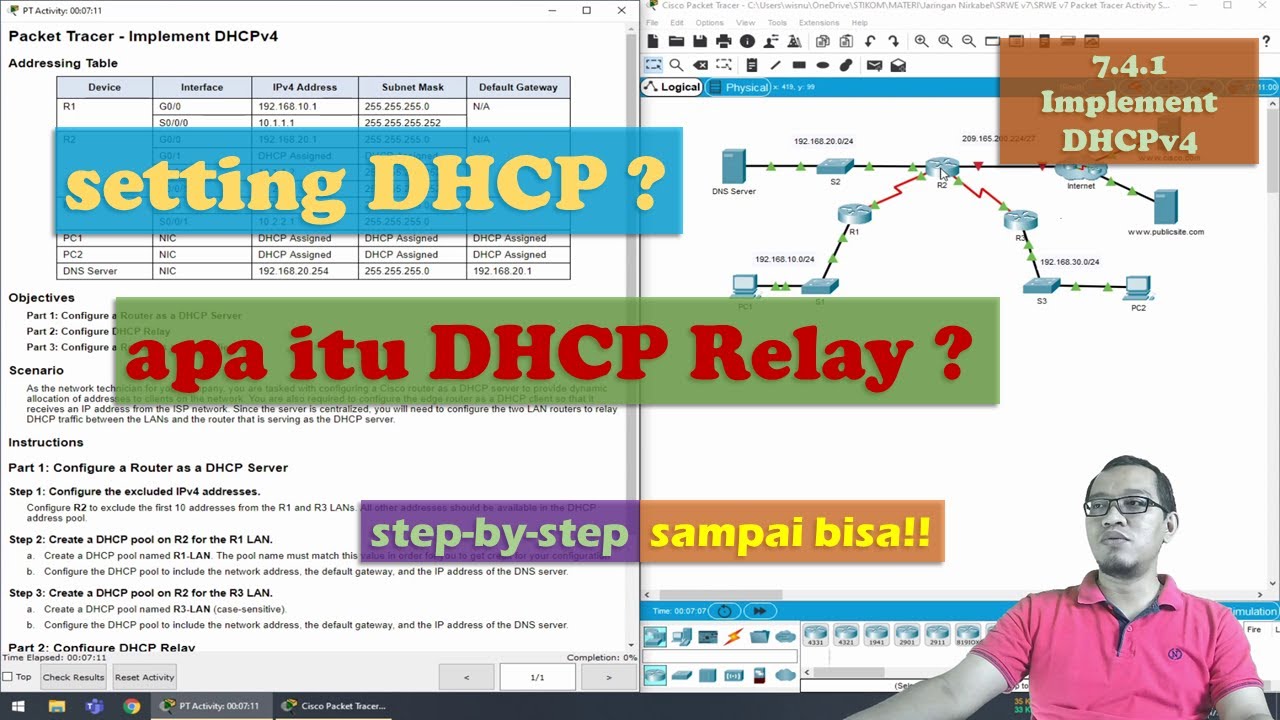
Apa itu DHCP ?
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the Digital Guru channel explains the importance of DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) in network connectivity. DHCP automates the process of assigning IP addresses to devices, along with essential network information like the default gateway and DNS servers. The video outlines the four main steps of DHCP — Discover, Offer, Request, and Acknowledgment — and explains how it simplifies network management, especially in large-scale environments. By eliminating manual configuration, DHCP ensures efficient IP address allocation, avoiding conflicts and optimizing network resources.
Takeaways
- 😀 DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, and it automates the assignment of IP addresses and network settings to devices on a network.
- 😀 Every time a device connects to a network, DHCP helps by providing it with an IP address along with other network details such as the default gateway, subnet mask, and DNS address.
- 😀 DHCP eliminates the need for manually assigning IP addresses, which can be time-consuming and error-prone, especially in large networks with many devices.
- 😀 There are four key steps in the DHCP process: Discover, Offer, Request, and Acknowledgment (ACK).
- 😀 The first step (DHCP Discover) occurs when a client device sends out a broadcast message to find a DHCP server on the network.
- 😀 In the second step (DHCP Offer), the DHCP server responds to the client with an available IP address offer.
- 😀 The third step (DHCP Request) happens when the client accepts the offer and requests the IP address from the server.
- 😀 The final step (DHCP Acknowledgment) involves the server confirming the IP address assignment, along with additional network settings.
- 😀 The DHCP server can either run on a home router or a dedicated server in a corporate network.
- 😀 DHCP assigns IP addresses temporarily through a lease system, and the client must renew the IP address lease once it expires or if the device disconnects from the network.
- 😀 By automating IP address assignment, DHCP reduces network configuration errors, saves time for administrators, and prevents IP address conflicts.
Q & A
What does DHCP stand for and what is its primary purpose?
-DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. Its primary purpose is to assign an IP address to a client device on a network and provide other network configuration details such as the default gateway, subnet mask, and DNS addresses.
How does DHCP work in terms of IP address assignment?
-DHCP works by providing a dynamic, temporary IP address to client devices through a four-step process: 1) DHCP Discover – the client looks for a DHCP server. 2) DHCP Offer – the server offers an IP address to the client. 3) DHCP Request – the client requests the offered IP address. 4) DHCP Acknowledgement – the server confirms the assignment and provides network details like the subnet mask and DNS.
What are the four main steps in the DHCP process?
-The four main steps in the DHCP process are: 1) DHCP Discover, where the client searches for a DHCP server. 2) DHCP Offer, where the server offers an IP address to the client. 3) DHCP Request, where the client accepts the offer. 4) DHCP Acknowledgement, where the server sends the IP address and configuration information to the client.
What is the role of the DHCP Discover message?
-The DHCP Discover message is sent by the client to broadcast its need for an IP address. This message is sent to all devices on the network, and the device acting as the DHCP server responds to it with an IP address offer.
Why is DHCP useful in large networks?
-DHCP is particularly useful in large networks because it automates the process of assigning IP addresses to many devices. Without DHCP, manually configuring IP addresses for hundreds or thousands of devices would be time-consuming and error-prone.
How does a client choose which IP address offer to accept?
-If multiple IP address offers are received, the client typically accepts the first offer it receives. The DHCP client then sends a DHCP Request to the server to confirm the selection.
What is the significance of the lease time in DHCP?
-The lease time is the duration for which the IP address is assigned to the client. Once the lease expires, the client must renew its IP address or be reassigned a new one. This prevents the waste of IP addresses by returning unused IPs to the available pool after the lease expires.
Can a DHCP server run on a router or access point?
-Yes, a DHCP server can run on a router or wireless access point, typically in home networks. However, in larger, corporate networks, DHCP services are often provided by dedicated servers.
What happens if a DHCP server is not available?
-If a DHCP server is not available, the client device will not be able to obtain an IP address and will be unable to connect to the network. In some cases, the device may default to a self-assigned IP address that is not valid for the network.
What is the purpose of the DHCP Offer message?
-The DHCP Offer message is sent by the server in response to a client's DHCP Discover message. It includes an available IP address and other necessary network configuration details, such as the subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server information.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)