Distance Formula | Introduction to Analytic Geometry|
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial introduces analytic geometry, focusing on the distance formula within the Cartesian coordinate system. It explains how to calculate the distance between two points using coordinates (x1, y1) and (x2, y2), applying the Pythagorean theorem. The formula d = √[(x2 - x1)² + (y2 - y1)²] is derived and demonstrated with sample problems, including a practical example and a reverse engineering approach to find the value of y when given a point and distance.
Takeaways
- 📚 Analytic geometry is a branch of mathematics that utilizes rectangular coordinates, also known as the Cartesian coordinate system.
- 🔍 The Cartesian coordinate system is named after René Descartes, who is considered the founder of analytic geometry.
- 📐 The distance formula is a fundamental concept in analytic geometry, used to calculate the distance between two points in a plane.
- 📈 The Cartesian coordinate plane consists of four quadrants, with the x-axis and y-axis being the intersecting lines that define these quadrants.
- 📍 A point in the coordinate plane is represented by its x and y coordinates, such as point P(x, y).
- 📝 The distance formula is derived from the Pythagorean theorem, which states that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
- 🧩 The formula for the distance (d) between two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) is given by \( \sqrt{(x2 - x1)^2 + (y2 - y1)^2} \).
- 🔢 The script provides a sample problem using the distance formula to calculate the distance between two points with given coordinates.
- 🔄 The script also discusses a reverse engineering approach to solving problems where the distance is given, and one needs to find the coordinates.
- 📉 The transcript includes a step-by-step guide on how to use a calculator to compute the distance between two points using the formula.
- 🔑 The final takeaway is a problem-solving example where the distance formula is used to find the value of 'y' when the coordinates of two points and the distance between them are known.
Q & A
What is analytic geometry?
-Analytic geometry is a branch of mathematics that uses a coordinate system to define and analyze geometric objects. It is also known as coordinate geometry or Cartesian geometry, named after René Descartes.
What is the Cartesian coordinate plane?
-The Cartesian coordinate plane is a two-dimensional plane that is defined by two perpendicular axes: the horizontal x-axis and the vertical y-axis. It is used to graph points and geometric shapes using ordered pairs of numbers.
What are the four quadrants of the Cartesian coordinate plane?
-The four quadrants of the Cartesian coordinate plane are numbered counterclockwise starting from the upper right. They are: the first quadrant (+,+), the second quadrant (-,+), the third quadrant (-,-), and the fourth quadrant (+,-).
What is the distance formula used for?
-The distance formula is used to calculate the distance between two points in a coordinate plane. It is derived from the Pythagorean theorem and is expressed as \( \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} \).
How is the distance formula derived?
-The distance formula is derived from the Pythagorean theorem by considering the coordinates of two points as the legs of a right triangle and the distance between the points as the hypotenuse.
What are the coordinates of point P mentioned in the script?
-The script does not provide specific coordinates for point P, but it describes point P as being represented by its coordinates (x, y) on the Cartesian coordinate plane.
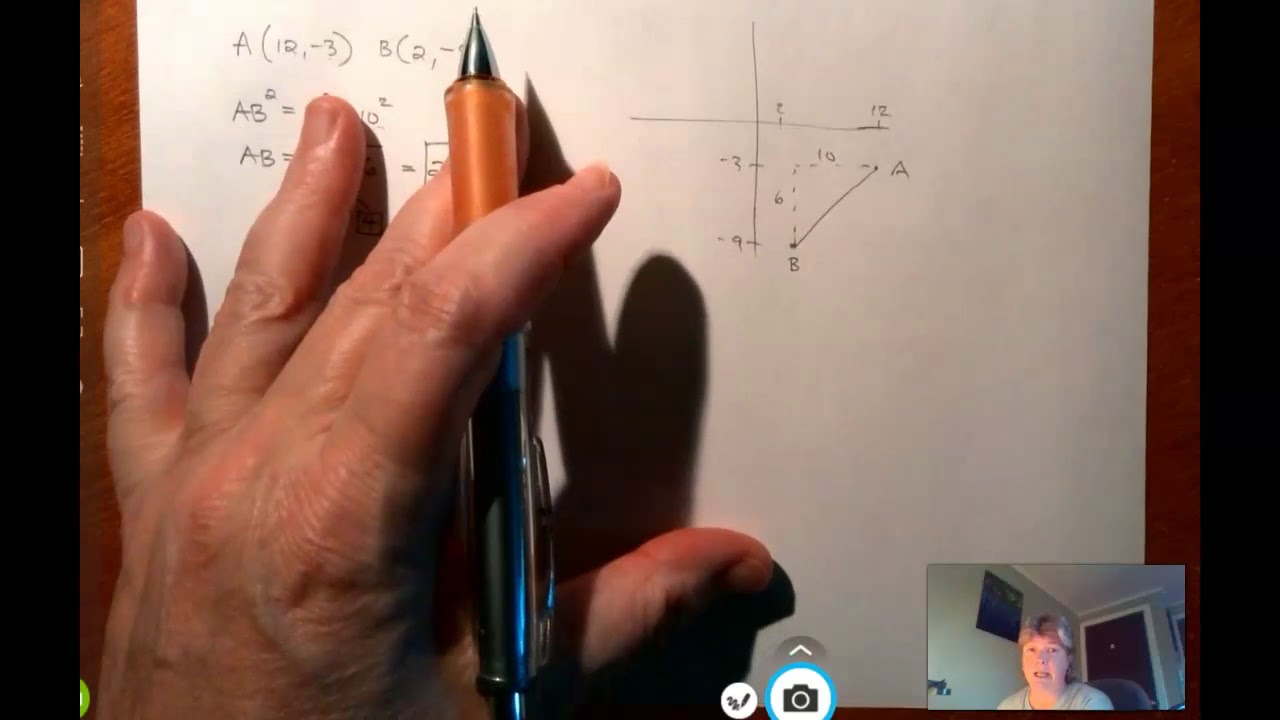
What is the purpose of the sample problem involving points A(-3, -2) and B(5, 5)?
-The purpose of the sample problem is to demonstrate how to use the distance formula to calculate the distance between two given points, A and B, in the Cartesian coordinate plane.
How is the distance between points A(-3, -2) and B(5, 5) calculated in the script?
-The distance is calculated using the distance formula: \( D = \sqrt{(5 - (-3))^2 + (5 - (-2))^2} \), which simplifies to \( D = \sqrt{8^2 + 7^2} \) and results in a distance of 10 units.
What is the second problem in the script about?
-The second problem involves finding the value of y in the point (3, y + 8) when the distance between this point and the point (7, y) is given as 13.
How is the value of y determined in the second problem?
-The value of y is determined by applying the distance formula to the given points and solving for y. The script suggests using reverse engineering from the given options to find the correct value of y, which is -5.
What is reverse engineering in the context of the second problem?
-Reverse engineering in this context refers to solving the problem by starting from the given distance and working backward to find the unknown variable, y, using the distance formula and the provided options.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
Distance and Midpoint

Cara Menghitung Jarak Antara Dua Titik Koordinat || Teorema Pythagoras Matematika Kelas 8
Questão de Geometria Analítica - equação da reta

APPLYING DISTANCE FORMULA TO PROVE GEOMETRIC PROPERTIES

Transformasi Geometri [Part 1] - Refleksi (Pencerminan)

Pensamiento Matemático II PROGRESION 11
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
