BACT/ALERT®: Blood Culture Collection: Winged Set Method
Summary
TLDRThe script outlines the critical steps for collecting blood cultures to diagnose sepsis, emphasizing the importance of proper disinfection, sufficient blood volume, and prompt transfer to the lab. It details the process from preparation, including confirming patient identity and using non-sterile gloves, to the actual collection, prioritizing aerobic bottles first. The summary also highlights the need for accurate labeling and mixing of the samples to ensure reliable test results.
Takeaways
- 🔍 Properly collected blood cultures are essential for accurate sepsis diagnosis and improving patient outcomes.
- 💉 Two sets of blood cultures should be obtained before administering antimicrobial agents.
- 📦 Ensure all materials, including culture bottles with lot numbers and expiration dates, are gathered and checked for quality.
- 🧼 Hand hygiene and the use of non-sterile examination gloves are crucial before starting the collection procedure.
- 🆔 Confirm the patient's identity and match the requested laboratory test and patient information to prevent errors.
- 🛡️ Prepare the collection materials in a clean area to minimize contamination.
- 🔄 Disinfect the blood culture bottles using an approved disinfectant and allow them to dry completely.
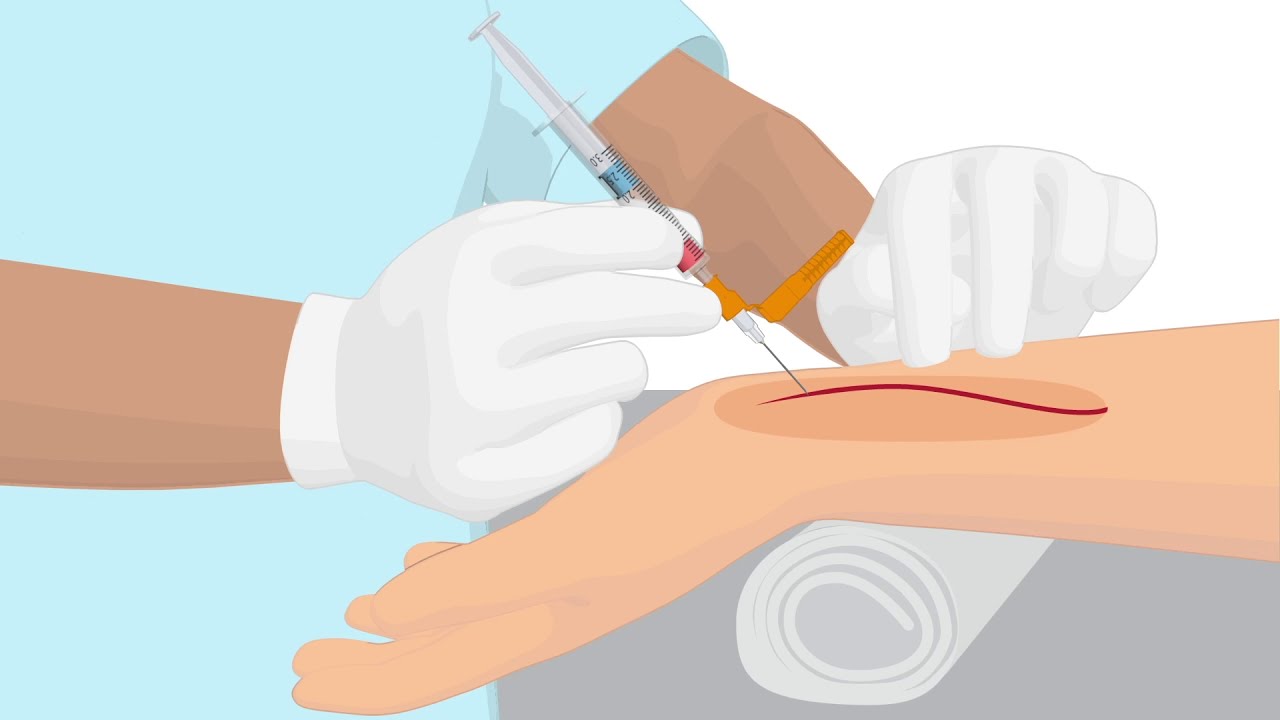
- 🩸 The arm is the recommended site for drawing blood cultures, and proper vein preparation is necessary.
- 🌐 Start with aerobic bottles first to avoid altering the anaerobe bottle's atmosphere with air from the tubing.
- 👶 For pediatric patients, a special pediatric aerobic bottle may be used with a specific inoculation volume.
- 💧 Use the fill-to mark to gauge the sample volume accurately, avoiding overfilling the bottles.
- 🔄 Mix blood culture bottles and tubes by inverting to ensure proper mixing.
- 🏷️ Properly label the bottles with all necessary information and ensure barcodes and level check windows are visible.
- 🚫 Dispose of all used materials correctly and promptly transfer inoculated culture bottles to the laboratory.
Q & A
Why is a properly collected blood culture important for sepsis patients?
-A properly collected blood culture is crucial for sepsis patients because it helps ensure accurate results that can improve patient outcomes by identifying the causative organisms and guiding appropriate antimicrobial therapy.
How many blood culture sets should be obtained for patients with suspected sepsis?
-Two blood culture sets should be obtained as soon as possible and before antimicrobial agents are administered to increase the chances of detecting the causative pathogen.
What should be checked before using the blood culture bottles?
-Before using the blood culture bottles, one should check the expiration date, ensure the media is not turbid or showing any visible defects, and confirm that the bottles are not damaged, deteriorated, or leaking.
Why is it necessary to wash hands or use an alcohol rub before starting the blood collection procedure?
-Washing hands or using an alcohol rub is necessary to minimize the risk of introducing contaminants into the blood culture, which could lead to false-positive results or culture contamination.
How should the patient's identity be confirmed during the blood culture collection process?
-The patient's identity should be confirmed by matching the requested laboratory test and patient information with the patient's identity, either using a printed label form or a mobile device.
What is the recommended site for drawing a blood culture?
-The arm is the recommended site for drawing a blood culture, as it is typically more accessible and less likely to be contaminated.
Why is it important to disinfect the chosen puncture site before inserting the needle?
-Disinfecting the puncture site is important to reduce the risk of introducing skin flora or other contaminants into the bloodstream, which could compromise the accuracy of the blood culture.
What should be done if the anaerobic bottle is collected first instead of the aerobic bottle?
-If the anaerobic bottle is collected first, the air in the tubing could alter the anaerobic environment, potentially affecting the culture's accuracy. Therefore, the aerobic bottle should always be collected first.
How much blood should be inoculated into the aerobic bottle for an adult patient?
-For an adult patient, 10 mL of blood should be inoculated into the aerobic bottle, as indicated by the fill-to mark on the bottle.
What should be done after collecting the blood samples to ensure proper mixing?
-After collecting the blood samples, the culture bottles and tubes should be gently mixed by inverting them 3 to 5 times to ensure proper mixing of the blood with the culture media.
How should the blood culture bottles be labeled after collection?
-The blood culture bottles should be labeled using the dedicated area on the bottle. If using a test label, it should be placed vertically with the same orientation as the bottle barcode, ensuring no coverage of the barcode, fill-to mark, or the window to check the blood level.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)