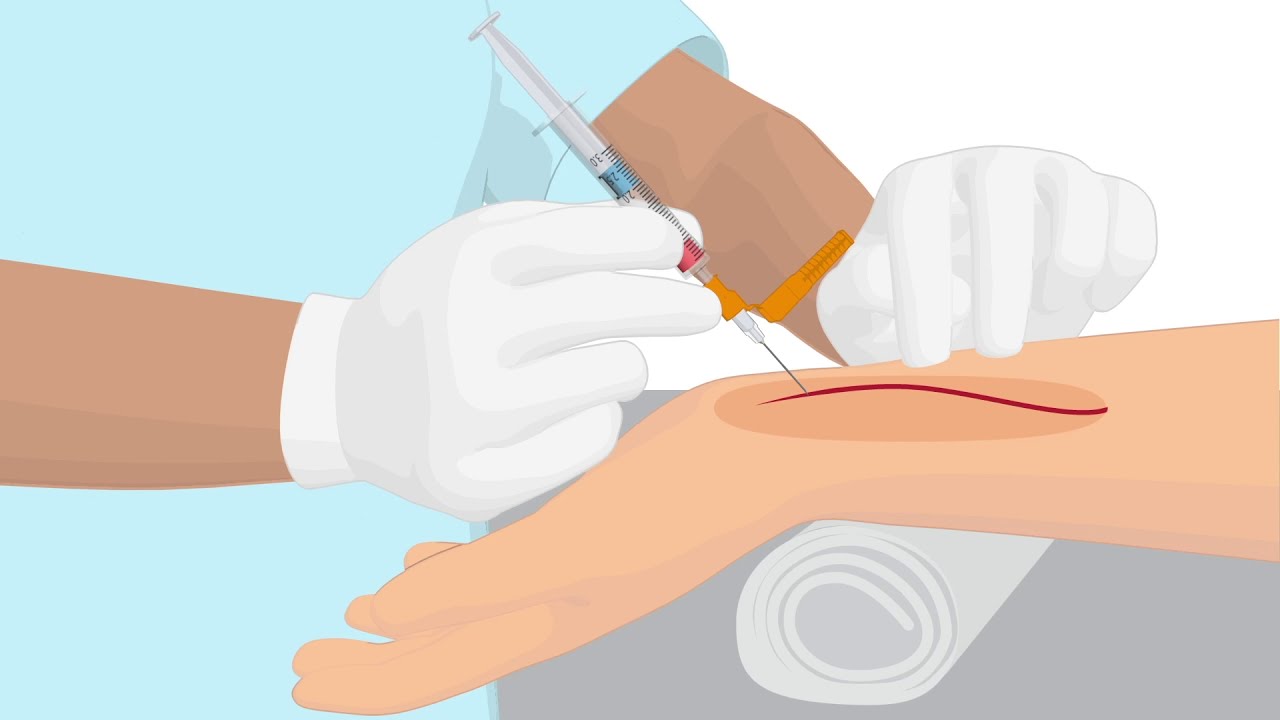
Perform a Venipuncture Collect a Venous Blood Sample Using the Vacuum Tube Method
Summary
TLDRThis instructional video script outlines the steps for collecting a venous blood specimen using the vacuum tube technique. It emphasizes the importance of verifying patient identity, explaining the procedure, and obtaining consent. The process includes selecting the appropriate arm and vein, applying a tourniquet, and performing the venipuncture with a needle and vacuum tubes. The script also covers safety measures, such as releasing the tourniquet before needle removal, applying pressure to the puncture site, and proper disposal of materials. Finally, it details labeling and documenting the procedure, ensuring a comprehensive guide for blood collection.
Takeaways
- 📝 Always read the provider's order and clarify any questions before starting the procedure.
- 🧪 Gather the appropriate tubes and supplies as specified on the requisition form.
- 🥼 Wear a fluid-impermeable lab coat and other necessary personal protective equipment.
- 🔍 Verify the patient's identity using at least three identifiers to ensure accuracy.
- 🗣️ Communicate clearly with the patient, explaining the procedure and obtaining their permission.
- 👀 Use protective eyewear and maintain hand hygiene to prevent contamination.
- 💉 Choose the arm for venipuncture based on the patient's preference and the visibility of veins.
- 🩸 Apply the tourniquet correctly, without restricting arterial blood flow, and for no longer than 60 seconds.
- 📍 Locate the venipuncture site by palpating the antecubital space and selecting the most suitable vein.
- 🌡️ Prepare the site by cleansing it with an alcohol pad and assembling equipment on the non-dominant side.
- 💉 Use the correct needle size and technique for inserting the needle into the vein at the appropriate angle.
- 🧴 Fill the vacuum tubes one by one, ensuring not to change the needle's position in the vein during this process.
- 🩹 After the last tube is filled, release the tourniquet and apply pressure to the puncture site.
- 🗑️ Dispose of all used materials properly, including the needle in a sharps container and biohazard waste.
- 🏷️ Label the tubes with patient information, date, time, and initials, and complete the requisition form.
- 📋 Document the procedure in the patient's record for future reference and compliance.
Q & A
What is the first step in the procedure described in the script?
-The first step is to read the provider's order and clarify any questions with the provider.
What are the necessary supplies for collecting a venous blood specimen using the vacuum tube technique?
-The necessary supplies include the appropriate tubes as specified on the requisition form, a fluid impermeable lab coat, protective eyewear, gloves, a tourniquet, an alcohol pad, and a sharps container for disposal.
How should the medical assistant verify the patient's identity?
-The medical assistant should verify the patient's identity using three identifiers such as full name, date of birth, and the spelling of the last name or by checking a photo ID.
What does the medical assistant need to explain to the patient before starting the procedure?
-The medical assistant needs to explain the procedure of venipuncture and obtain the patient's permission for the blood draw.
Why is it important to check both arms of the patient before selecting a venipuncture site?
-It is important to check both arms to find the vein that will give the greatest chance of success for the blood draw.
What is the proper way to apply a tourniquet during venipuncture?
-The tourniquet should be applied around the patient's arm, three to four inches above the elbow, without restricting blood flow in the artery, and should not remain in place longer than 60 seconds.
How should the venipuncture site be prepared before needle insertion?
-The site should be cleansed starting in the center and working outward in a circular pattern with an alcohol pad.
What is the recommended angle for needle insertion into the vein during venipuncture?
-The recommended angle for needle insertion is 15 to 20 degrees.
How should the vacuum tube be filled with blood?
-The tube should be filled to its maximum capacity without changing the needle's position in the vein, and the tube should be gently inverted immediately after removal to mix the additives and blood.
What should be done after the last tube is filled and the tourniquet is released?
-The last tube should be removed from the holder, and the needle should be quickly removed from the arm while applying pressure to the puncture site with gauze or a cotton ball.
What are the final steps after the blood draw is completed?
-The final steps include labeling the tubes, checking the venipuncture site for bleeding, applying a bandage, disposing of blood-contaminated materials, disinfecting the work area, removing and disposing of gloves and protective eyewear, and documenting the procedure in the patient's record.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)