Layers of the Earth 🌎 | Crust, Mantle, Outer Core, Inner Core | Educational Science Lesson & Quiz
Summary
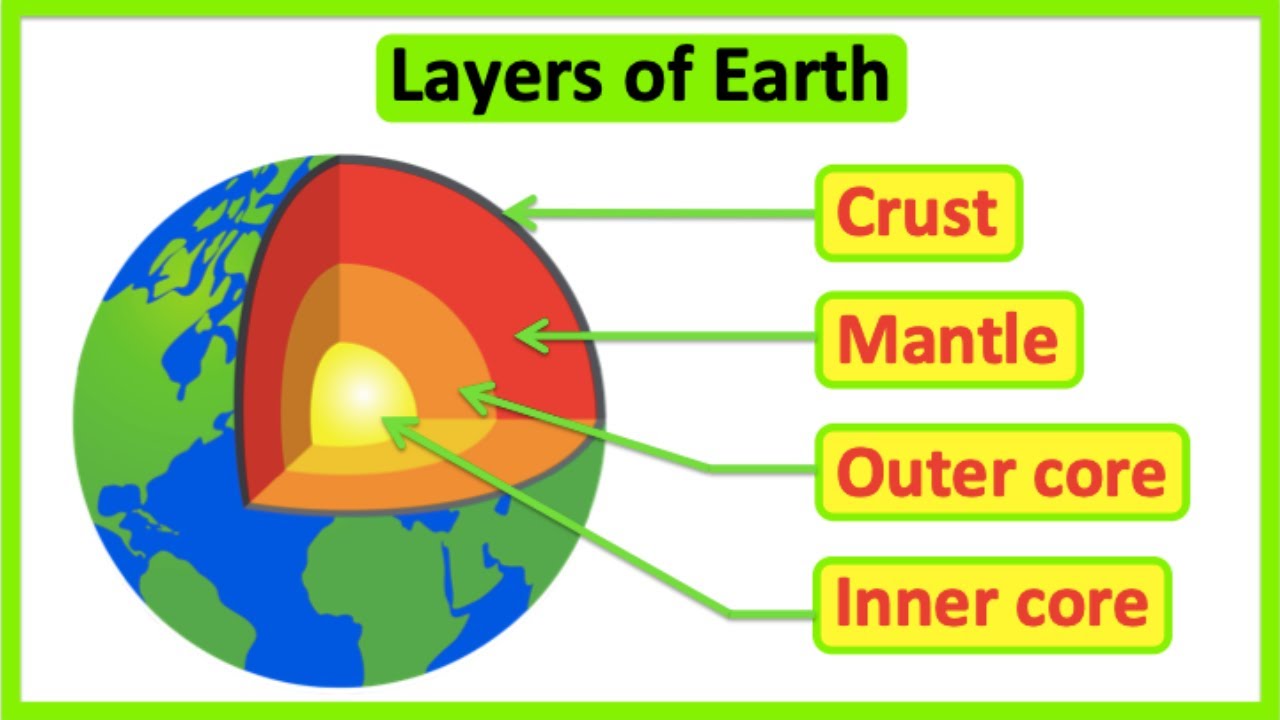
TLDRThis video script delves into the Earth's structure, highlighting its four main layers: the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core. The crust, our solid rock surface, varies in thickness from 15-25 km for continental to 5-10 km for oceanic. Beneath lies the mantle, a 2,900 km thick layer of hot, solid rock and magma, contributing to 85% of Earth's mass. The outer core, 2,200 km thick, consists of liquid iron and nickel, while the inner core, the hottest part, is a solid sphere of iron and nickel under extreme pressure, approximately 1,200-1,500 km thick. The script explains the dynamic nature of tectonic plates and the role of magma in volcanic activity.
Takeaways
- 🌏 The Earth is composed of four main layers: the crust, the mantle, the outer core, and the inner core.
- 📏 The crust is the thin outer layer, varying in thickness from 15 to 25 km, with continental crust being thicker than oceanic crust.
- 🌍 There are two types of crusts: continental and oceanic, with the continental crust being approximately 25 km thick and the oceanic crust about 5 km thick.
- 🧩 The crust is divided into tectonic plates that move slowly, causing earthquakes when they interact.
- 🔥 The mantle is the thickest layer, making up about 85% of Earth's mass and is composed of hard, hot, and partially molten rock.
- 🌋 Magma, found within the mantle, can cause volcanic eruptions when it pushes through the crust.
- 🌡 The outer core surrounds the inner core and is a liquid layer composed of iron and nickel, both metals.
- ☀️ The inner core, made of iron and nickel, is the hottest part of the Earth, nearly as hot as the Sun's surface.
- 🏔️ The extreme pressure at the Earth's center turns the molten iron and nickel of the inner core into a solid state.
- 📐 The inner core is estimated to be between 12,000 to 15,000 km thick.
- 🌌 To summarize, the Earth's layers are characterized by the solid rock crust, the magma-rich mantle, the liquid outer core, and the solid inner core.
Q & A
What are the four main layers of the Earth?
-The four main layers of the Earth are the crust, the mantle, the outer core, and the inner core.
How many types of crust are there and what are they?
-There are two types of crust: continental crust and oceanic crust.
What is the approximate thickness of the Earth's crust?
-The crust is about 15 to 25 km thick, with continental crust being approximately 25 km thick and oceanic crust about 5 km thick.
What is the crust made up of and what is its role?
-The crust is made up of solid rock, soil, and everything else we can find on the Earth's surface. It serves as the solid layer that we live on.
How are the Earth's crust and tectonic plates related?
-The crust is broken into plates, known as tectonic plates, which move around very slowly, causing earthquakes when they interact.
What is the mantle's composition and its proportion of the Earth's mass?
-The mantle is made up of very hard rocks and hot solid rocks, including magma. It makes up about 85% of the total mass of the Earth.
How thick is the mantle layer of the Earth?
-The mantle is about 2,900 km thick.
What causes volcanic eruptions and what is magma?
-Volcanic eruptions are caused by magma pushing through holes or cracks in the crust. Magma is liquid or semi-liquid rock found within the Earth's surface.
What are the main components of the outer core?
-The outer core is made up of very hot liquid iron and nickel.
How is the inner core different from the outer core?
-The inner core is solid due to extreme pressure, even though it is nearly as hot as the surface of the Sun, and is also composed of iron and nickel.
What is the approximate thickness of the inner core?
-The inner core is about 12 to 1,500 km thick.
Why does the inner core remain solid despite its high temperature?
-The inner core remains solid due to the extreme pressure at the center of the Earth, which counteracts the heat.
How do the Earth's layers relate to geological activities such as earthquakes and volcanic eruptions?
-The movement of tectonic plates within the crust can cause earthquakes, and the movement of magma from the mantle can lead to volcanic eruptions when it reaches the surface as lava.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
Layers of the Earth | Structure of the Earth | Educational Science Lesson

Mexus education

Penjelasan Lengkap Struktur Lapisan Bumi dan Karakteristiknya
INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH | Unit 1 Module 2 - Grade 10 Science Lesson | MELC-Based [TEACH]

Materi Dinamika Litosfer (Lapisan Bumi) : Materi Geografi SMA dan SIMAK UI | Part 1

Layers of the Earth-5.23 - Earth Science for Kids!
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
