Never Miss A Percentage Question On The SAT: The Three Setups You MUST Know
Summary
TLDRThis educational video focuses on solving percent increase and decrease problems, a common and challenging question type on the SAT's calculator section. The instructor introduces a straightforward method using '1 plus or minus the percentage as a decimal' to simplify calculations. Examples include project duration adjustments due to weather, tomato yield comparisons, and sequential price changes of a painting. The video emphasizes the importance of understanding the framework of these problems to tackle them efficiently, offering a valuable strategy for students preparing for the SAT.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video focuses on solving percent increase and decrease questions, which are often among the most challenging on the SAT's calculator section.
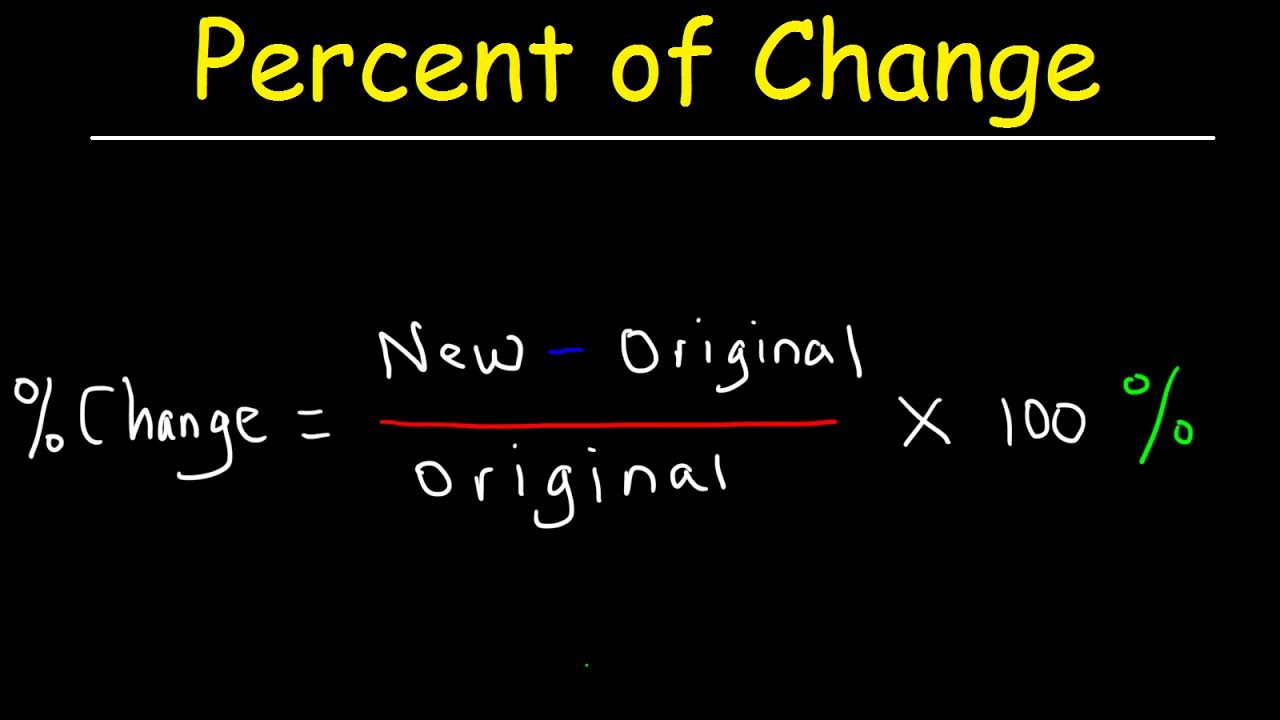
- 🔢 Percent increase or decrease problems can be approached by using the formula of '1 plus or minus the percentage expressed as a decimal'.
- 🛠️ For an increase, multiply the original amount by '1 plus the percentage as a decimal', and for a decrease, divide by '1 minus the percentage as a decimal'.
- 🌨️ An example problem involves Jarvis Construction Company, which initially planned for a project to take 250 days but expected it to take 12% longer due to bad weather.
- 🚀 The video suggests a shorthand method for students to quickly grasp the concept of percent increase and decrease, making it easier to solve complex problems.
- 🔄 The concept of 'percent reversal' is introduced, where the task is to undo a percent change that has already occurred, using division to find the original amount.
- 🎨 Multiple percent changes in a sequence are also discussed, with the emphasis on applying the '1 plus or minus' framework to each change before multiplying the results.
- 📉 The video explains how to calculate the original price of an item after it has undergone a series of price changes, using multiplication of the adjusted values.
- 📈 The difference from 1 in the final calculated value represents the overall percent increase or decrease from the original value.
- 📝 The script provides a step-by-step method for solving SAT questions involving percent changes, including simplifying expressions to find the original quantity.
- 🔑 The importance of understanding the '1 plus or minus' framework is highlighted as a key to solving a variety of percent increase and decrease problems on the SAT.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The main topic of the video is teaching how to solve percent increase and decrease problems, which often appear as difficult questions on the SAT calculator section.
Why are percent increase and decrease questions considered difficult on the SAT?
-Percent increase and decrease questions are considered difficult because they often appear as the last multiple-choice questions (29 and 30) on the SAT calculator section, and they require a specific approach to solve efficiently.
What is the basic formula used for percent increase and decrease problems?
-The basic formula used for percent increase and decrease problems is to multiply or divide by one plus or minus the percent change expressed as a decimal.
How does the video suggest simplifying the approach to percent increase problems?
-The video suggests simplifying the approach by using the shorthand method of 'one plus or minus the percent expressed as a decimal' to quickly calculate the changes.
What is an example of a percent increase problem presented in the video?
-An example given is Jarvis Construction Company's project initially estimated to take 250 days but expected to take 12 percent longer due to bad weather, which simplifies to 250 days multiplied by 1.12 to get 280 days.
How does the video handle percent decrease problems?
-For percent decrease problems, the video suggests dividing the final amount by one minus the percent decrease expressed as a decimal to find the original amount.
What is the concept of 'percent reversal' mentioned in the video?
-'Percent reversal' refers to problems where you are given the amount after a percent change has occurred, and you need to reverse the process to find the original amount.
Can you explain the strategy for solving problems with multiple percent changes in a row?
-The strategy involves multiplying the original amount by a series of 'one plus or minus the percent change' factors for each change, and then interpreting the final result as a percentage increase or decrease from the original.
What is the common mistake students make with percent increase and decrease problems according to the video?
-The common mistake students make is not correctly applying the 'one plus or minus' framework, which leads to incorrect calculations of the final percentage change.
How does the video suggest using the framework for recent SAT examples?
-The video suggests applying the 'one plus or minus' framework to recent SAT examples by setting up the equation based on the given information and solving for the original or final amount as required by the question.
What is the purpose of the video's suggestion to plug in numbers for testing understanding?
-The purpose of plugging in numbers is to test and reinforce understanding of the framework by using concrete values to verify the calculations and results.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)