FACTORING USING COMMON MONOMIAL FACTOR || GRADE 8 MATHEMATICS Q1
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Monica explains how to find the greatest common factor (GCF) of numbers and polynomials using methods like listing and prime factorization. She covers the definition and examples of monomials, polynomials, and the process of factoring polynomials using the distributive property. Through detailed examples, Monica demonstrates step-by-step procedures to determine the GCF and factor polynomials completely. The video aims to enhance understanding of these mathematical concepts, making it easier for viewers to solve related problems.
Takeaways
- 📘 Understanding how to find the Greatest Common Factor (GCF) of polynomials.
- 📊 Two methods to find the GCF: Listing factors and Prime Factorization.
- 🔢 Explanation of monomials and polynomials, including their components like constants and variables.
- 🧩 Importance of arranging polynomials in standard form for easier factoring.
- 🧮 Definition of GCF: The greatest numerical factor with variables having the least degree.
- 🔍 Step-by-step example of finding GCF by listing factors and using prime factorization.
- 📐 Factoring pairs of monomials using prime factorization to identify common factors.
- 🔗 Applying the distributive property to factor polynomials using the GCF.
- 📈 Detailed examples of factoring various polynomials using GCF and distributive property.
- 📝 Rewriting polynomials as products of smaller degree polynomials for simpler solutions.
Q & A
What is the greatest common factor (GCF)?
-The greatest common factor (GCF) is the largest number that divides two or more numbers without leaving a remainder.
How can we find the GCF by listing factors?
-To find the GCF by listing factors, list all the factors of each number, then identify the largest factor that appears in each list.
What is prime factorization?
-Prime factorization involves breaking down a number into its prime factors, which are prime numbers that multiply together to give the original number.
How do we use prime factorization to find the GCF?
-To use prime factorization to find the GCF, break down each number into its prime factors, then identify the common prime factors and multiply them together.
What is a monomial?
-A monomial is a type of polynomial that has only one term, which can be a constant, a variable, or the product of constants and variables.
How do we factor polynomials using the GCF?
-To factor polynomials using the GCF, first find the GCF of all the terms in the polynomial, then divide each term by the GCF and write the polynomial as the product of the GCF and the resulting polynomial.
What is the standard form of a polynomial?
-The standard form of a polynomial is when its terms are arranged in descending order of their degrees, from highest to lowest.
How do you determine the GCF of monomials with variables?
-To determine the GCF of monomials with variables, find the GCF of the numerical coefficients and the lowest power of each common variable.
What is the distributive property?
-The distributive property states that a(b + c) = ab + ac, which allows us to factor out a common factor from a polynomial.
How do you use the distributive property to factor polynomials?
-To use the distributive property to factor polynomials, find the GCF of the terms, factor it out, and write the polynomial as the product of the GCF and the remaining polynomial.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
How to Find the LCM (2 Different Ways) | Least Common Multiple | Math with Mr. J

Factoring Polynomials using Greatest Common Monomial Factor

GCF: Greatest Common Factor - Math Antics Extras
Greatest Common Factor | How to Find the Greatest Common Factor (GCF)

VIDEO TATA CARA PENGGUNAAN CONGKLAK KPK & FPB
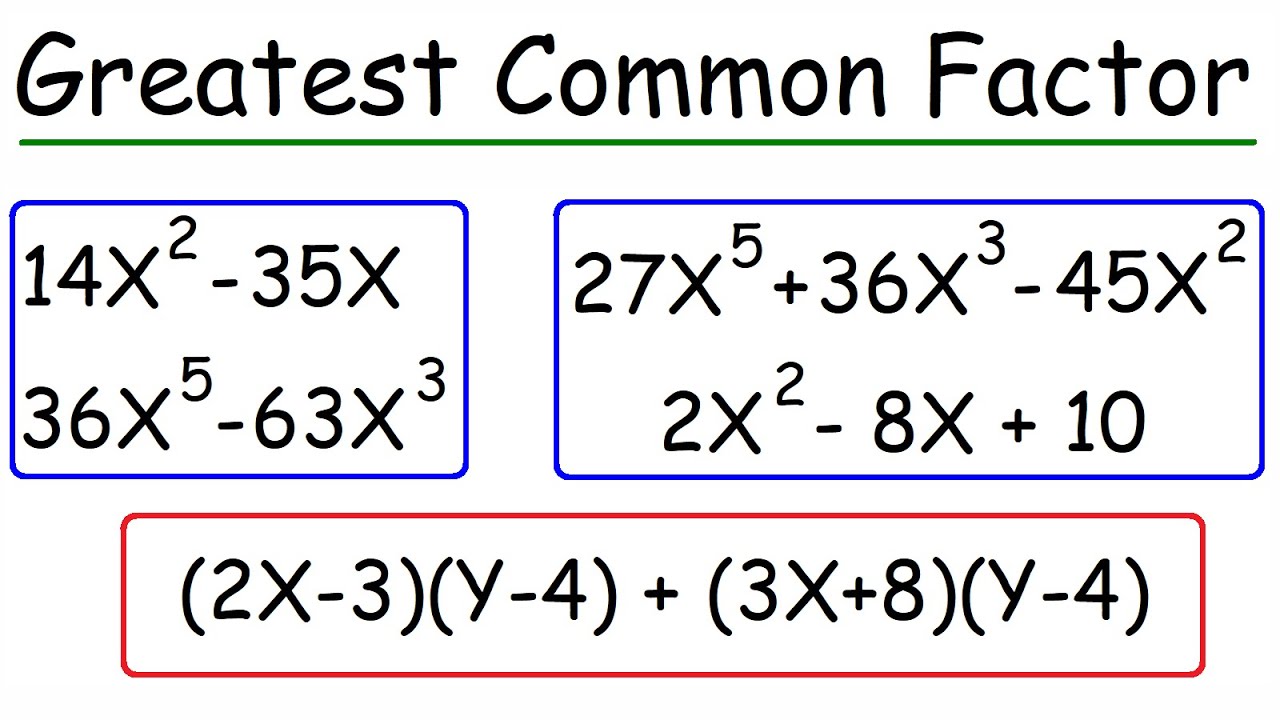
How To Factor The Greatest Common Factor In a Polynomial | Algebra
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
