Single Phase Induction Motor, How it works ?
Summary
TLDRThe script explains the working principle of single-phase induction motors, which operate with a single power phase and are common in domestic and industrial settings. It details the main components, including the rotor, stator winding with main and auxiliary windings, and the role of a capacitor. The script delves into the double revolving field theory, where the fluctuating field in the motor induces electricity in the rotor bars, creating torque. It highlights Nikola Tesla's ingenious solution using an auxiliary winding and capacitor to provide the initial rotation needed for the motor to start and continue operating, with a centrifugal switch eventually cutting the auxiliary winding once the motor reaches speed.
Takeaways
- 🔌 Single-phase induction motors operate with just one power phase and are common in both domestic and industrial settings.
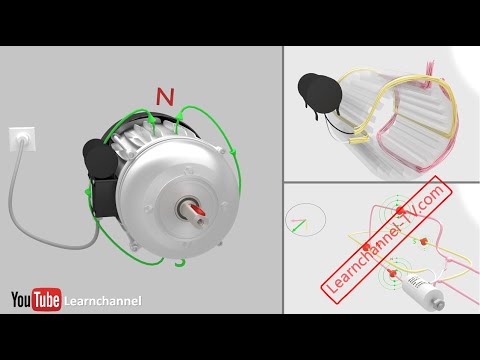
- 🌀 The main components of a single-phase motor include a rotor, a stationary stator winding with two parts (main and auxiliary windings), and a capacitor connected to the auxiliary winding.
- ⚙️ The auxiliary winding is positioned perpendicular to the main winding to create a different magnetic field interaction.
- 🧲 When no current flows through the auxiliary winding, the AC current in the main winding generates a fluctuating magnetic field.
- 🔄 The concept of the double revolving field theory explains that the fluctuating field is equivalent to the sum of two oppositely rotating magnetic fields.
- 🌀 The rotor will continue to rotate in the same direction due to the effect of the fluctuating field, which is a result of the double revolving field theory.
- 🌐 Electromagnetic induction causes electricity to be induced in the rotor bars when they are within the varying magnetic field, leading to a force that starts the rotor's rotation.
- 🔄 Initially, the rotor experiences equal and opposite torques from the two magnetic fields, resulting in no net torque and preventing the rotor from starting.
- 🚀 Providing an initial rotation to the rotor allows one torque to dominate, creating a net torque in the direction of the initial rotation, which starts the motor.
- 💡 Nikola Tesla's ingenious solution to the starting problem involves using the auxiliary winding and capacitor to cancel one of the rotating fields, allowing the motor to start.
- 🔄 Once the rotor reaches a specific speed, the motor can continue to operate even if the auxiliary winding is disconnected, thanks to a centrifugal switch.
Q & A
What is a single-phase induction motor and what is its primary use?
-A single-phase induction motor is a type of electric motor that operates with just one power phase. It is commonly used in both domestic and industrial applications.
What are the main components of a single-phase induction motor?
-The main components of a single-phase induction motor include a rotor, which is the rotating part, and a stator winding, which is stationary and consists of two parts: a main winding and an auxiliary winding.
How is the auxiliary winding positioned in relation to the main winding?
-The auxiliary winding is placed perpendicular to the main winding.
What role does a capacitor play in the auxiliary winding of a single-phase induction motor?
-A capacitor is connected in the auxiliary winding to help provide an initial starting torque to the motor by creating a rotating magnetic field that can initiate the rotor's rotation.
Why is it important for the rotor to be initially rotating for the motor to work properly?
-The initial rotation is important because it allows one of the torques produced by the oppositely rotating magnetic fields to be greater than the other, resulting in a net torque that keeps the rotor rotating in the same direction.
What is the double revolving field theory and how does it relate to the operation of a single-phase induction motor?
-The double revolving field theory refers to the concept that a fluctuating magnetic field is equivalent to the sum of two oppositely rotating magnetic fields. This theory is crucial for understanding how a single-phase induction motor can generate a net torque to start and maintain rotation.
How does electromagnetic induction affect the rotor bars in a single-phase induction motor?
-Electromagnetic induction causes electricity to be induced in the rotor bars due to the varying magnetic field. This induced current in the current-carrying bars, when immersed in the magnetic field, produces a force that causes the rotor to start rotating.
What problem does Nikola Tesla's solution address in single-phase induction motors?
-Nikola Tesla's solution addresses the problem of providing an initial rotation to the rotor, which is necessary for the motor to start and generate a net torque in the direction of rotation.
How does the auxiliary winding with a capacitor arrangement help start the motor?
-The auxiliary winding with a capacitor arrangement produces a magnetic field that can cancel one of the rotating fields from the main winding, allowing the other to create a single revolving magnetic field that provides the necessary starting torque.
What is the purpose of a centrifugal switch in a single-phase induction motor?
-A centrifugal switch is used to automatically cut the auxiliary winding once the rotor has attained a specific speed, allowing the motor to continue operating efficiently without the need for the auxiliary winding's contribution.
What happens to the motor after the rotor reaches a specific speed and the auxiliary winding is cut?
-After the rotor reaches a specific speed and the auxiliary winding is cut, the motor will continue to rotate due to the established rotating magnetic field and the inertia of the rotor.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

AC MOTORS AND GENERATORS

PERBEDAAN ANTARA LISTRIK 1 PHASE DAN LISTRIK 3 PHASE | PASTI BANYAK YANG BELUM PAHAM INI

Single phase Induction Motor / Capacitor start capacitor run motor / Capacitor start induction motor

5 Formulas Electricians Should Have Memorized!
Single Phase Induction Motor (Capacitor Induction Motor or AC Motor) explained

energy meter | energy meter working principle | single phase induction type energy meter | in hindi
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
