Plant Nutrition: Mineral Absorption | Part 3
Summary
TLDRThe video script delves into the critical role of mineral absorption in plant nutrition, highlighting the significance of nitrate and magnesium ions. It explains the concept of 'essential mineral elements' introduced by Arnon and Stout in 1939, emphasizing their irreplaceability and direct involvement in plant metabolism. Nitrogen, crucial for protein synthesis and other vital processes, is absorbed as nitrate or ammonium, particularly in aerobic soils. Magnesium, integral to chlorophyll and enzyme activation, plays a pivotal role in photosynthesis, respiration, and nucleic acid synthesis. The script underscores the indispensable nature of these nutrients for plant growth and life cycle completion.
Takeaways
- 🌱 The term 'essential mineral element' was introduced by Arnon and Stout in 1939, defining three main criteria for an element's essentiality in plant life.
- 🔍 An element is considered essential if the plant cannot complete its life cycle without it, it is irreplaceable, and it plays a direct role in the plant's metabolism.
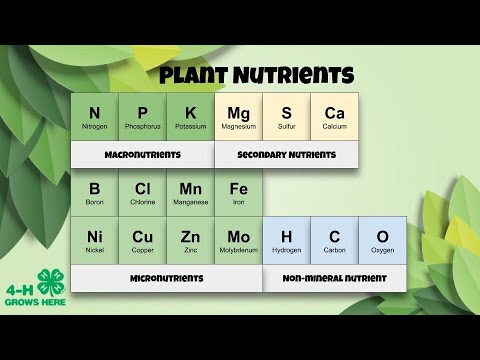
- 🌿 There are at least 17 essential nutrients required by plants, with nitrate and magnesium being two of the most critical.
- 🌿 Nitrogen is an essential element for plant growth, but it must be absorbed in the form of nitrate or ammonium, as plants cannot take it directly from the atmosphere.
- 🌱 In aerobic soils, plants primarily absorb nitrate through their roots, which is then partially reduced to ammonium by enzymes within the plant.
- 🌼 Nitrate is crucial for the synthesis of amino acids, which are vital components of proteins, photosynthetic pigments, coenzymes, nucleotides, vitamins, and protoplasm.
- 🍃 Magnesium is a vital element for plant nutrition, playing a central role in the chlorophyll molecule and activating enzymes involved in photosynthesis and respiration.
- 🌿 Magnesium is also important for the synthesis of DNA and RNA, contributing to the genetic stability and function of the plant.
- 🌱 The absorption of nitrate and ammonium is a critical process for nitrogen utilization in plants, highlighting the importance of nitrogen in various biological molecules.
- 🌟 The presence of magnesium in the porphyrin structure of chlorophyll is essential for the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
- 🌱 Both nitrate and magnesium are indispensable for the proper growth and metabolic functions of plants, emphasizing the importance of mineral nutrition in agriculture and plant health.
Q & A
What is the significance of the term 'essential mineral element' as introduced by Arnon and Stout in 1939?
-The term 'essential mineral element' refers to elements that are crucial for a plant's life cycle, cannot be replaced by other elements, and are directly involved in the plant's metabolism.
How many essential nutrients are known to be required by plants based on the script?
-There are at least 17 elements known as essential nutrients required by plants.
Why can't plants absorb nitrogen directly from the atmosphere?
-Plants cannot absorb nitrogen directly from the atmosphere because it is inert in its diatomic form. They need to take it up in the form of nitrate or ammonium.
In aerobic soils, how do plants absorb nitrate?
-In aerobic soils, plants absorb nitrate with the help of their roots.
What happens to the nitrate once it enters the plant?
-Once nitrate enters the plant, some of it is reduced to ammonium by enzymes and then incorporated into amino acids with the help of more enzymes.
What role does nitrogen play in plant proteins, pigments, and other components?
-Nitrogen is a component of many proteins, photosynthetic pigments, coenzymes, purines, pyrimidines, vitamins, and protoplasm.
Why is magnesium important for plant nutrition?
-Magnesium is important for plant nutrition because it is present in the center of the chlorophyll molecule, serves as an activator of enzymes involved in photosynthesis and respiration, and is also important in DNA and RNA synthesis.
What is the role of magnesium in the structure of chlorophyll?
-Magnesium is present in the center of the porphyrin structure of chlorophyll, which is crucial for the pigment's function in photosynthesis.
How does magnesium act as an activator of enzymes in photosynthesis and respiration?
-Magnesium acts as a cofactor for certain enzymes, enhancing their activity and thus facilitating the processes of photosynthesis and respiration.
What is the significance of the enzymes that reduce nitrate to ammonium within the plant?
-The enzymes that reduce nitrate to ammonium are significant because they enable the plant to use the absorbed nitrate in the synthesis of amino acids, which are essential for protein formation and other metabolic processes.
How does the incorporation of nitrogen into amino acids contribute to plant growth?
-The incorporation of nitrogen into amino acids is a critical step in protein synthesis, which is essential for plant growth and development, including cell division and the formation of new tissues.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

6. Plant Nutrition (Part 1) (Cambridge IGCSE Biology 0610 for exams in 2023, 2024 and 2025)

Xylem and Phloem - Part 2 - Transpiration - Transport in Plants | Biology | FuseSchool
Plant Nutrients

Potassium Cycle

Plant Nutrition | Plants | Biology | FuseSchool

NCERT Class 7 Science- Chapter 1 in Bengali : NUTRITION IN PLANTS
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
