Plant Nutrition | Plants | Biology | FuseSchool
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explores plant nutrient deficiencies, illustrating how each essential element like nitrogen, magnesium, potassium, and phosphorus plays a critical role in plant health. It explains the consequences of deficiencies on growth and appearance, and discusses agricultural practices like hydroponics, crop rotation, and fertilization to ensure nutrient availability. The video also touches on the impact of these practices on farming and crop yields, encouraging viewers to learn more about plant nutrition and its significance in agriculture.
Takeaways
- 🌱 Plants are autotrophic, meaning they produce their own food through photosynthesis.
- 💧 Nutrient deficiencies in plants can lead to stunted growth and various visible symptoms, such as yellowing leaves.
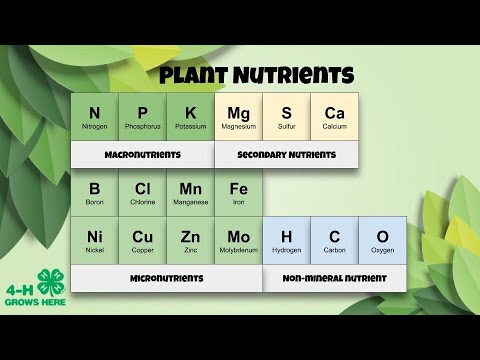
- 🌿 Nitrogen is essential for plant growth, particularly in the production of proteins, and its deficiency can cause older leaves to turn yellow and become shriveled.
- 🍃 Magnesium is required for the production of chlorophyll, and a deficiency results in yellow leaves as chlorophyll production is limited.
- 🍂 Potassium deficiency affects the older leaves, causing them to turn yellow while the veins remain green, and impacts the plant's immune system and overall growth.
- 🌳 Phosphorus is involved in energy transfer, and its deficiency can cause older leaves to darken, sometimes with purple veins, and stunt root growth.
- 🌾 Farmers are crucially dependent on nutrient availability for optimal plant growth and yield, such as fruit production.
- 🌊 Hydroponics is an innovative agricultural method where plants grow in nutrient-rich water instead of soil, allowing farmers greater control over nutrient levels.
- 🔄 Crop rotation is a traditional farming practice used to maintain soil health by alternating crops with different nutrient demands.
- 💩 Fertilizers, both artificial (NPK) and natural (like manure), are used to supplement soil nutrients and support plant growth.
- 📚 The video educates viewers on the importance of various nutrients for plants and their impact on farming practices.
Q & A
What is the primary cause of the poor condition of the plants in the video?
-The primary cause is nutrient deficiencies, particularly a lack of micronutrients necessary for their growth.
How do plants obtain their food, and what does 'autotrophic' mean in this context?
-Plants are autotrophic, meaning they produce their own food through the process of photosynthesis, which does not require external nutrients.
What is the role of nitrogen in plant growth, and how does a deficiency affect them?
-Nitrogen is essential for making proteins in plants. A deficiency leads to stunted growth, yellowing of older leaves, and sometimes shriveling.
Why is magnesium important for plants, and what are the visible symptoms of magnesium deficiency?
-Magnesium is crucial for the production of chlorophyll, the green pigment in chloroplasts. A deficiency results in yellowing of the plant due to a lack of chlorophyll, limiting photosynthesis and growth.
What is the impact of potassium deficiency on plant growth, and how can it be identified?
-Potassium deficiency affects growth and the immune system of the plant. It can be identified by yellowing of older leaves while the veins remain green.
What role does phosphorus play in plants, and how does a phosphate deficiency manifest?
-Phosphorus is involved in energy transfer within the plant. A deficiency is indicated by older leaves turning darker green, sometimes with purple veins, and stunted growth including the roots.
How does nutrient availability affect farming and crop yields?
-Nutrient availability is crucial for farmers as plants lacking essential nutrients grow slower and produce smaller yields, such as fewer fruits.
What is hydroponics, and how does it differ from traditional farming?
-Hydroponics is a method of agriculture where plants grow with their roots suspended in nutrient-rich water, not soil. It allows farmers to have more control over the minerals the plants receive compared to traditional farming.
What is crop rotation, and how does it benefit nutrient management in farming?
-Crop rotation is a practice where the type of crop grown in a field is changed every year or two. It helps manage nutrient requirements as different crops have varying nutrient needs.
What are NPK fertilizers, and what elements do they contain?
-NPK fertilizers are artificial fertilizers containing Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium, which are essential for plant growth.
What are natural fertilizers, and how do they contribute to plant growth?
-Natural fertilizers include organic matter such as human or animal waste. They contain various nutrients needed for plant growth and can be used as an alternative to artificial fertilizers.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Plant Nutrients

Plant Nutrient Deficiency Symptoms (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium)

Plant Nutrition 101: All Plant Nutrients and Deficiencies Explained

Series 22 - Practical Nutrient Management VI - Fertilizer Management

08. KHT - Ilmu Tanah Hutan - Unsur Hara

Farm Basics #1152 Mobile and Immobile Nutrients In Plants (Air Date 5-3-20)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)