Gastrulation - Embryology
Summary
TLDRThis script details the intricate process of embryonic development, focusing on the transformation from a bilaminar to a trilaminar disk. It describes the formation of the primitive streak, gastrulation, and the emergence of the notochord, which serves as the embryo's structural backbone. The video explores the critical stages of cell migration, differentiation into ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm, and the establishment of key embryonic structures such as the amniotic cavity and yolk sac, highlighting the complexity and wonder of early human development.
Takeaways
- 🌱 By day 13, the blastocyst has implanted firmly in the endometrium, initiating the development stages described in the script.
- 🧪 The outermost layer of the blastocyst is the syncytiotrophoblast, which secretes beta HCG, a hormone detected in pregnancy tests.
- 🌀 The cytotrophoblast is followed by the extraembryonic mesoderm, which surrounds the chorionic cavity where the developing embryo sits.
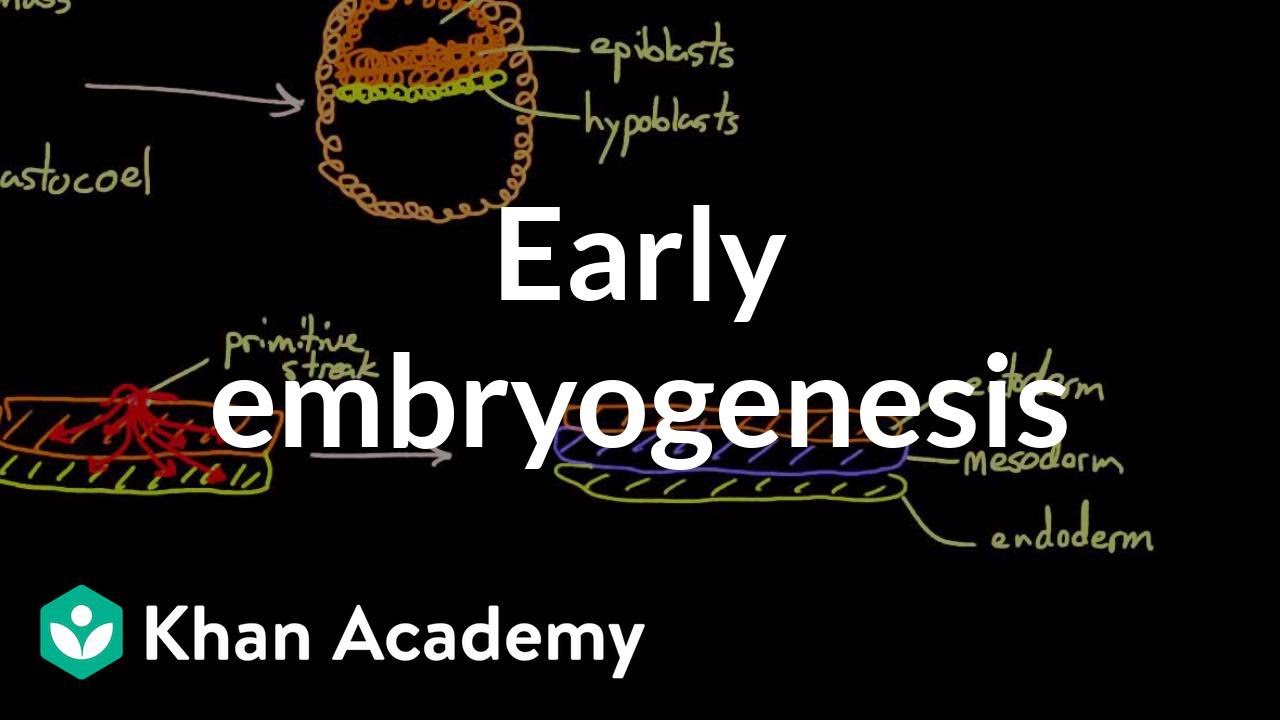
- 🛑 The bilaminar disk consists of the hyperblast and the embryo, with the hyperblast cells extending to form the yolk sac.
- 🔍 The epiblast develops into the amniotic cavity, and the removal of outer elements allows for a closer look at the bilaminar disk's structure.
- 📍 The prochordal plate at the cranial end of the hyperblast serves as a marker for the embryo's cranial aspect.
- 🔄 The gastrulation process involves cells of the epiblast moving inward, downward, and differentiating into three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
- 🎯 The primitive streak is a groove in the epiblast that marks the beginning of gastrulation, with cells migrating to form the primitive node.
- 🌀 The notochord process is a hollow rod that forms by day 16, curving toward the cranial end and connecting to the pro caudal plate.
- 💡 The notochord eventually fuses with the endohypoblast, allowing passage between the amniotic cavity and the yolk sac, important for pressure equilibration.
- 🦴 The notochord acts as the structural backbone of the developing embryo, with the intraembryonic mesoderm filling the space between the ectoderm and endoderm.
Q & A
What is the blastocyst and what happens by day 13?
-The blastocyst is an early stage in embryonic development, and by day 13, it is firmly implanted in the endometrium, the lining of the uterus.
What is the function of the syncytiotrophoblasts?
-Syncytiotrophoblasts are the outermost layer of the blastocyst and they secrete the hormone beta-hCG, which is detected in pregnancy tests.
What is the role of the cytotrophoblasts?
-Cytotrophoblasts are part of the trophoblast layer and contribute to the formation of the placenta and the maintenance of the uterine lining.
What is the chorionic cavity and what is its significance?
-The chorionic cavity is a space within the extraembryonic mesoderm that houses the developing embryo. It is significant as it provides a protective environment for the embryo.
What is the bilaminar disk and what does it consist of?
-The bilaminar disk is a structure that consists of the hyperblast and the developing embryo. It is the foundation upon which the embryo develops.
What is the yolk sac and how does it relate to the hyperblast?
-The yolk sac is a space formed by the extension of cells from the hyperblast. It plays a role in early nutrition and waste exchange for the developing embryo.
What is the significance of the prochorionic plate?
-The prochorionic plate is an area at the cranial end of the hyperblast where columnar cells are present, serving as a marker for the embryo's cranial aspect.
What is gastrulation and what is its endpoint?
-Gastrulation is the process by which the embryo transitions from a bilaminar to a trilaminar disc, forming the three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
What is the primitive streak and its role in gastrulation?
-The primitive streak is a groove in the surface of the epiblast that marks the beginning of gastrulation. Cells migrate through it, differentiating into the three germ layers.
What is the notochord and its developmental significance?
-The notochord is a hollow rod that develops from the notochordal process and eventually fuses with the endohypoblast. It acts as the structural backbone of the developing embryo.
What is the significance of the communication between the amniotic cavity and the yolk sac?
-The brief communication between the amniotic cavity and the yolk sac is theorized to allow pressure equilibration between the two cavities, which is important for the early development of the embryo.
What structural elements of the embryo exist as ectoderm and endoderm?
-The oropharyngeal membrane and the cloacal membrane are structural elements of the embryo that exist as ectoderm and endoderm, respectively.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Gastrulação: Ectoderma, Mesoderma e Endoderma - Terceira Semana do Desenvolvimento (Embriologia)
Early embryogenesis - Cleavage, blastulation, gastrulation, and neurulation | MCAT | Khan Academy

Pregnancy - How a Wonder is Born! (Animation)

Development of the Face and Palate

General Embryology - Detailed Animation On Second Week Of Development

General Embryology Review in 20 minutes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
