General Embryology Review in 20 minutes
Summary
TLDRThe video explains the process of human fertilization, starting with sperm deposition during intercourse and ending with early embryonic development. It covers key stages such as sperm capacitation, acrosomal reaction, fertilization, and the formation of the zygote. The zygote undergoes cleavage, forming a blastocyst that implants in the uterine wall. The video also details embryonic development through the formation of the bilaminar disc, neural tube, and body folds, establishing the primary germ layers that differentiate into tissues and organs.
Takeaways
- 🌟 During ejaculation, approximately 200 million sperm are deposited into the vagina.
- 🏊♂️ Sperm swim through the cervix and uterus, propelled by their tails, towards the uterine tubes.
- 🌀 The journey of sperm to the oocyte can take between 30 minutes to 2 hours.
- 🏁 Only around 200 sperm reach the secondary oocyte, and only one can fertilize it.
- 🔄 Capacitation and the acrosomal reaction are crucial processes for sperm to fertilize the oocyte.
- 🛡 The zona pellucida plays a key role in selecting the sperm that will fertilize the oocyte through receptor proteins called zp3.
- 🚫 The block to polyspermy ensures that only one sperm penetrates and fuses with the oocyte to prevent multiple fertilizations.
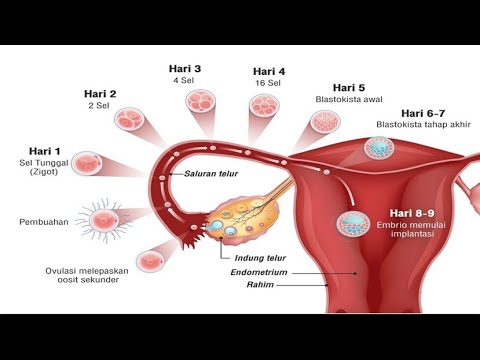
- 💞 After fertilization, the zygote undergoes rapid cell division known as cleavage.
- 🌱 The morula, a cluster of 16 cells, develops into a blastocyst, which eventually hatches into the uterine cavity.
- 🌱 Implantation occurs approximately six to seven days after fertilization, requiring a prepared endometrial wall.
Q & A
How many sperm are typically deposited into the vagina during ejaculation?
-Approximately 200 million sperm or spermatozoa are deposited into the vagina during ejaculation.
What propels the sperm through the cervix and towards the uterine tubes?
-The whip-like motions of their tails or flagella, along with muscular contractions of the uterus, propel the sperm through the cervix and towards the uterine tubes.
What is the significance of the acrosomal reaction in the fertilization process?
-The acrosomal reaction is significant as it triggers the release of enzymatic contents from the acrosome, which helps the sperm digest a path through the zona pellucida to reach and fuse with the secondary oocyte.
What are the two processes that must occur before fertilization can take place?
-Capacitation and the acrosomal reaction are the two processes that must occur before fertilization can take place.
How does the zona pellucida play a role in the fertilization process?
-The zona pellucida expresses specific receptor proteins called ZP3, which bind to proteins on the sperm head, facilitating the sperm's entry into the perivitelline space and fusion with the oocyte.
What are the fast and slow blocks to polyspermy, and how do they prevent multiple sperm from fertilizing the oocyte?
-The fast block to polyspermy involves the oocyte membrane depolarizing after fusion to prevent other sperm from fusing with it. The slow block is stimulated by the same depolarization and involves the release of intracellular calcium, causing the zona pellucida to become impermeable by rendering ZP3 inactive.
What is the process by which the zygote undergoes rapid mitotic division after fertilization?
-The process by which the zygote undergoes rapid mitotic division after fertilization is known as cleavage, with the first cleavage producing two identical cells called blastomeres.
What is the significance of the blastocyst cavity in the development of the embryo?
-The blastocyst cavity is significant as it allows for the development of a central fluid-filled space within the morula, which eventually forms the blastocyst, a stage in embryonic development before implantation.
How does the endometrial wall prepare for implantation of the blastocyst?
-The endometrial wall prepares for implantation by becoming sufficiently prepared by the correct levels of hormones, allowing the blastocyst to attach and eventually embed within the endometrium.
What is the role of the primitive streak in the gastrulation process?
-The primitive streak is a thickened structure that forms along the midline of the epiblast and is crucial in the gastrulation process as it defines the major body axes of the embryo and initiates the formation of the three primary germ layers.
How does embryonic folding contribute to the development of the embryo?
-Embryonic folding contributes to the development of the embryo by changing its shape from a flat trilaminar disc into a cylinder, which helps establish the major body plan and allows for the differentiation of the three germ layers into specific tissues and organ systems.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)