How to calculate Shannon Wiener Diversity Index
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a clear, step-by-step guide to calculating the Shannon–Wiener diversity index, a key measure of biodiversity that accounts for both species richness and evenness. Using examples based on species counts and percent cover, it explains how to determine species proportions and apply the formula to calculate diversity values. The video highlights that communities with the same number of species can differ in diversity due to uneven distribution. It also covers practical field techniques, including quadrat sampling and adjusting percent cover when vegetation does not fully occupy a plot, helping ecologists accurately assess and compare biodiversity in plant communities.
Takeaways
- 🌱 Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H) measures biodiversity by considering both species richness and evenness.
- 📊 Species richness alone (number of species) is insufficient to assess true diversity.
- ⚖️ Evenness, or how equally species are represented, significantly impacts the diversity index.
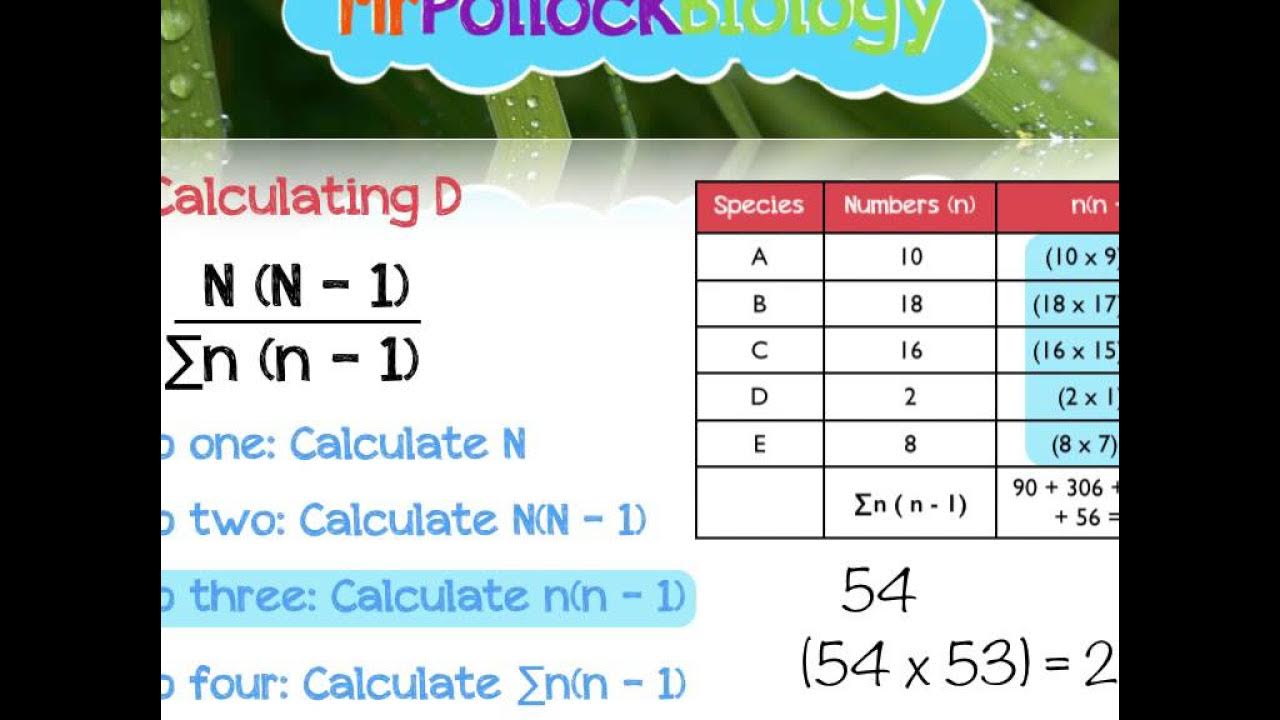
- 🧮 The Shannon-Wiener formula: H = -Σ (pᵢ * ln(pᵢ)), where pᵢ is the proportion of species i.
- 📈 Proportions (pᵢ) can be calculated from counts, biomass, or percent cover of species.
- 👥 In a highly even community, all species have equal proportions, resulting in higher diversity values.
- 📉 Communities dominated by one species have lower Shannon-Wiener index values despite equal species richness.
- 🌿 Percent cover estimates can be used directly as proportions, but must be adjusted if the plot isn’t fully covered.
- 🧮 Adjusted percent cover proportions = (percent cover of species) / (total percent cover of all species in plot).
- 🔍 Observer consistency is crucial for accurate percent cover estimation; group consensus can help reduce bias.
- 📊 High diversity can exist even with bare ground if species are evenly distributed.
- ✅ Shannon-Wiener index allows comparison of different communities by combining richness and evenness into a single value.
Q & A
What is the difference between species richness and diversity?
-Species richness refers to the number of species in a community, while diversity considers both species richness and evenness, which is the relative abundance of each species. A community can have the same number of species but different diversity levels if the species are not evenly distributed.
What does the Shannon-Wiener Index (H) represent?
-The Shannon-Wiener Index (H) is a measure of biodiversity that accounts for both species richness and evenness in a community. Higher values of H indicate higher diversity.
How is the Shannon-Wiener Index calculated?
-The Shannon-Wiener Index is calculated using the formula H = -Σ(p_i * ln(p_i)), where p_i is the proportion of individuals in each species relative to the total number of individuals in the community. The sum of all species' proportions is taken, and the result is negated.
What does 'p_i' represent in the Shannon-Wiener formula?
-In the Shannon-Wiener formula, 'p_i' represents the proportion of individuals of species i in the community. It is calculated by dividing the number of individuals of species i by the total number of individuals in the community.
How do you calculate proportions when using counts of individuals?
-To calculate proportions from counts, divide the number of individuals of each species by the total number of individuals in the community. For example, if a species has 4 individuals out of 16 total, its proportion is 4/16 = 0.25.
Why is evenness important in measuring biodiversity?
-Evenness is important because it indicates how evenly individuals are distributed among species. A community with high evenness (where all species have similar numbers) is considered more diverse than one where a few species dominate.
What is the significance of calculating diversity based on percent cover?
-Percent cover provides an estimate of the relative abundance of species in a given area. It is often easier to measure in the field compared to counting individual plants, and it can be used to calculate the Shannon-Wiener Index in a similar way to counts.
How do you calculate the proportions when percent cover is less than 100%?
-When percent cover is less than 100%, you adjust the proportions by dividing each species' cover percentage by the total percent cover observed. This ensures that the proportions add up to 1 (or 100% when expressed as percentages).
Can diversity still be high in communities with a lot of bare ground?
-Yes, diversity can still be high in areas with bare ground if the species present are evenly distributed, even if some species have low cover. Bare ground does not inherently reduce diversity, as the evenness of species is more critical.
Why is it important to ensure consistency when estimating percent cover across different sites?
-Consistency in estimating percent cover is crucial for accurate comparisons between sites. Different individuals may have biases in estimating coverage, so it's recommended to have one person make the estimates or reach a consensus to minimize variability.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Analisis Indeks Kemerataan spesies - Indeks Dominansi spesies - Indeks Kekayaan spesies

Simpson's Diversity Index Explained
Index of Species Diversity

Biodiversity: Richness, Evenness, and Importance

APES Notes 2.1 - Introduction to Biodiversity
Video Olah Data LIT Data Karang Menggunakan Microsoft Excel
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
