O que é um diodo?
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the concept of diodes is explained in an easy-to-understand way, focusing on their role in electronics. A diode allows electric current to flow in one direction only, much like a valve. The video covers key features such as the voltage drop (0.7V), power loss, and the importance of understanding a diode's maximum current capacity and switching speed. Various types of diodes, such as LEDs, Zener diodes, and rectifiers, are introduced, with practical tips on how to test them using a multimeter. Ideal for beginners in electronics!
Takeaways
- 😀 A diode is an electronic component that allows current to flow in one direction, similar to a valve controlling water flow.
- 😀 LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) are common examples of diodes that emit light when current flows through them.
- 😀 The direction of current flow in a diode is indicated by its schematic symbol, with an arrow pointing from the anode to the cathode.
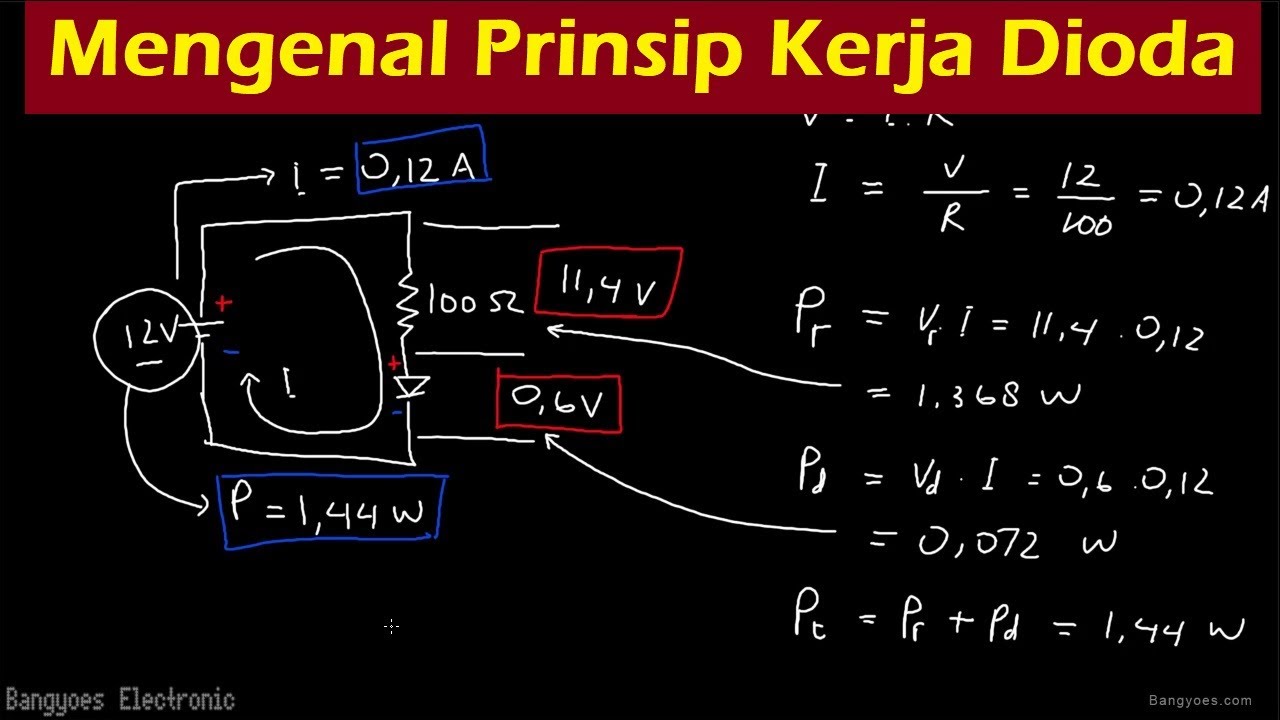
- 😀 Diodes have a voltage drop, typically 0.7V for silicon diodes, which is necessary for current to flow.
- 😀 If the voltage across a diode is less than its voltage drop (e.g., 0.7V), no current will flow through it.
- 😀 The power dissipated by a diode (in the form of heat) is calculated by multiplying the voltage drop by the current passing through it.
- 😀 It's important to know the maximum current a diode can handle, as exceeding this can cause overheating.
- 😀 Diodes should not be connected in parallel to support more current, as this could lead to unequal current distribution and overheating.
- 😀 Diodes have varying switching speeds, with some suitable for low-frequency applications (e.g., 50-60Hz AC line rectifiers) and others for high-frequency uses.
- 😀 Diodes have a maximum reverse voltage rating, which is the highest voltage they can withstand in reverse without allowing current to flow.
- 😀 Testing a diode with a multimeter involves checking if it conducts in one direction and blocks current in the opposite direction, indicating it's working properly.
Q & A
What is a diode?
-A diode is an electronic component that allows electric current to flow in one direction only. It can be compared to a valve that lets water flow in one direction.
How does a diode work?
-A diode allows current to flow from the anode to the cathode, and it blocks current in the reverse direction. The direction of current flow is indicated by the arrow on the diode symbol.
What does the arrow on the diode symbol represent?
-The arrow on the diode symbol indicates the direction of current flow, from the anode to the cathode.
What is the typical voltage drop across a diode?
-A typical silicon diode has a voltage drop of around 0.7V when current flows through it.
What happens if the voltage across a diode is less than 0.7V?
-If the voltage across a silicon diode is less than 0.7V, the diode will not conduct electricity.
How can a diode be used in AC to DC conversion?
-A diode can be used as a rectifier, where it allows only the positive half of an AC voltage to pass through, effectively converting AC to DC.
Why does a diode heat up during operation?
-A diode heats up because of the energy lost as heat due to the voltage drop (approximately 0.7V) when current flows through it.
Can diodes be connected in parallel to support higher current?
-No, diodes should not be connected in parallel to support higher current because the current will not be divided evenly, causing one diode to overheat and fail.
What factors affect the voltage drop across a diode?
-The voltage drop across a diode can be affected by the current, the temperature, and the type of diode used.
How can you test a diode with a multimeter?
-To test a diode with a multimeter, set it to the continuity or diode testing mode. Place the positive lead on the anode and the negative lead on the cathode. You should hear a beep if the diode is working in one direction, and no beep in the reverse direction.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)