Elektronika Dasar - Mengenal Prinsip Kerja Dioda dalam Rangkaian Listrik
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an insightful introduction to diodes, focusing on their role as semiconductor components that allow current to flow in one direction. It explains the structure of diodes, consisting of P-type and N-type materials, and highlights the importance of threshold voltage for operation. The video illustrates forward and reverse bias conditions, demonstrating how diodes conduct or block current based on polarity. Through practical examples and circuit analysis, viewers learn how to calculate power consumption and understand circuit functionality. Overall, it serves as an informative guide to understanding diodes in electrical circuits.
Takeaways
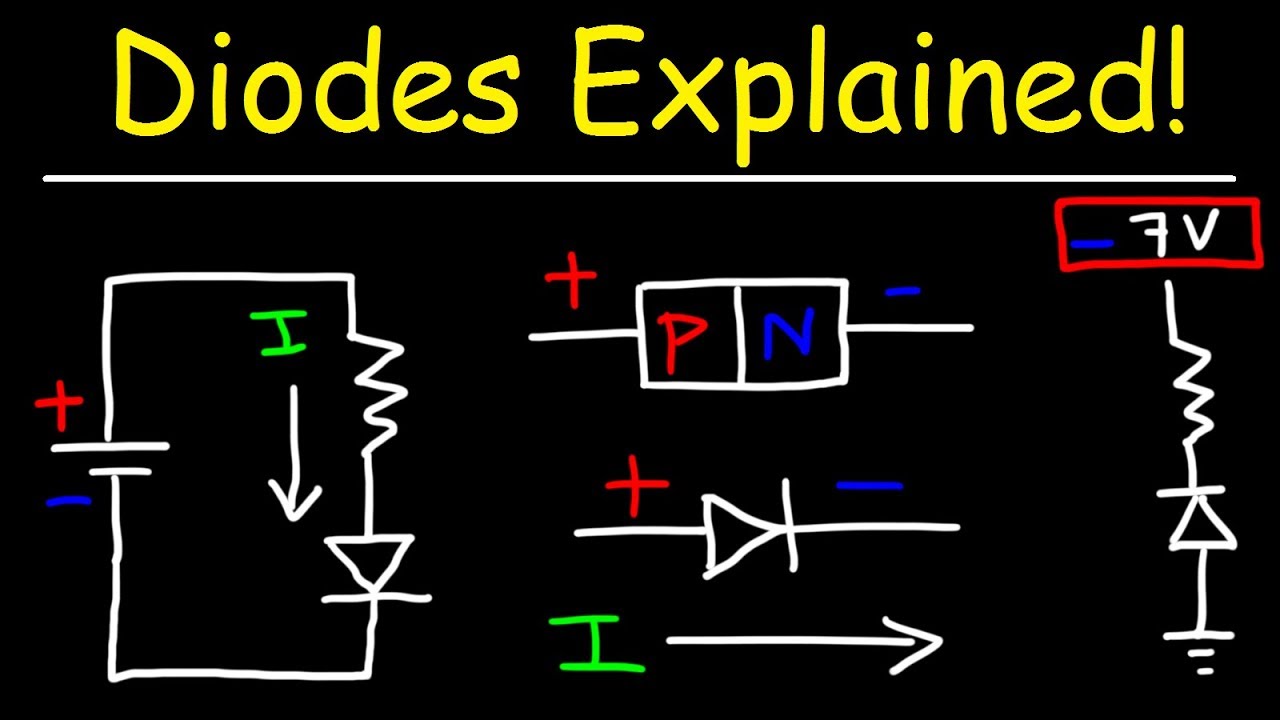
- 😀 A diode is a semiconductor component that allows current to flow in one direction only.
- 😀 The diode has two terminals: anode (positive) and cathode (negative).
- 😀 Current flows from the anode to the cathode when the diode is in forward bias (positive to negative).
- 😀 A diode typically requires a threshold voltage (0.6 to 0.7 volts) to conduct electricity.
- 😀 In reverse bias, when the polarity is reversed, no current flows through the diode.
- 😀 Diodes can be made from P-type and N-type semiconductor materials, forming a PN junction.
- 😀 The output voltage across a conducting diode is approximately 0.6 volts for silicon diodes.
- 😀 Power consumption in a circuit can be calculated using Ohm's Law: P = I * V.
- 😀 In practical examples, if the input voltage exceeds the diode's threshold, the circuit will be active.
- 😀 When configured in reverse, a diode prevents current flow unless subjected to very high reverse voltage.
Q & A
What is a diode?
-A diode is a semiconductor component that allows electric current to flow in only one direction.
What are the two terminals of a diode called?
-The two terminals of a diode are called the anode and the cathode.
What is the significance of the threshold voltage in diodes?
-The threshold voltage, or forward bias voltage, is the minimum voltage required (usually between 0.6 and 0.7 volts for silicon diodes) for the diode to conduct electricity.
How does current flow through a diode?
-Current flows from the anode to the cathode when the diode is forward biased; it does not flow in the reverse direction.
What happens when a diode is reverse biased?
-When a diode is reverse biased, it does not conduct electricity unless a very high reverse voltage (above the breakdown voltage) is applied.
What is a PN junction?
-A PN junction is the interface between P-type and N-type semiconductor materials that form the basic structure of a diode.
How do you calculate the current in a circuit containing a diode and a resistor?
-Using Ohm's Law, the current can be calculated by dividing the voltage across the resistor by its resistance (I = V/R).
What is the power consumption in a circuit with a diode?
-Power consumption can be calculated by summing the power dissipated across the diode and the resistor, where power is given by P = V * I.
In the example circuit, what is the total power consumption when using a 12-volt battery with a diode and resistor?
-The total power consumption in the example circuit is 1.44 watts.
Why is it important to understand the biasing of diodes in circuits?
-Understanding biasing is crucial because it determines whether the diode will conduct or block current, which affects the overall functioning of the circuit.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)